Structural scheme of LAN organizations. Wired Local Area Network (LAN)
Introduction
The object of undergraduate practice is an educational institution MBOU secondary school d.Novaya Derevnya.
The purpose of undergraduate practice is to create an information system (IS) of the school.
The information system is a local computer network for the school. Its main purpose is to connect school computers to each other in a local network with subsequent access to the Internet.
A local network will be created for the sharing of peripheral equipment and information resources. Internet access is necessary for the school to communicate with other organizations (for example, GorUO), as well as for students and teachers to access information resources the Internet. In addition to solving the basic issues of IS design, electronic checkpoint systems (EPS), a unified information system (UIS) and a video surveillance system (VNS) will be introduced in the building being designed.
The designed local area network (LAN) must meet the latest requirements for networks of educational institutions, provide reliable centralized storage and data protection, transfer data at high speed and communicate with other educational institutions. In addition, further expansion of the network should not be associated with high costs. With the further acquisition of a PC by the school, the network should allow simple expansion. It is also necessary to make maximum use of available software and hardware.
Purpose: to gain practical skills in network design. Learn how to choose network technologies and components and be able to justify your choice. Design the school information system.
Design a LAN;
Implement systems of BOT, UIS, SVN;
Organize access to the Internet;
Ensure the use of peripheral devices;
Select the required software;
Test IS.
1 Diagram of a local area network
The design will use a star topology. The hierarchical star consists of the main switch to which the workstations are connected. The star topology has a number of advantages:
– inexpensive cable and quick installation;
– easy association of working groups;
– simple network expansion.
The advantage of this topology is also the ability to easily exclude a failed node. The star topology provides cable break protection. If the cable workstation will be damaged, it will not lead to the failure of the entire network segment. It also makes it easy to diagnose connection problems because each workstation has its own cable segment connected to the switch. For diagnostics, it is enough to find a cable break that leads to a non-working station. The rest of the network continues to function normally.
A client-server architecture was chosen for the school. In doing so, I was guided by the following reasons:
– the number of users exceeds ten;
– centralized resource management is required, or backup;
– a specialized server is required;
- need access to global network;
– it is required to share resources at the user level;
– Provides centralized management of user accounts, security, and access to simplify network administration.
The client-server architecture is the concept of an information network in which the bulk of its resources are concentrated in servers serving their clients. This architecture defines two types of components: servers and clients.
A server is an object that provides a service to other network objects at their request. Service is the process of serving customers. The server works on the instructions of clients and manages the execution of their tasks. After each job is completed, the server sends the results to the client that submitted the job.
A process that calls a service function with certain operations is called a client. It can be a program or a user.
Clients are workstations that use server resources and provide convenient user interfaces.
Client-server architecture networks have the following advantages:
− provide centralized management of user accounts, security and access, which simplifies network administration;
− allow organizing networks with a large number of workstations;
− provide efficient access to network resources;
- provide access to all network resources, based on account user.
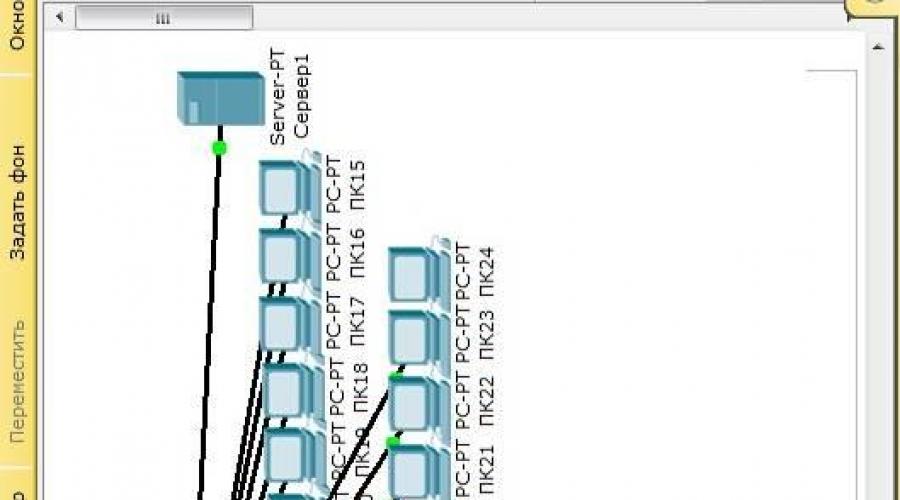
Figure 1 shows the projected scheme of the IS of the school.
|
Figure 1 - IS scheme |
2 Modeling a local area network

3 Information system
3.1 Electronic gate system (EP)
A modern school, in addition to organizing the educational process, must ensure the safety of students at school and promptly inform parents about emerging problems. SEP is specially designed for educational institutions, not only prevents the entry of outsiders, but also notifies parents via SMS messages about the time the child arrives at school and leaves it. The control of absenteeism and lateness of students contributes to the improvement of attendance and, as a result, the growth of the quality of knowledge. Parents' confidence in the safety of the child at school and the growth of knowledge quality indicators increase the rating of the educational institution. For the implementation of the BOT, a set of electronic checkpoints was purchased. The kit included:
Ip turnstile;
Basic software;
Remote control;
Contactless access cards.
The operating principle of the EPS is presented in Table 10.
Table 10 - Principle of operation
Table 10 continued
|
Pupils, teachers and employees of the educational institution are issued electronic plastic pass cards. |
|
|
Information about students and school staff and the cards issued to them is entered into the system's memory. |
|
|
To pass through the turnstile, you need to bring your pass card to a special board on the turnstile. |
|
|
Information from the card is read automatically, and if the card is registered in the system, the turnstile will open for passage. |
|
Table 10 continued
The concept itself local network means joining multiple computers or computer devices V single system for the exchange of information between them, as well as the sharing of their computing resources and peripheral equipment. Thus, local networks allow:
Exchange data (movies, music, programs, games, etc.) between network members. At the same time, to watch movies or listen to music, it is absolutely not necessary to record them on your own. HDD. The speeds of modern networks allow you to do this directly from remote computer or multimedia device.
Connect simultaneously several devices to the global Internet through one access channel. This is probably one of the most requested features of local area networks, because today the list of equipment that can use a connection to the World Wide Web is very large. In addition to all kinds of computer technology and mobile devices, now TVs, DVD / Blu-Ray players, multimedia players and even all kinds of Appliances ranging from refrigerators to coffee makers.
Share computer peripherals such as printers, MFPs, scanners, and network storages data (NAS).
Share the computing power of computers of network participants. When working with programs that require complex calculations, such as 3D visualization, to increase performance and speed up data processing, you can use the free resources of other computers on the network. Thus, having several weak machines connected to a local network, you can use their total performance to perform resource-intensive tasks.
As you can see, creating a local network, even within the same apartment, can bring a lot of benefits. Moreover, the presence of several devices at once at home that require an Internet connection is not uncommon for a long time, and combining them into a common network is an urgent task for most users.
Basic principles of building a local network
Most often, local networks use two main types of data transfer between computers - by wire, such networks are called cable networks and use Ethernet technology, as well as using a radio signal over wireless networks built on the basis of the IEEE 802.11 standard, which is better known to users under the name Wi -Fi.
To date, wired networks still provide the highest throughput, allowing users to exchange information at speeds up to 100 Mbps (12 Mbps) or up to 1 Gbps (128 Mbps) depending on the equipment used (Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet). And although modern wireless technologies, purely theoretically, can also provide data transfer up to 1.3 Gb / s (Wi-Fi 802.11ac standard), in practice this figure looks much more modest and in most cases does not exceed 150 - 300 Mb / s. The reason for this is the high cost of high-speed WiFi equipment and the low level of its use in current mobile devices.
As a rule, all modern networks are arranged according to the same principle: user computers (workstations) equipped with network adapters are interconnected through special switching devices, which can be: routers (routers), switches (hubs or switches), access points or modems. We will talk in more detail about their differences and purposes below, but for now just know that without these electronic boxes, it will not work to combine several computers at once into one system. The maximum that can be achieved is to create a mini-network of two PCs by connecting them to each other.
We must not forget that the local network is a "product" with individual solutions for each specific case, which does not tolerate an ill-conceived approach. That is why, like any quality product, a local network must be built by professionals. Let's take a look at what we need to know in order to conduct a quality installation.
At the very beginning, you need to determine the basic requirements for your future network and its scale. After all, the number of devices, their physical placement and possible ways connection, the choice of the necessary equipment will directly depend.  Most often, a home local area network is combined and it can include several types of switching devices at once. For example, stationary computers can be connected to the network via wires, and various mobile devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones) via Wi-Fi.
Most often, a home local area network is combined and it can include several types of switching devices at once. For example, stationary computers can be connected to the network via wires, and various mobile devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones) via Wi-Fi.
For example, consider a diagram of one of the possible options for a home local network. It will involve electronic devices designed for various purposes and tasks, as well as using different type connections.
As can be seen from the figure, several desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, set-top boxes (IPTV), tablets and media players and other devices can be combined into a single network at once. Now let's figure out what kind of equipment you need to build your own network.
LAN card

A network card is a device that allows computers to communicate with each other and exchange data on a network. All network adapters by type can be divided into two large groups– wired and wireless.
Wired NICs allow you to connect electronic devices to a network using Ethernet technologies using a cable, and wireless network adapters use Wi-Fi radio technology.
As a rule, all modern desktop computers already equipped with built-in motherboard network Ethernet cards, and all mobile devices (smartphones, tablets) are network Wi-Fi adapters. At the same time, laptops and ultrabooks are mostly equipped with both network interfaces at once.
At the same time, laptops and ultrabooks are mostly equipped with both network interfaces at once.
Despite the fact that in the vast majority of cases, computer devices have built-in network interfaces, sometimes it becomes necessary to purchase additional boards, for example,  to equip system block Wi-Fi wireless communication module.
to equip system block Wi-Fi wireless communication module.
According to their constructive implementation, individual network cards are divided into two groups - internal and external. Internal cards designed for installation in desktop computers using interfaces and their corresponding PCI and PCIe slots. External boards are connected via USB connectors or outdated PCMCIA (laptops only).
Router (Router)

The main and most important component of a home local network is a router or router - a special box that allows you to combine several electronic devices into a single network and connect them to the Internet through a single channel provided to you by your ISP.
The router is multifunction device or even a minicomputer with its built-in operating system A that has at least two network interfaces. The first of them - LAN (Local Area Network) or LAN (Local Area Network) is used to create an internal (home) network, which consists of your computer devices. The second - WAN (Wide Area Network) or WAN (Global Computing Network) is used to connect a local area network (LAN) to other networks and the World Wide Web - the Internet.
The main purpose of devices of this type is to determine the paths (routing) of data packets that the user sends to other, larger networks or requests from them. It is with the help of routers that huge networks are divided into many logical segments (subnets), one of which is the home LAN. Thus, at home, the main function of the router can be called the organization of the transfer of information from the local network to the global network, and vice versa.
Another important task of a router is to restrict access to your home network from the World Wide Web. Surely you are unlikely to be satisfied if anyone can connect to your computers and take or delete from them whatever they want.
To prevent this from happening, the data flow intended for devices belonging to a specific subnet must not go beyond its limits. Therefore, the router from the total internal traffic generated by the members of the local network selects and sends to the global network only that information that is intended for other external subnets. This ensures the security of internal data and saves overall throughput networks.
The main mechanism that allows the router to restrict or prevent access from common network(outside) to devices on your local network is called NAT (Network Address Translation). It also provides all users of the home network with access to the Internet by converting several internal addresses of devices into one public external address provided by your Internet service provider. All this makes it possible for computers on the home network to easily exchange information with each other and receive it from other networks. At the same time, the data stored in them remains inaccessible to external users, although at any time access to them can be provided at your request.
In general, routers can be divided into two large groups - wired and wireless. Already by the names it is clear that all devices are connected to the first ones only with the help of cables, and to the second ones, both with the help of wires and without them using Wi-Fi technology. Therefore, at home, it is wireless routers that are most often used, which allow providing Internet and networking computer equipment using various communication technologies.

To connect computer devices using cables, the router has special sockets called ports. In most cases, the router has four LAN ports for connecting your devices and one WAN port for connecting an ISP cable.
In many cases, the router may be the only component needed to build your own local network, as there will simply be no need for the rest. As we have already said, even the simplest router allows you to connect up to four computer devices using wires. Well, the number of equipment that receives simultaneous access to the network using Wi-Fi technology can even be in the tens, or even hundreds.
If, nevertheless, at some point the number of LAN ports of the router ceases to be enough, then to expand the cable network, one or more switches can be connected to the router (we will discuss them below), which act as splitters.
Modem
In modern computer networks, a modem is a device that provides access to the Internet or access to other networks through ordinary wired telephone lines (xDSL class) or using wireless mobile technology(class 3G).
 Conventionally, modems can be divided into two groups. The first includes those that connect to the computer through USB interface and provide access to the network only one specific PC, to which the modem is directly connected. In the second group, LAN and / or Wi-Fi interfaces already familiar to us are used to connect to a computer. Their presence indicates that the modem has a built-in router. Such devices are often called combined, and they should be used to build a local network.
Conventionally, modems can be divided into two groups. The first includes those that connect to the computer through USB interface and provide access to the network only one specific PC, to which the modem is directly connected. In the second group, LAN and / or Wi-Fi interfaces already familiar to us are used to connect to a computer. Their presence indicates that the modem has a built-in router. Such devices are often called combined, and they should be used to build a local network.

When choosing DSL equipment, users may encounter certain difficulties caused by confusion in its names. The fact is that often in the assortment of computer stores, two very similar classes of devices coexist at once: modems with built-in routers and routers with built-in modems. What is their difference?
There are practically no key differences between these two groups of devices. Manufacturers themselves position a router with a built-in modem as a more advanced option, endowed with a large number of additional features and improved performance. But if you are only interested in basic features, such as, for example, connecting all computers on a home network to the Internet, then there is not much difference between modem routers and routers where a DSL modem is used as an external network interface.
So, to summarize, a modern modem with which you can build a local network is, in fact, a router with an xDSL or 3G modem acting as an external network interface.
Switch
A switch or switch is used to connect various nodes of a computer network and exchange data between them via cables.
The role of these nodes can be either separate devices, such as a desktop PC, or entire groups of devices already combined into an independent network segment. Unlike a router, a switch has only one network interface– LAN and is used in the home as an auxiliary device, mainly for scaling local networks.

To connect computers using wires, like routers, switches also have special socket-ports. In models focused on home use, usually their number is five or eight. If at some point the number of switch ports is no longer enough to connect all devices, you can connect another switch to it. Thus, it is possible to expand home network as much as you like.
Switches are divided into two groups: managed and unmanaged. The first, as the name implies, can be controlled from the network using special software. With advanced functionality, they are expensive and not used in the home. Unmanaged switches distribute traffic and regulate the speed of data exchange between all network clients in automatic mode. It is these devices that are ideal solutions for building small and medium-sized local networks, where the number of participants in the exchange of information is small.
Depending on the model, the switches can provide a maximum data transfer rate of either 100 Mbps (Fast Ethernet) or 1000 Mbps (Gigabit Ethernet). Gigabit switches are best used for building home networks where you plan to transfer files frequently. big size between local devices.
Wireless access point
To provide wireless access to the Internet or local network resources, in addition to the wireless router, you can use another device called a wireless access point.
Unlike a router, this station does not have an external WAN network interface and is equipped in most cases with only one LAN port for connecting to a router or switch. Thus, you will need an access point if your local network uses a regular router or modem without Wi-Fi support.

The use of additional access points in the network with wireless router may be justified in cases where a large Wi-Fi coverage area is required. For example, the signal strength of one wireless router may not be enough to cover the entire area in a large office or multi-storey country house.
Access points can also be used to organize wireless bridges that allow you to connect individual devices, network segments or entire networks using a radio signal in places where cabling is undesirable or difficult.
Network cable, connectors, sockets
Despite the rapid development of wireless technologies, many local networks are still built using wires. Such systems have high reliability, excellent throughput and minimize the possibility of unauthorized connections to your network from outside.

To create a wired local area network in home and office environments, Ethernet technology is used, where the signal is transmitted over the so-called "twisted pair" (TP-Twisted Pair) - a cable consisting of four copper twisted pairs of wires with each other (to reduce interference).
When building computer networks predominantly unshielded CAT5 cable is used, and more often an improved version of CAT5e. Cables of this category allow you to transmit a signal at a speed of 100 Mbps when using only two pairs (half) of wires, and 1000 Mbps when using all four pairs.

To connect to devices (routers, switches, network cards, and so on), the ends of the twisted pair use 8-pin modular connectors, commonly referred to as RJ-45 (although their correct name is 8P8C).
Depending on your desire, you can either buy ready-made (with crimped connectors) network cables of a certain length, called “patch cords” in any computer store, or purchase twisted pair and connectors separately, and then make cables of the required size yourself in the right amount.
Using cables to connect computers to a network, of course, you can connect them directly from switches or routers to connectors on PC network cards, but there is another option - using network outlets.
In this case, one end of the cable is connected to the switch port, and the other to the internal contacts of the socket, in the external connector of which you can later connect computer or network devices.

Power outlets can be built into the wall or mounted outside. The use of sockets instead of protruding cable ends will give a more aesthetic look to your workplace. It is also convenient to use sockets as reference points for various network segments. For example, you can install a switch or router in the hallway of the apartment, and then from it thoroughly lay cables to sockets located in all necessary rooms. Thus, you will get several points located in different parts apartments, to which it will be possible at any time to connect not only computers, but also any network devices, for example, additional switches to expand your home or office network.
Another little thing that you may need when building a cable network is an extension cable, which can be used to connect two twisted pairs with already crimped RJ-45 connectors.
In addition to their direct purpose, extension cords are convenient to use in cases where the end of the cable ends with not one connector, but two. This option is possible when building networks with a bandwidth of 100 Mbps, where only two pairs of wires are sufficient to transmit a signal.
 You can also use a network splitter to connect two computers to one cable at once without using a switch. But again, it is worth remembering that in this case the maximum data exchange rate will be limited to 100 Mbps.
You can also use a network splitter to connect two computers to one cable at once without using a switch. But again, it is worth remembering that in this case the maximum data exchange rate will be limited to 100 Mbps.
Read more about twisted pair crimping, connecting sockets and the characteristics of network cables in a special material.
Network topology
Now that we've seen the basic components of a LAN, it's time to talk about topology. If to speak plain language, then a network topology is a diagram that describes the locations and how network devices are connected.
There are three main types of network topology: Bus, Ring, and Star. With a bus topology, all computers on the network are connected to one common cable. To combine PCs into a single network using the "Ring" topology, they are serial connection with each other, with the last computer connected to the first. With a star topology, each device is connected to the network through a special hub using a separate cable.
Probably, the attentive reader has already guessed that to build a home or small office network, the Star topology is mainly used, where routers and switches are used as hub devices.
Creating a network using the Zvezda topology does not require deep technical knowledge and large financial investments. For example, using a switch that costs 250 rubles, you can network 5 computers in a few minutes, and using a router for a couple of thousand rubles, you can even build a home network, providing several dozen devices with access to the Internet and local resources.
Another undoubted advantage of this topology is good scalability and ease of upgrade. Thus, network branching and scaling is achieved by simply adding additional hubs with the necessary functionality. Also, at any time, you can change the physical location of network devices or swap them in order to achieve more practical use of equipment and reduce the number and length of connecting wires.
Despite the fact that the Zvezda topology allows you to quickly change the network structure, the location of the router, switches and other necessary elements must be thought out in advance, in accordance with the layout of the room, the number of connected devices and how they are connected to the network. This will minimize the risks associated with the purchase of unsuitable or redundant equipment and optimize the amount of your financial costs.
Conclusion
In this article, we reviewed general principles building local networks, the main equipment that is used and its purpose. Now you know that the main element of almost any home network is a router, which allows you to network many devices using both wired (Ethernet) and wireless (Wi-Fi) technologies, while providing all of them with an Internet connection through one single channel.
Switches are used as ancillary equipment to expand the points of connection to the local network using cables, which are essentially splitters. For the organization of wireless connections, access points are used, which allow using Wi-Fi technology not only to connect all kinds of devices wirelessly to the network, but also in the "bridge" mode to interconnect entire segments of the local network.
In order to understand exactly how much and what kind of equipment you will need to purchase to create a future home network, be sure to first draw up its topology. Draw a diagram of the location of all devices participating in the network that will need to cable connection. Depending on this, select the optimal location for the router and, if necessary, additional switches. There are no uniform rules here, since the physical location of the router and switches depends on many factors: the number and type of devices, as well as the tasks that will be assigned to them; the layout and size of the room; requirements for the aesthetics of the type of switching nodes; possibilities for laying cables and others.
So, as soon as you have a detailed plan for your future network, you can begin to move on to the selection and purchase of the necessary equipment, its installation and configuration. But we will talk about these topics in our next materials.
Information flows in the enterprise LAN
Consider the organizational and staffing structure of the unit. The department is headed by the CEO of the company. The unit consists of 4 departments, one of which is a specialized department of direct subordination to the head. Each department has a different number of departments under its control. In each department, in turn, employees serve according to the staff list.
All of the above is illustrated in Fig. 2.1.
Orders
Operative information
Reports
Rice. 1.1. Organizational structure of the unit
In total, 23 people are involved in the unit, each of which is supposed to be allocated a personal computer for use.
Network structure planning
Computer network
A computer network is a number of computers within a limited area (located in the same room, in one or more closely spaced buildings) and connected to a single communication line. Today, most computer networks are local area networks (Local-Area Networks), which are located within a single office building and are based on computer model client/server. network connection consists of two computers participating in communication and a path between them. It is possible to create a network using wireless technologies, but this is not yet common.
In the client/server model, network communication is divided into two areas: the client side and the server side. By definition, a client requests information or services from a server. The server, in turn, serves the client's requests. Often, each side in a client/server model can act as both a server and a client. When creating a computer network, there are various components to choose from that determine what software and hardware you can use to form your corporate network. A computer network is an integral part of today's business infrastructure, and a corporate network is just one of the applications used in it and, accordingly, should not be the only factor determining the choice of network components. The components necessary for the Intranet should be an addition to the existing network without leading to a significant change in its architectures.
Network management method
Each company formulates its own requirements for the network configuration, determined by the nature of the tasks to be solved. First of all, it is necessary to determine how many people will work in the network. From this decision, in essence, all subsequent stages of creating a network will depend.
The number of workstations directly depends on the expected number of employees. Another factor is the hierarchy of the company. For a company with a horizontal structure, where all employees must have access to each other's data, optimal solution is a simple peer-to-peer network.
A company built on the principle of a vertical structure, in which it is known exactly which employee and what information should have access, should focus on the more expensive version of the network - with a dedicated server. Only in such a network is it possible to administer access rights (Fig. 3.1).
|
| | |
||||||||||
|
Rice. 3.1 Selecting the type of network.
In this case, the enterprise has 23 workstations, which need to be combined into a corporate network. Moreover, they are grouped into the following groups:
§ director of the enterprise - 1 workstation;
§ Department of direct subordination - 2 workstations;
§ secretary - 1 workstation;
§ departments 1, 2 and 3 of the 2nd department with 3, 2 and 4 workstations, respectively;
§ departments 4 and 5 of the 3rd department, 3 and 4 workstations each;
§ department 6 of the 4th department - 3 workstations.
Following from the network type selection scheme, we can decide that in this case a server installation is required, since we have a vertical structure of the enterprise, that is, differentiated access to information.
One of the main stages of planning is the creation preliminary scheme. In this case, depending on the type of network, the question arises of limiting the length of the cable segment. This may not be significant for a small office, but if the network spans several floors of a building, the problem appears in a completely different light. In this case, it is necessary to install additional repeaters (repeater).
In the situation with the Shuttle-S enterprise, the entire network will be located on one floor, and the distance between the network segments is not so great that the use of repeaters is required.
Floor plan
 The layout of the premises affects the choice of network topology much more strongly than it might seem at first glance (Fig. 3.2).
The layout of the premises affects the choice of network topology much more strongly than it might seem at first glance (Fig. 3.2).
Rice. 3.2. Floor plan
After determining the location of the server installation, you can immediately determine how much cable is required.
Server hosting
Unlike a peer-to-peer network setup, when building a LAN with the server, another question arises - where is the best place to install the server.
Several factors influence the choice of location:
§ due to the high noise level, it is desirable to install the server separately from other workstations;
§ it is necessary to provide constant access to the server for maintenance;
§ for reasons of information security, it is required to restrict access to the server;
Thus, the only possible place for installing the server was chosen, which does not require restructuring of the internal premises. It was decided to install the server in the checkout room, since only this room meets the requirements, that is, the noise level in the checkout room is minimal, the checkout room is isolated from others, therefore, access to the server will be limited (Figure 2.3). At the same time, it is more convenient to maintain the server at the cash desk, since when installing the server in the office of the director or deputy. the director's service will be difficult due to the performance of their official duties, and in the office of the personnel department, access to the server for unauthorized persons is not very difficult. Placing a server in computer science classrooms does not meet any condition.
Network architecture
Network architecture is the combination of topology, access method, and standards required to create a workable network.
The choice of topology is determined, in particular, by the layout of the room in which the LAN is deployed. In addition, purchase and installation costs are of great importance. network equipment, which is an important issue for the company, the range of prices here is also quite large.
The star topology is a more productive structure, each computer, including the server, is connected by a separate cable segment to a central hub (HAB).
 The main advantage of such a network is its resistance to failures that occur due to malfunctions on individual PCs or due to damage to the network cable.
The main advantage of such a network is its resistance to failures that occur due to malfunctions on individual PCs or due to damage to the network cable.
Figure 3.3 shows the topology of an enterprise network.
Rice. 3.3 Enterprise network topology.
The most important characteristic information exchange in local networks are the so-called access methods (access methods), regulating the order in which the workstation gets access to network resources and can exchange data.
The abbreviation CSMA / CD hides the English expression "Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection" (multiple access with carrier sense and collision detection). By using this method All computers get equal access to the network. Each workstation checks whether the channel is free before starting data transmission. At the end of the transmission, each workstation checks whether the sent data packet has reached the destination. If the answer is negative, the node repeats the data transmission/reception control cycle and so on until it receives a message about the successful reception of information by the addressee.
the Ethernet architecture that the enterprise network will use uses this particular access method.
The Ethernet specification was proposed by the Xerox Corporation in the late seventies. Later, Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) and Intel Corporation joined this project. In 1982, the specification for Ethernet version 2.0 was published. Based on Ethernet, the IEEE 802.3 standard was developed by the IEEE.
Twisted-pair (10Base-T) cable technology is currently the most popular. Such a cable does not cause difficulties when laying.
A twisted-pair network, unlike thin and thick coax, is built on a star topology. To build a network using a star topology, you need large quantity cable (but the price of twisted pair is not high). Such a scheme also has an invaluable advantage - high fault tolerance. The failure of one or more workstations does not lead to the failure of the entire system. True, if the hub fails, its failure will affect all devices connected through it.
Another advantage this option is the ease of network expansion, since when using additional hubs (up to four in series), it becomes possible to connect a large number of workstations (up to 1024). When using unshielded twisted pair (UTP), the length of the segment between the hub and the workstation should not exceed 100 meters, which is not observed in the enterprise.
Network resources
The next important aspect of network planning is sharing network resources(printers, faxes, modems).
The listed resources can be used both in peer-to-peer networks and in networks with a dedicated server. However, in the case of a peer-to-peer network, its shortcomings are immediately revealed. To work with the listed components, they must be installed on a workstation or connected to it with peripheral devices. When this station is disabled, all components and related services become unavailable for shared use.
In networks with a server, such a computer exists by definition. The network server never shuts down except for short maintenance shutdowns. Thus, round-the-clock access of workstations to network periphery is provided.
The enterprise has ten printers: in each separate room. The administration went to the expense to create the most comfortable working conditions for the team.
Now the question of connecting the printer to the LAN. There are several ways to do this.
1. Connect to a workstation.
The printer is connected to the workstation that is closest to it, as a result of which this workstation becomes the print server. The disadvantage of this connection is that when performing print jobs, the performance of the workstation decreases for a while, which will negatively affect the work application programs when using the printer intensively. Also, if the machine is turned off, the print server will become inaccessible to other hosts.
2. Direct connection to the server.
The printer is connected to the server's parallel port using a special cable. In this case, it is permanently available to all workstations. The disadvantage of this solution is due to the limitation in the length of the printer cable, which ensures correct data transfer. Although the cable can be run for 10 meters or more, it must be run in conduits or floors, which will increase networking costs.
3. Connect to the network through a special network interface.
The printer is equipped with a network interface and connects to the network as a workstation. The interface card works like network adapter, and the printer is registered to the server as a LAN node. Software server sends print jobs over the network directly to a connected network printer.
In networks with a bus topology, a network printer, like workstations, is connected to a network cable using a T-connector, and when using a "star" - through a hub.
An interface card can be installed in most printers, but its cost is quite high.
4. Connect to a dedicated print server.
An alternative to the third option is to use dedicated print servers. Such a server is a network interface arranged in a separate housing with one or more connectors (ports) for connecting printers. However, in this case, using a print server is impractical.
In our case, due to the unprofitability of installing a special network printer, buying a separate interface card for the printer, the most suitable way to connect a network printer is to connect to a workstation. This decision was also influenced by the fact that printers are located near those workstations that need the greatest printer.
Modern computer technologies cannot be imagined without combining all kinds of devices in the form of stationary terminals, laptops or even mobile devices into a single network. Such an organization allows not only to quickly exchange data between different devices, but also to use the computing capabilities of all pieces of equipment connected to the same network, not to mention the possibility of access to peripheral components such as printers, scanners, etc. But what are the principles by which such Union? To understand them, it is necessary to consider the local network, often called the topology, which will be discussed further. To date, there are several main classifications and types of association of any devices that support network technologies, to one network. Of course, we are talking about those devices on which special wired or wireless network adapters and modules are installed.
Schemes of local computer networks: the main classification
First of all, in considering any type of organization of computer networks, it is necessary to start solely from the method of combining computers into a single whole. There are two main directions used in creating a local network diagram. The network connection can be either wired or wireless.
In the first case, special coaxial cables or twisted pairs are used. This technology is called Ethernet connection. However, if coaxial cables are used in the local computer network, their maximum length is about 185-500 m at a data transfer rate of not more than 10 Mbps. If twisted pairs of classes 7, 6 and 5e are used, their length can be 30-100 m, and the throughput ranges from 10-1024 Mbps.

The wireless scheme for connecting computers in a local network is based on the transmission of information via a radio signal, which is distributed between all connected devices, distributing devices, which can be routers (routers and modems), access points (regular computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets), switching devices (switches, hubs), signal repeaters (repeaters), etc. With this organization, fiber optic cables are used that are connected directly to the main signal-distributing equipment. In turn, the distance over which information can be transmitted increases to about 2 km, and in the radio frequency range, frequencies of 2.4 and 5.1 MHz are mainly used (IEEE 802.11 technology, better known as Wi-Fi).
Wired networks are considered to be more secure from external influences, since it is not always possible to directly access all terminals. Wireless structures in this respect lose quite a lot, because if desired, a competent attacker can easily calculate the network password, gain access to the same router, and through it get to any device, in this moment using a Wi-Fi signal. And very often in the same state structures or in the defense enterprises of many countries, the use of wireless equipment is strictly prohibited.
Classification of networks according to the type of connection between devices
Separately, it is possible to single out a fully connected topology of schemes for connecting computers in a local network. Such a connection organization implies only that absolutely all terminals included in the network have a connection with each other. And as it is already clear, such a structure is practically not protected in terms of external intrusion or when intruders penetrate the network through special virus worms or spyware applets that could initially be recorded on removable media, which the same inexperienced employees of enterprises unknowingly could connect to your computers.
That is why other connection schemes in the local network are most often used. One of these can be called a cellular structure, from which certain initial connections have been removed.
General scheme for connecting computers in a local network: the concept of the main types of topology
Now let's take a quick look at wired networks. They can use several of the most common types of local area networking schemes. The most basic types are star, bus, and ring structures. True, it is the first type and its derivatives that have received the greatest use, but mixed types of networks can often be found, where combinations of all three main structures are used.
Star topology: pros and cons
The “star” local network scheme is considered the most common and widely used in practice when it comes to using the main types of connection, so to speak, in its purest form.

The essence of such a combination of computers into a single whole is that they are all connected directly to the central terminal (server) and do not have any connections with each other. Absolutely all transmitted and received information passes directly through the central node. And it is this configuration that is considered the most secure. Why? Yes, only because the introduction of the same viruses into the network environment can be done either from the central terminal, or get through it from another computer device. However, it looks very doubtful that in such a scheme of the local network of an enterprise or government institution a high level of protection of the central server will not be provided. And injecting spyware from a separate terminal will only work if you have physical access to it. In addition, and from the side of the central node for each network computer quite serious restrictions can be imposed, which can be especially often observed when using network operating systems, when computers do not even have hard disks, and all the main components of the applied OS are loaded directly from the main terminal.
But even here there are drawbacks. First of all, this is due to the increased financial costs for laying cables if the main server is not located in the center of the topological structure. In addition, the speed of information processing directly depends on the computing capabilities of the central node, and if it fails, respectively, on all computers included in the network structure, communications are broken.
Bus scheme
The connection scheme in the local network according to the “bus” type is also one of the most common, and its organization is based on the use of a single cable, through the branches of which all terminals, including the central server, are connected to the network.

The main disadvantage of such a structure can be called the high cost of laying cables, especially for those cases when the terminals are at a sufficiently large distance from each other. But if one or more computers fail, communications between all other components in the network environment are not broken. In addition, when using such a scheme, the local network passing through the main channel is very often duplicated in different areas, which makes it possible to avoid its damage or the impossibility of its delivery to its destination. But security in such a structure, alas, suffers quite a lot, since malicious virus codes can penetrate all other machines through the central cable.
Ring structure
The ring scheme (topology) in a sense can be called obsolete. To date, it is not used in almost any network structure (except perhaps only in mixed types). This is due precisely to the very principles of combining individual terminals into one organizational structure.

Computers are connected to each other in series and with only one cable (roughly speaking, at the input and output). Of course, such a technique reduces material costs, but if at least one network unit fails, the integrity of the entire structure is violated. If I may say so, in a certain area where there is a damaged terminal, the transmission (passage) of data simply stops. Accordingly, when dangerous computer threats penetrate the network, they pass from one terminal to another in the same way. But in case of presence at one of the sites reliable protection The virus will be eliminated and will not pass further.
Mixed types of networks
As mentioned above, the main types of local area network schemes in their pure form are practically not found. Mixed types look much more reliable in terms of security, cost, and ease of access, in which elements of the main types of network diagrams may be present.

So, very often you can find networks with a tree structure, which initially can be called a kind of “star”, since all branches come from one point, called the root. But the organization of branches in such a LAN connection scheme can contain both ring and bus structures, dividing into additional branches, often defined as subnets. It is clear that such an organization is quite complex, and when creating it, it is necessary to use additional technical devices such as network switches or splitters. But, as they say, the end justifies the means, because thanks to such a complex structure, important and confidential information can be protected very reliably by isolating it in subnet branches and practically restricting access to it. The same applies to the failure of components. With such a construction of local network schemes, it is not necessary to use only one central node. There can be several of them, and with completely different levels of protection and access, which further increases the degree of overall security.
Logistic topology
When organizing network structures, it is especially important to pay attention to the methods of data transmission used. In computer terminology, such processes are usually called logistic or logical topology. At the same time, the physical methods of information transfer in various structures can differ significantly from the logical ones. It is logistics, in essence, that determines the routes of reception / transmission. Very often it can be observed that when building a network in the form of a "star", information exchange is carried out using a bus topology, when the signal can be received simultaneously by all devices. In ring logical structures, situations can be encountered when signals or data are received only by those terminals for which they are intended, despite even sequential passage through all related links.
The most famous networks
So far, only the construction of local area network schemes based on Ethernet technology has been considered above, which in itself simple expression uses addresses, protocols, and TCP/IP stacks. But after all, in the world you can find a huge number of network structures that have principles different from the above. network organization. The best known of all (except Ethernet using a logical bus topology) are Token Ring and Arcnet.

The Token Ring network structure was once developed by the notorious IBM company and is based on the logical scheme of the local network “token ring”, which determines the access of each terminal to the transmitted information. Physically, a ring structure is also used, but it has its own characteristics. To combine computers into a single whole, it is possible to use either twisted pair or fiber optic cable, but the data transfer rate is only 4-16 Mbps. On the other hand, the "star" type marker system allows to transmit and receive data only to those terminals that have the right to do so (marked with a marker). But the main disadvantage of such an organization is that in certain moment only one station can have such rights.
No less interesting is the Arcnet LAN scheme, created in 1977 by Datapoint, which many experts call the most inexpensive, simple and very flexible structure.

To transfer information and connect computers, coaxial or fiber optic cables can be used, but the possibility of using a twisted pair cable is also not excluded. True, in terms of the speed of reception / transmission, this structure cannot be called particularly productive, since at the maximum packet exchange can be carried out at a connection speed of no more than 2.5 Mbps. As physical connection the "star" circuit is used, and in the logical one - the "marker bus". With the rights to receive / transmit, the situation is exactly the same as in the case of Token Ring, except that the information transmitted from one machine is available to absolutely all terminals included in the network environment, and not to any one machine.
Brief information about setting up a wired and wireless connection
Now let's briefly look at some important points creation and application of any of the described local network schemes. Third-party programs when using any of the known operating systems are not needed to perform such actions, since the main tools are provided in their standard sets from the very beginning. However, in any case, it is necessary to take into account some important nuances regarding the configuration of IP addresses, which are used to identify computers in network structures. There are only two varieties - static and dynamic addresses. The first, as the name already implies, are constant, and the second can change with each new connection, but their values are exclusively in the same range set by the communication service provider (provider).
In wired corporate networks to provide high speed communication between network terminals, static addresses are most often used, assigned to each machine on the network, and when organizing a network with a wireless connection, dynamic addresses are usually used.
To set the specified parameters of a static address in Windows systems, the parameters of the IPv4 protocol are used (in the post-Soviet space, the sixth version has not yet become particularly widespread).

It is enough to write an IP address for each machine in the protocol properties, and the subnet mask and default gateway parameters are common (unless a tree structure with multiple subnets is used), which looks very convenient in terms of quick connection setup. Despite this, dynamic addresses can also be used.

They are assigned automatically, for which there is a special item in the TCP / IP protocol settings, at each specific point in time they are assigned to network machines directly from the central server. The range of allocated addresses is provided by the provider. But this does not mean at all that the addresses are repeated. As you know, there cannot be two identical external IPs in the world, and in this case we are talking either about the fact that they change only within the network or are transferred from one machine to another when some external address is free.
In the case of wireless networks, when routers or access points are used for the initial connection, distributing (broadcasting or amplifying) the signal, the setup looks even easier. The main condition for this type of connection is to set the automatic receipt of an internal IP address. Without this, the connection will not work. The only changeable parameter is the DNS server addresses. Despite the initial setting of their automatic receipt, it is often (especially when the connection speed is reduced) that it is recommended to set such parameters manually, using, for example, free combinations distributed by Google, Yandex, etc.
Finally, even if there is only a certain set of external addresses by which any computer or mobile device is identified on the Internet, they can also be changed. For this, there are many special programs. The local network scheme can have any of the above variations. And the essence of using such tools, which are most often either VPN clients or remote proxy servers, is to change the external IP, which, if anyone does not know, has a clear geographical reference, to an unoccupied address located in a completely different location (even at the end of the world). You can use such utilities directly in browsers (VPN clients and extensions) or make changes at the level of the entire operating system (for example, using the SafeIP application) when some applications running in the background need to access blocked or inaccessible for a certain region Internet resources.
Epilogue
Summing up all of the above, several main conclusions can be drawn. The first and most important thing is that the basic connection schemes are constantly changing, and they are almost never used in the initial version. The most advanced and most secure are complex tree structures, in which several subordinate (dependent) or independent subnets can additionally be used. Finally, no matter what anyone says, present stage development computer technology wired networks, despite the high financial costs of their creation, are still head and shoulders above the simplest wireless ones in terms of security. But wireless networks have one indisputable advantage - they allow you to combine computers and mobile devices that can be geographically distant from each other over very long distances.
The local wired network (LAN) is the backbone of the home information space and multimedia.. LAN construction criteria.. Wireless connection - pros and cons.. Fast Ethernet technology.. Structural scheme LAN networks.. Star network topology.. Selection of LAN network equipment.. Router (router).. Router configuration.. Built-in ADSL modem.. WI-FI access point.. Switch or hub?.. Characteristics D -Link DSL-6740U.. Specifications D-Link DIR-615/K1A.. UTP Cat 5e cable (dual twisted pair).. Technical task.. An example of a local network project.. Equipment layout.. LAN-network wiring diagram.
Today it is impossible to imagine a house, apartment or office without numerous complex devices and devices, communication with which is already becoming a problem in our time.
A person voluntarily becomes dependent on computers, the Internet, audio and video systems, remote controls, security systems and other electronic devices that give us new opportunities and conveniences, but take away all our free time.
To cope with this problem and make life as convenient and comfortable as possible, you need to set yourself new tasks that can be implemented using smart home technologies.
The following systems are most in demand in a modern house:
Wired LAN
Multimedia
Lighting control
Heating and climate control
Security and fire alarm
CCTV
Intercom and access control.
Implementation of smart home systems can be complex (in the case of a major overhaul or construction of a new house) or partial.
It all depends on the priorities of the choice of certain systems and the possibilities of their implementation.
Today we will consider a wired local area network.
Wired Local Area Network (LAN)
 Wired LAN (Local Area Network) serves for centralized connection to the Internet and communication of computers and various peripherals in the house among themselves. In fact, the local network is the basis of the home information space and multimedia.
Wired LAN (Local Area Network) serves for centralized connection to the Internet and communication of computers and various peripherals in the house among themselves. In fact, the local network is the basis of the home information space and multimedia.
Designing and building computer, telephone and television networks in your home, you will provide the necessary communications for all multimedia and computer equipment in the house.
It always makes sense to consider and design these networks together.
Why Wired.
The choice is always yours. I'm just pointing out that when there is a possibility,
you need to choose wired technologies.
Whenever possible, I try to justify this choice.
Wired and wireless connection: advantages and disadvantages
Of the pros wireless equipment can be noted a large number of connections, which is limited only by the transfer rate per user. Another option is the ability to connect mobile devices (smartphones, communicators, tablets), as well as freedom of movement indoors. Perhaps that's all.
Minuses: Wireless technologies tend to be more complex and therefore less reliable than wired ones. For an unskilled user, this can turn into difficulties during operation, in particular, in diagnosing and troubleshooting. This is especially true as the number of devices increases.
Wireless connection will be slower.
No one will argue that the technical indicators of the signal level over the cable are higher than the radio signal. Speed wireless communication inferior to wired almost twice as in objective reasons(wireless data transfer protocol is slower), and due to external interference (metal wall reinforcement, interference from home electronics, etc.).
There will always be equipment in the house that is demanding on the speed and quality of the connection - for example, the same multimedia HD media players, information from which can be requested from several devices (computers, TVs, etc.) If you want to watch a BluRay quality movie on a projector high definition, then Wi-Fi speed using even modern equipment may not be enough.
By cost wireless equipment will cost one and a half times more expensive than their wired counterparts.
Electromagnetic "pollution" and mutual interference of wireless equipment also has not been canceled yet.
Therefore, before using the network connection via wireless technology Wi-Fi, you need to weigh the pros and cons and make sure that you can’t do without wireless equipment.
If possible, it is best to minimize harmful emissions in the workspace where you spend most of your time.
On practice the home local area network is most often combined. For example, stationary computers can be connected to the network using wires using Ethernet technology, and various mobile devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones) can be connected via wireless standard WiFi.
LAN construction criteria
When choosing a network standard and network topology
the decisive factor is the speed of data transfer and the possibility of further expansion of the system. These conditions are fully met by wired Ethernet technology.
This standard provides parallel data transfer. This means that in ethernet data is not transmitted to all devices in turn (as in RS-485), but directly desired device. This significantly increases the speed of information transfer. In addition, this protocol provides compatibility with existing network devices and future developments. Using protocol ethernet, you can be sure that the local network under construction will be able to develop in the future.
There are currently three specifications that differ in transmission speed:
classic ethernet(10 Mbps);
fast ethernet(100 Mbps);
gigabit ethernet(1 Gbps).
For home network The most optimal in terms of price / quality / complexity is the star topology and the network standard 802.3 100Base-TX. This is a 100-megabit Ethernet on a dual twisted pair, which is still unbeatable in terms of price / performance ratio.
The switch is the backbone of the network., to which network devices are connected by cables with a maximum length of 100m.
Big plus of star topology- its scalability, that is, further expansion, and this is what is very important in home networks. This is achieved by connecting each computer (or other device) to a dedicated Ethernet port on a hub or switch. That is, one switch port - one computer. Typically, the number of Ethernet ports on the switch is oversized, so it is always possible to connect a new device to the spare port. Accordingly, each computer must be equipped with a network adapter with an RJ-45 connector.
The task is made easier by the fact that all modern computers and laptops already have a built-in Ethernet port connector.
Equipment selection criteria
All home local networks are arranged according to the same principle: User computers equipped with network adapters are interconnected through special switching devices. In this capacity, they can serve routers (routers), hubs (hubs), switches (switches), access points and modems.
Routers
The main component of a home LAN is a router or router., which is a multifunctional device with an embedded operating system, having at least two network interfaces:
1.
LAN (Local Area Network)- serves to create an internal (local) network, which consists of your computer devices.
2.
WAN (Wide Area Network)- serves to connect a local area network (LAN) to the worldwide global network - the Internet.
Routers are divided into two classes type external connection: ethernet or ADSL. Accordingly, they have a WAN port or an ADSL port for connecting a provider cable and up to four LAN ports for connecting network devices using Ethernet technology.
The router for connecting to the ADSL line has a built-in ADSL modem.
Wireless routers, among other things, have a built-in WiFi access point to connect wireless devices. The number of equipment accessing the network simultaneously using Wi-Fi technology can, in principle, be in the tens. Taking into account the fact that the bandwidth of the channel is divided between all connected clients, the throughput of the communication channel decreases with an increase in their number.
When the number of connected computers does not exceed four, the router turns out to be the only component that is needed to build a local network, since there is simply no need for the rest.
When choosing a router for a home network, a router using technology is preferable IEEE 802.11n, which provides better performance and signal coverage. In addition, these routers support User's VPN and have a built-in USB port that can be used to connect a flash drive, printer or external hard disk (NAS).
Before buying a router you need to check with the provider in advance what type of connection you will use, and what optional equipment you will need for this. The delivery set of routers should include an external power adapter and an RJ-45 cable, and for models with an ADSL port, an additional RJ-11 cable and a splitter.
Healthy consult with technical support provider on the subject technical requirements to the client's equipment, in terms of its compatibility with the provider's servers. Having received professional information, you can more intelligently make your choice from commercially available router models.
About the number of equipment. If you are designing a local network for a 2 or 3-storey cottage, then one WiFi router you can't do it. To ensure a sufficient level of wireless signal, it will be necessary to build a distributed wifi network, consisting of several routers or access points. To reduce the load on the wireless network and increase the data transfer rate, you can WiFi access leave only for mobile devices, and organize computers (possibly laptops) on wired access.
One more moment: Today, buying a router without Wi-Fi support is simply pointless. The difference in the cost of a good wired router and its wireless counterpart is very small. Even if you do not plan to use the Wi-Fi module in the router in the near future, you can disable it. When you have such a need (for example, a device with Wi-Fi connection appears at home), you can always turn on the Wi-Fi module in the router and start using wireless Internet.
About setting up the router
There are a lot of recommendations on the Internet setting up routers,
including and detailed instructions By specific models. Here I want to point out the following:
Taking into account the interests of users, developers have long made it easy to configure router settings with built-in step-by-step configuration software, making it accessible even for beginners.
In most cases, when you first enter the router menu, a wizard is launched that offers a quick step by step setup its main parameters. This relieves novice users from searching for the necessary options among numerous menu sections.
If necessary, the installation wizard can also be launched manually using the menu item in different options: Quick Setup, Setup Wizard, etc.
It should only be taken into account that in certain situations, connecting to the Internet may require special settings, the possibility of entering which is simply not available in wizard mode. In these cases, you will need to contact manual mode parameter settings.
Switches
If you want to build a more extensive wired network, then four LAN ports of the router will not be enough. In this case, an additional switching device is connected to one of the ports of the router - concentrator(hub) or switch(switch).
Unlike a router, switches and hubs have only one network interface - LAN and are used only for scaling (expanding) local networks.
To create a wired Ethernet network It is better to use a switch (switch) rather than a hub (hub). The switch analyzes outgoing traffic from computers and directs it only to the person to whom it is intended. The hub simply repeats any traffic to all ports. As a result, the performance of an Ethernet network on hubs is highly dependent on the overall load. The network on the switch is free from this shortcoming.
Previously, you had to choose: either price or performance, since hubs were significantly cheaper than switches. Now both types of devices are almost equal in price, so the choice in favor of the switch is beyond doubt.
Which switch should you choose?
At present, there are many models and types of network switches, their price and functions vary greatly. When choosing, you must proceed from the minimum cost of a device that will meet your requirements for data transfer speed and the number of ports. Also, the dimensions of the switch can be of some importance.
Work speed
For a home local area network, in terms of price / performance ratio, Fast Ethernet (100 Mbit / s) remains optimal.
Number of ports
This indicator characterizes the number of network devices that can be connected to this switch. In many ways, this parameter determines the price of the device.
The choice depends on the number of users of your future network. It is necessary to add 1-2 ports in reserve to the number of users.
In home-oriented models, the number of Ethernet ports is usually 5 or 8. If at some point the number of switch ports is no longer enough to connect all devices, you can connect another switch to it. Thus, you can expand your home network as much as you like.
Cables
 As transmission medium 100Base-TX (Fast Ethernet) unshielded cable is used UTP Cat5e(dual twisted pair), where one pair is used to transmit data, and the second - to receive them. Cat 5e cable type 100BASE-T4 (quad twisted pair) is possible: two redundant pairs can be used later to upgrade the network to 1000 Mbps (Gigabit Ethernet).
As transmission medium 100Base-TX (Fast Ethernet) unshielded cable is used UTP Cat5e(dual twisted pair), where one pair is used to transmit data, and the second - to receive them. Cat 5e cable type 100BASE-T4 (quad twisted pair) is possible: two redundant pairs can be used later to upgrade the network to 1000 Mbps (Gigabit Ethernet).
Shielded cables (FTP, STP, SFTP) are used when laying trunk lines and in industrial premises with large electromagnetic fields. Home LANs typically use an unshielded UTP cable.
For telephone network applied cable UTP Cat 3(double twisted pair).
Is it possible to use one of the pairs of a four-pair cable used for computer networks for wiring a telephone in order to save money?
It is possible, but hardly necessary. Why create yourself additional problems with installation. It is best to use separate unshielded twisted-pair wiring, as this significantly increases noise immunity. telephone communication. In addition, the redundant twisted pair of Cat 3 cable may be useful in the future to repair a damaged pair or to connect an additional device.
There are two types of twisted pair conductors in cables., from a single conductor and stranded. The core diameter in single-core twisted pairs is 0.51 mm. Cables with single-core conductors are used for mounting networks in boxes, cable channels and along walls. With stranded conductors, the cable is used only where it can be subjected to frequent bending, for example, to connect a computer to an RJ45 socket (patch cord).
According to the star topology all cables from network devices converge to the switch, and sockets with RJ45 sockets are installed at opposite ends of the cables. Both cables and sockets must be category 5e or 6.
All cable segments must be no more than 100 meters - only in this case the stable operation of the network is guaranteed. Please note that the requirement for a maximum cable segment length of 100 m includes the entire length of the cable connecting the computer to the switch. If the cabling terminates on the computer side with a wall socket and on the switch side with a cross-panel, then patch cables connecting the computer to the socket and the cross-panel to the switch must be included in the length of the segment.
It is recommended to take a maximum length of 90 m for the internal wiring cable segment, leaving 10 m for patch cables.
Of course, all cables must be solid, no "twisting" is allowed.
Sample LAN project
The basis for the creation of any project is the terms of reference (TOR).
Ideally, a detailed design specification should be provided by the customer. In practice, especially for private households, the designer actually has to participate in the collection of initial data and the development of technical specifications, since without a complete understanding of the features of the object and consultations with the customer, it is impossible to complete the project.
Approximate sequence of actions of the designer when drawing up the terms of reference for the design of a "smart" house, was considered in detail in the article "From classic electrics to smart home" .
Consider the actions of the designer on the basis of the TOR agreed with the customer for the design of a local network for a two-story country house with an area of 200m2.
As noted, computer, telephone and television networks are combined in one project.
Initial data
1. There is a floor plan of the house.
2. High-speed Internet access - via dedicated ADSL line
3. Access mode to the city PBX - pulse
4. Number of Ethernet sockets - 6
5. Number of telephone sockets - 1
6. The following should also be provided:
WI-FI points access to connect wireless devices.
Spare port for additional wired connection of 1 computer.
7. Television: terrestrial + satellite TV
8. Number of TV outlets TV + SAT - 6
Equipment layout
Although we are talking about a relatively small local area network, but taking into account the equipment of telephone and television networks and two levels (floors), it makes sense to use installation low-voltage cabinets, and to connect network devices - appropriate sockets. It is convenient to use a network outlet because when you change the location of the computer (or TV), you do not need to extend the entire cable segment - just create a new patch cord connecting the device to the outlet.
On the plan of the house the locations of the proposed placement of installation cabinets, computers, telephones and television receivers are determined.
The placement of equipment on the plan of the 1st floor is shown in fig.1.
Fig.1
Equipment selection
Internet connection will be carried out via a dedicated ADSL channel in telephone line leading from the PBX to the house. This means that when choosing equipment, we need to provide for the presence of an ADSL modem in its composition.
Wireless devices require at least two WI-FI access points (2 floors). The task is facilitated by the fact that the number of Net-sockets on each floor does not exceed three. This allows you to minimize the amount of equipment required to build a local network.
A home LAN network for a two-storey house with an area of 200m2 can be implemented on an ADSL router and an Ethernet switch.
The block diagram of the network is shown in fig.2.
Fig.2.
The main characteristics of the devices used:
D-Link DSL-6740U
 Device type: DSL modem, router, Wi-Fi hotspot
Device type: DSL modem, router, Wi-Fi hotspot
Support: VDSL2, ADSL2
Wireless standard: 802.11b/g/n, frequency 2.4 GHz
Max. speed wireless connection: up to 300 Mbps (802.11n)
WPA/WPA2 encryption technology
Switch: 4xLAN
Port speed: 100 Mbps
Dimensions (WxDxH): 228x175x40 mm
Weight: 460 g
Contents: Router, power adapter, RJ-45 cable, RJ-11 cable, splitter, software disk.
D-Link DIR-615/K1A
 Device type: Wi-Fi hotspot, Switch
Device type: Wi-Fi hotspot, Switch Max. wireless connection speed, Mbps - 300
Wireless standard: 802.11n, frequency 2.4 GHz
Data encryption: WPA, WPA2
Number of Ethernet ports - 4
Port speed: 100 Mbps
Dimensions (LxWxH): 117x193x31 mm
Weight: 940 g
Contents: Router, network adapter, RJ-45 cable, 2 external antennas, CD with software.
Network diagram
Mounting (low current) cabinet it is best to place it in a place where it is most convenient to bring cables from all rooms and provide reliable coverage of the WI-FI access point. IN this project- in the lobby on the first floor. There you will also need to run a cable from the provider.
The second mounting cabinet is installed in the hall on the second floor. The cabinets also include electrical sockets to power routers.
From low current cabinet"star-shaped" cables diverge separately for the Ethernet network, telephone and television. At the ends of these cables, separate sockets are installed for each system: telephone and computer (symmetrical) and television (coaxial). The living room has a double socket (telephone + computer).
So Thus, three cable systems and three types of sockets are formed in the building. Such a scheme is more reliable and convenient for installation - each cable system can be mounted almost independently.
The wiring diagram for telephone, television and Ethernet networks is shown in fig.3.
Fig.3
Installing and connecting routers does not cause any difficulties. The main thing is to determine the place in the wiring closet where it will be located, and fix it well. For mounting in a vertical position, there are special curly grooves in the bottom of the router, for which it is suspended and fixed in a cabinet or on a wall. Some models are equipped with special stands or panels for vertical positioning.
If you liked the article and you appreciate the efforts invested in this project –
You have the opportunity to contribute to the development of the site on the page
Project support.
"Electrics for the home". It focuses on the basics of electrical engineering and electricity, with a focus on home electrical installations and the processes that take place in them.



