The right choice of motherboard - instructions from "A" to "Z. How to choose a computer case - criteria and characteristics Motherboard chipsets
Read also
How to choose a motherboard | Form factors
While large manufacturers can assemble ready-made PCs of any configuration and format, ATX format motherboards and its variations fill the market for solutions for self assembly computers. Smaller ATX versions limit expansion options and make you more dependent on integrated or external devices, while still allowing you to build a miniature system. Even considering the fact that integrated audio and network controllers have grown to the point where they no longer need expansion cards, the same cannot be said about integrated graphics. If you use your computer for more than just watching videos and running work applications, then you will probably want to install a discrete graphics card to support 3D content. While office workstations and media players can perform only one function during their life cycle, when building a multi-purpose configuration, it would be nice to have additional space for expansion cards.
ATX over Mini-ITX
The ATX format was developed to address three shortcomings of the predecessor AT form factor, and it has a number of improvements. Firstly, the part of the board dedicated to the processor is located away from long video cards, while in AT-boards the processor was installed behind or instead of the slots for video cards. Secondly, the introduction of a separate I / O panel on the motherboard makes it possible to do without brackets covering the USB, Ethernet and audio inputs on the slots. Thirdly, cooling goes from the front lower edge to the rear upper edge through the power supply and / or fan. All three innovations help to delimit the processor and expansion slots on the platform.
The most significant of the improvements was the addition of a power switch on motherboard, which allowed the system to turn itself off at shutdown, as well as enable wake-on-ring (using a modem), wake-on-LAN (using network adapter), power up/power down and keyboard shortcuts.
ATX-derived formats use the same processor socket, so smaller motherboards can fit into larger cases if needed. The ATX standard includes micro-ATX and Flex-ATX form factors. Most Shuttle-designed PCs (often referred to as SFF - Shuttle Form Factor or Small Form Factor) use a two-slot variant of the Flex-ATX board, shrunk to about 20 cm. Later, VIA reduced the mini-ITX form factor to 17 cm, reducing the number of connectors. up to one.
ATX sizes are in fractional inches and rounding to the nearest millimeter is the most probable cause why motherboard mounting holes are slightly offset from mounting points in many cases. Even the creator of the ATX, Intel, has recently been rounding up values when converting sizes from the original designations (in inches).

The image above compares the maximum size and maximum number of slots in various form factors, and the dotted lines show how the mounting holes in smaller form factor boards match those in larger cases. Also shown in the figure is a long time ago forgotten decision mini-ITX problems.
Even before there were powerful mini-ITX gaming configurations, AMD tried to set the standard for gaming Shuttle devices with the introduction of the new DTX form factor, and its two-slot variant called mini-DTX resembles mini-ITX except that , in size that it is a little deeper, which allows you to place four memory modules and a full-fledged processor voltage regulator. While most mini-ITX gaming cases are suitable for DTX motherboards, the persistence of the mini-ITX form factor discourages manufacturers from developing solutions for DTX. As shown above, the same rule applies when a smaller motherboard fits a larger case.
Custom Form Factors
Oversized motherboards have been around for as long as any of the form factors we've listed above. One of the oldest is the EATX with a depth of 13 inches (33 cm from back to front). Foxconn's attempt to develop a 10-slot form factor was only successful in introducing 10-slot cases to the market, and other manufacturers responded with 9-slot XL-ATX (34.5 cm), where the tenth slot in the case is used to install an oversized video card into the bottom slot of the platform. The corresponding cases are labeled as XL-ATX compatible and will fit a wide variety of smaller motherboards up to mini-ITX.
How to choose a motherboard | Connectors
In terms of processor sockets, motherboards used to be divided into two classes according to age and price, but AMD has created a third class of low power platforms. We will rank them by popularity:
Intel LGA 1150
Supporting the widest range of Intel processors, LGA 1150 socket motherboards connect to two DDR3 memory channels and up to 16 PCI Express 3.0 lanes at full speed (8 GTex/s), which can be shared among up to three additional devices. The processor itself contains the memory and PCIe 3.0 controllers, eliminating the need for an additional northbridge on the chipset. Instead, a one-piece controller hub acts as a traditional southbridge. It uses a secondary PCIe 2.0 controller to connect devices that require less bandwidth.

Since the connector is designed for a large number of PCIe connections, the LGA 1150 is generally best for those who need only a few expansion slots. PCIe 3.0's bandwidth advantage allows for luxurious levels of performance in multi-processor configurations such as SLI and CrossFire, but adding a third card to the array can be problematic (Nvidia even blocks SLI compatibility in quad-lane slots). In addition, all eight PCIe 2.0 lanes are capable of throughput 2 GB/s with all connected devices, including 6 SATA 6 Gb/s ports, all 6 USB 3.0 ports and any GbE network controllers.
AMD Socket AM3+
The AMD AM3+ socket has been flagship for three years now, and even as the company is less focused on the hi-end PC market and continues to upgrade mainstream components. The 990FX chipset helps secure the title of the top platform: it provides 42 PCI Express 2.0 lanes via the northbridge and two more lanes via the southbridge. The memory controller integrated into the processor supports dual-channel memory up to DDR3-1866 (and a little more with overclocking). Speaking of overclocking, the supported range of CPUs ranges from a liquid-cooled octa-core processor overclocked to 4.7 GHz (far beyond its core architecture specifications) to a quad-core model in the $110 price range.

Considering that soon this platform will be withdrawn from the market, we recommend it only to those buyers who have carefully considered all options and decided to stop there.
Intel LGA 2011-v3
Offering support for Intel Haswell-E (5900 and 5800 series) Core i7 processors (up to 8 physical cores), the LGA 2011-v3 connector routes up to 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes from processor to expansion slots. The large PCIe 3.0 controller, in addition to four DDR4 memory channels, is the best choice for users who need not only high processing power, but also support for high bandwidth expansion cards.

Unlike the previous connector for high-end platforms, Intel is also differentiating its top 5900 series models in the product line by disabling twelve of the integrated PCIe 3.0 lanes on lower-end 5800 series processors. based on the 5800 series processor, artificially scaring off buyers who may have a not very powerful processor and a very expensive video card. Depending on the chosen motherboard, the reduction in the number of available lanes may also prevent access to the simultaneous use of three video cards in SLI mode.
The 8-lane PCIe 2.0 controller is integrated into the chipset and operates at 2 GB/s data speed, just like the LGA 1150.
Intel LGA 2011
Supporting Intel processors Ivy Bridge-E (4900 and 4800 series) and Sandy Bridge-E (3900 and 3800 series) Core i7 (up to 8 physical cores), LGA 2011 routes 40 PCIe lanes directly to multiple slots from the processor. Since the 40-lane controller resided on the processor, the new CPU Ivy Bridge adds support for PCIe 3.0 mode to a platform that natively only works with PCIe 2.0.

Existing platforms on LGA 2011 should be considered almost obsolete, as Intel has released a "v3" replacement. Some customers looking to save money can choose this product, which has a 40-line controller for the 4800 series processor, which has been reduced to 28 lines on the 5800 series processor. Similarly, the DDR3 memory standard is more widely available in the mainstream market and costs less, than DDR4. But when considering options for an upgrade, you should not forget about the end of the life cycle of this platform.
AMD Socket FM2+
AMD's version of the mainstream platform resembles Intel's solution: 16 PCIe 3.0 lanes connect one or two high-bandwidth expansion cards. Compared to Intel, AMD eliminates the impact of the chipset's 2GB/s connections on platform capabilities by giving the processor four of the eight PCIe 2.0 lanes.

Unlike Intel's solution, Nvidia does not support SLI on AMD's FM2+ chipset, but provides CrossFire compatibility and even supports hybrid mode to boost the performance of a low-end AMD graphics card when combined with integrated graphics. However, we have encountered some problems with this technology and do not recommend it to our readers.
AMD socket AM1
In this case, AMD integrates the entire chipset with the CPU in order to save power consumption and save customers money. These low-end processors support one PCIe 2.0 x4 graphics card, four PCIe devices (integrated card slot or expansion slot), two USB 3.0 connectors, and a pair of SATA 6Gb/s devices. This solution has to compete primarily with motherboards that have an integrated processor, but adding a socket to the platform gives AMD more opportunity to better position other CPU models.
Assembling your own PC is not an easy task. It is important to carefully consider every detail of the system. But most users do not think about how to choose a motherboard or power supply. They throw all their energy into buying a processor and video card. All this leads to the fact that components can be unbalanced or, even worse, incompatible.
Importance
Understanding how to choose a motherboard for a computer is a must. All other elements of the system are connected to this platform. It affects the service life and stability of the PC.
In addition to being compatible with all devices, it should provide an opportunity to improve the system in the future. Therefore, it is very important to look to the future when choosing a motherboard, as technology develops, and gaming computers are updated every 1-2 years.
Motherboard
Motherboards can be not only in a computer, but also in other devices. But since we are considering exactly the PC system, we will not delve into third-party topics and consider the components of the computer board.
The motherboard has major non-removable parts. These include:
- connector for ;
- slots for random access memory;
- north and south bridges;
- boot ROM;
- various expansion slots;
- interfaces and controllers of peripheral devices.
In order for the system unit to be complete, a power supply and a cooling system are connected to the motherboard.
Choice
How to choose a motherboard? There are many parameters to consider when purchasing this device. This includes:
- manufacturer;
- price;
- form factor;
- socket;
- chipset;
- memory;
- slots and connectors;
- electronic components;
- power schemes;
- cooling systems;
- equipment and much more.
In order not to make a mistake in choosing a platform, it is important to consider each of these points in more detail and understand which element is responsible for what.
Manufacturer and price
This option is not always the key to the question of how to choose a motherboard. This is due to the fact that not all users follow the release of platforms. They do not know who is the sales leader, which company is focused on the production of budget or gaming motherboards. Therefore, in this case, it is more often focused on the cost.
But still, you can get a general picture and point to the leading manufacturers. It is not easy to name a leader, but most experienced users will agree that Asus is one of the best. It manufactures mid to high end boards. The quality of materials is always good, but the cost is sometimes too high.
Asus hardly works with platforms entry level, and if they are released, then the overpayment for the brand is definitely not worth it. But if you look closely at the models of the middle segment, then it may make sense to pay extra to get a really high-quality and durable device.

Entry-level motherboards work best with Gigabyte and ASRock. The last manufacturer is a subsidiary of Asus. Both companies have a proven track record of developing low cost solutions for work PCs.
Many people ask which motherboard to choose for Intel. In addition to the manufacturers described above, it is worth paying attention to Intel itself. The corporation produces stable and high-quality platforms based on its own chipset. The only drawback is that they are less functional and more expensive, so they are more popular in the corporate sector.
Chipset
The next important factor is the choice of chipset. In general, this is a paramount parameter on which the entire system as a whole depends. When a user decides to assemble the system on his own, he must immediately decide: he will give preference by Intel or AMD.

You need to decide on this right away, since you will have to select the processor further, and, accordingly, the socket.
Chipset from Intel
If the choice fell on Intel, then you will have to figure out the four main chipsets. For example, if you don't know which one to choose, take a closer look at the models with the B250/H270 and Z270 chipsets. The latter is also a great option for professional systems. If you need a corporate computer, then the Q270 is suitable, and for cool powerful PCs, the X99 / X299.
If you are going to buy an 8th generation processor, then you need to pay attention to the B350 / H370 and Z370, for medium and powerful systems, respectively.
For an average multimedia or gaming PC, the B250/H270 or equivalent 8th generation will do. If you are going to experiment and change the processor multiplier, you will have to take a more expensive model with Z270 and Z370 chipsets.
Chipset from AMD
AMD has also easily separated all of its motherboards by index. For an office or multimedia PC, you need to choose the A320 chipset. The gaming system can be assembled based on the B350 chipset. Those who like to experiment are provided with the X370 platform.
The first option is the easiest, because it does not even have the ability to overclock the processor. But the gaming version of the chipset can cope with this task. The X370 is good because, in addition to overclocking, it allows you to install several video cards on the board.
Form Factor
The next important aspect is the form factor of the system platform. Experts so call the dimensions of the device. In addition to the rather unusual form factors, there are three main ones: ATX, MicroATX (mATX) and Mini-ITX.

ATX is the most common full size platform format and is considered the best for PC. Since it is the largest of all, many devices can fit on it. For example, if you do not know which motherboard to choose for, then you should definitely pay attention to the ATX dimensions.
MicroATX also often becomes a platform for a gaming system. But this is a reduced platform format, which also has fewer connectors. Can be installed in both a full-size chassis and a compact chassis.
Mini-ITX is a very compact motherboard that is used to build mini PCs. Such a computer is limited in size and needs special cooling.
socket
Many are wondering how to choose a motherboard for a processor. If you have already given preference to one of the companies, Intel or AMD, you will have to opt for one of the processors. Otherwise, you will not be able to pick up the platform, because the processor socket data is needed.
What is socket? This is a connector format for connecting the chip to the platform. The motherboard must have the same connector as the processor that will be installed on it.
The manufacturer very often experiments with processor sockets. They change from year to year and acquire new modifications. Therefore, it is important to purchase a chip and a board that would have the most modern socket. Thus, you can further improve the system without extra spending.

Now all available sockets of Intel or AMD processors can be divided into obsolete, obsolete and modern. If we are talking about Intel, then outdated and obsolete are: Socket 478, 775, 2011, 1150. But the new ones are: version 2, and 2066.
Among the most modern are AM4 and TR4. But they have already become obsolete and obsolete: AM1, AM2, and others.
Memory
Memory slots also affect the choice of motherboard. If we talk about the compact MicroATX form factor, then there are rarely more than 2 slots. But full-size platforms are equipped with 4 slots.
Of course, many may not need more than two memory slots. Although if you want to further increase the RAM, then free slots will be very useful.
It is also worth paying attention to the type of memory module. Modern platforms already support the DDR4 type. More budget versions can work with high speeds, up to 2666 MHz. But the middle and high class motherboards boast speeds up to 3.6 GHz.

To choose a gaming motherboard, it is not necessary to spend money on platforms that support 3 GHz speeds. Their cost is much higher, but a tangible increase gaming performance No. In addition, the RAM modules themselves are not cheap. The higher the speed of the memory, the more difficult it is for the processor to cope with it. The best option is DDR4 memory with a frequency of 2.4 GHz.
video card
The connectors for connecting a graphics adapter are universal on almost every motherboard. All modern platforms are equipped with a PCI-Express interface. It happens that several such slots are placed on the platform, which means that several graphics adapters can be installed on it at once. Some experts believe that in this case it is better to purchase a more powerful video card than a few average ones.
Expansion slots can also be occupied by other devices, for example, by installing a solid state drive or a sound card.

Connectors
Slots on the system platform are often bypassed, because it is quite difficult to understand them. But this is no less important factor. To connect HDD need a universal 3. The latest motherboards also got an M.2 slot, which is needed to connect solid state drives latest generation. We'll have to take a closer look at the power connector of the motherboard. Modern models are equipped with a 24-pin connector.
The chip can be powered by a 4 or 8 pin slot.
Integrated devices
Very often, the manufacturer places integrated devices on the platform. Some systems can work without a graphics card because the motherboard has an integrated graphics adapter. However, it is important to purchase a processor that has an integrated video core.
The platform also has an integrated sound card. Most often it is enough for any task. But there is also a slot for an additional sound card on the platform. It may be needed, for example, by those who want to record music.
Among other integrated devices, there is also a network card, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. For everyday use, the standard settings are enough.
Interface panel
Modern boards have all standard external connectors. Therefore, at this point it is not so important to pay attention. If you need to connect some specific devices, then you will have to study the list of available interface panel connectors.

Cryptocurrency mining
Which motherboard to choose for mining? If you have asked this question, then you understand what is important in this process. The main thing is that the platform supports multiple video cards.
When choosing a motherboard, it is important to pay attention to:
- Number and location of PCI-E slots. It is important that their location does not interfere with the connection of several types and their cooling.
- Compatibility of the board with an inexpensive chip. In mining, processor performance is unimportant.
- Optimization for cryptocurrency mining. It is necessary that the platform does not have any extra functions that could distract the system from the main task.
- Price.
If the user does not want to buy asics, but is ready to assemble a computer for mining on his own, he will have to thoroughly understand all the components. Manufacturers quickly picked up the whole story with cryptocurrencies and began producing special devices for their mining.

ASRock showed itself in this matter. It has released platform models that are optimized for the most efficient use of the mind. Although other companies do not lag behind this manufacturer: Asus, MSI, Gigabyte.
conclusions
Choosing a motherboard is easy if you understand its tasks and capabilities. The main thing is to decide on the chipset, choose the processor, and hence the socket. After dealing with the required amount and type of RAM, and finally, resolve the issue with the number of video cards.
Otherwise, motherboards have a similar number of internal and external connectors, most models support an integrated video core, sound and network cards.
Assembling or upgrading a computer is a solution to a problem with several inputs, and the result should satisfy all the “Wishlist” as much as possible and meet all the “mogelki” so as not to deplete the family budget. Well, let's start talking about the parts that make up any computer, from the basics, from the basis, from the mother of our systems. As you understand, today we will talk about how to choose a motherboard, which model can be the best purchase, what you can save on without overpaying for unnecessary functions. Today is the first part, and we will look at the lower and middle price range, leaving the models "for overclocking" and games for next time.
Criterias of choice
As always, we are dancing from the traditional item of Russian life, “from the stove”, for which we will choose the “folk” socket 1151, for which manufacturers have released a huge number of motherboards. With such a choice, sometimes the eyes really “run up”. We have to figure out how the fees differ, and for what the manufacturer wants to take this or that amount from us, and what to give for this amount.
Armed with knowledge, we will distribute all the boards into several classes. Naturally, this division is conditional, and does not mean at all that only dull performance, suitable only for office use, can be expected from a motherboard from the budget segment.
Not at all. Even ready-made system blocks from well-known manufacturers, moreover, positioned as gaming ones, are often equipped with motherboards based on the H110 chipset, which seem to be hardly suitable for this.
And yet, in terms of functionality and, most importantly, expansion options, motherboards differ. How they differ and depending on the purpose for which they are selected. If you are interested in the possibility of overclocking the processor and memory, this is one class of devices. If the assembled computer will have to work in normal mode until it is replaced / upgraded in the form in which it is bought, then what is the point of overpaying for redundant functions?
I will not limit the form factor either. ATX, mATX, Mini-ITX, Mini-STX and others - we'll leave everything and consider it. The only thing that we will leave out of the brackets is the preferences of a particular brand, the quality of service.
Budget motherboards
Models fall into this section not so much by price, but by their capabilities. Agree, the H110 chipset cannot be attributed to top solutions. This is typically a budget option for building systems with rather limited expansion and configuration options.
At the same time, such motherboards perform their work no worse than more expensive models, and within the limits of their capabilities, they work as they should. So let's see what's on sale right now. Let's go in ascending order.
ASRock H110M-DGS R3.0
One of the cheapest models, the price of which is around 3000 rubles. Has PCI-E x16 slots, 1 PCI-E x1 slot, 4 SATA3 slots, 2 slots for DDR4-2133 memory. A typical budget option with, however, a radiator is used for cooling.
R3.0 means that this is the 3rd revision of the board, and it should already support 7th generation Kaby Lake processors out of the box. If an earlier board came across, then that's okay too. In extreme cases, you will have to update the BIOS.
The board has a microATX form factor. The 8-pin CPU power connector is located close to the socket, which can cause problems when installing bulky coolers. It may not be possible to lay the cable qualitatively and neatly. Naturally, there is no talk of using two video cards. Moreover, there is only DVI for connecting a monitor.
MSI H110M PRO-D
 In fact, it is a direct analogue of the previous one, the cost, if different, is 100-200 rubles in one direction or another, depending on the store. Of the differences - 2 PCI-E x1 slots, 6 power phases, 2 USB 3.1 slots and, perhaps, that's all. A slightly larger size allowed the board to be laid out more traditionally, placing the connectors for connecting drives along the bottom edge.
In fact, it is a direct analogue of the previous one, the cost, if different, is 100-200 rubles in one direction or another, depending on the store. Of the differences - 2 PCI-E x1 slots, 6 power phases, 2 USB 3.1 slots and, perhaps, that's all. A slightly larger size allowed the board to be laid out more traditionally, placing the connectors for connecting drives along the bottom edge.
In general, this is a more than worthy choice for a minimum of money, and the board shows excellent performance. If you are ready to put up with DVI only, no M.2, only two memory slots, and don't plan on installing a lot of additional devices, then this board is definitely a bargain.
ASUS H110M-R/C/SI
 At a price of about 3300 rubles. differs from those listed, perhaps, only by the presence of HDMI. There are no more benefits. So, if only DVI is not enough to connect a monitor, then in this case the whole “zoo” is present - VGA, DVI, HDMI. An overpayment of a couple of hundred rubles for the wide possibility of connecting a monitor is fully justified.
At a price of about 3300 rubles. differs from those listed, perhaps, only by the presence of HDMI. There are no more benefits. So, if only DVI is not enough to connect a monitor, then in this case the whole “zoo” is present - VGA, DVI, HDMI. An overpayment of a couple of hundred rubles for the wide possibility of connecting a monitor is fully justified.
Of the features, it is worth mentioning the unsuccessful arrangement of contacts for connecting front audio connectors. They are located right in front of the PCI-E x16 slot, and the installed video card covers these pins. Yes, and one of the SATA stands out from the row, being a little deeper in the board.
MSI H110M PRO-VD (PLUS)
 Unremarkable "mothers" at a price of just over 3300 rubles. At the same time, the PLUS version differs from the usual one in a smaller number of USB ports on the back wall (4 versus 6) and the presence of two full-fledged PS / 2 together with one combined one. Here is such a plus.
Unremarkable "mothers" at a price of just over 3300 rubles. At the same time, the PLUS version differs from the usual one in a smaller number of USB ports on the back wall (4 versus 6) and the presence of two full-fledged PS / 2 together with one combined one. Here is such a plus.
USB version 3.1 is used. DVI and VGA are used to connect the monitor. There are 4 SATA, 2 memory slots, 1 PCI-E x16 and 2 PCI-E x1.
In the rest - normal boards, if there are no cheaper alternatives, then you can take it.
ASUS H110M-CS
An incomprehensible fee, or rather, the price of it. For 3800 rubles. everything is offered the same as in the case of the cheapest ASRock H110M-DGS R3.0. The difference is in the presence of a second PCI-E x1 slot and the replacement of DVI with the already archaic VGA. For what to overpay, for a brand?
MSI H110M ECO
 The price is just over 3800 rubles. seems overpriced, although compared to the previous one, it is somewhat compensated by the presence of VGA, DVI, HDMI, as well as the use of a network controller on an Intel chip, which is a little faster than solutions based on Realtek chips.
The price is just over 3800 rubles. seems overpriced, although compared to the previous one, it is somewhat compensated by the presence of VGA, DVI, HDMI, as well as the use of a network controller on an Intel chip, which is a little faster than solutions based on Realtek chips.
The board provides ample opportunities for energy saving. It is possible to manually turn off unused elements (fans, lights, etc.). There are also auto mode, where you can set up to 3 energy saving profiles. while using a high-quality element base.
Otherwise, there are no clear arguments in favor of this fee, as well as reasons to overpay. There are no advantages over cheaper alternatives.
MSI H110M Gaming
 Behind beautiful name, belonging to gaming boards and for red connectors, the manufacturer wants 700 rubles more than for the previous, "environmentally friendly" version. You will have to pay for external attractiveness.
Behind beautiful name, belonging to gaming boards and for red connectors, the manufacturer wants 700 rubles more than for the previous, "environmentally friendly" version. You will have to pay for external attractiveness.
True, there will be not 4 USB connectors on the rear panel (which is not enough in our times), but 6, and 4 of them are versions 3.1. Otherwise, it is an analogue of the previous one, functionally not having any advantages.
MSI H110M GRENADE
Price - about 4700 rubles. It differs from most of the previous ones by the presence of an Intel network chip, an M.2 connector on the PCI-E bus and USB Type-C. Is it worth all the overpayment - you decide. The presence of M.2 to install an SSD under the operating system can be useful when assembling compact computers.
ASRock H110M-STX
 Mini-STX form factor board for building very compact systems. The cost is about 5200 rubles. The layout is specific, in which the connectors are located not only on the rear edge of the board, but also on the front. Of the features - support for processors with a TDP of up to 65 W, the use of an Intel network chip, SO-DIMM DDR4 memory modules. There is USB Type-C, 2 SATA3. You can use VGA, HDMI, or DisplayPort to connect a monitor.
Mini-STX form factor board for building very compact systems. The cost is about 5200 rubles. The layout is specific, in which the connectors are located not only on the rear edge of the board, but also on the front. Of the features - support for processors with a TDP of up to 65 W, the use of an Intel network chip, SO-DIMM DDR4 memory modules. There is USB Type-C, 2 SATA3. You can use VGA, HDMI, or DisplayPort to connect a monitor.
2 M.2 connectors installed:
- Key E (Socket 1) - for installing Wi-fi or Bluetooth modules.
- Key M (Socket 3) - for installing SSD drives on the PCIe Gen3 x4 2280 bus.
Please note that this board does not support M.2 drives running on the SATA bus, only PCIe!
An external 19 V power supply is used.
ASUS H110T
 Form factor - Thin Mini-ITX. Price - about 5300 rubles. Of the differences from the previous model - the presence of two gigabit network interfaces(based on Intel and Realtek chips), no USB Type-C, support for M.2 SSDs in sizes 2242/2260. Lack of support for the most popular 2280 SSD size may negate the use of this slot.
Form factor - Thin Mini-ITX. Price - about 5300 rubles. Of the differences from the previous model - the presence of two gigabit network interfaces(based on Intel and Realtek chips), no USB Type-C, support for M.2 SSDs in sizes 2242/2260. Lack of support for the most popular 2280 SSD size may negate the use of this slot.
To connect the monitor, you can use HDMI, DisplayPort. Memory - notebook, SO-DIMM.
Other options
Naturally, these are not all models. I have listed only those that, in my opinion, may be of some interest. For about the same cost, you can find other options that do not differ in almost anything. So, the cheapest models can be competed with, for example, Gigabyte GA-H110M-S2, but at the same or slightly higher (50-100 rubles) cost, there are no advantages. The whole difference comes down to the number of power phases and layout.
MSI H110M PRO-VH is a typical competitor to the MSI H110M PRO-VD (PLUS) models, and differs only in the presence of HDMI, for which you will have to pay about 60 rubles.
You can pay a few hundred rubles extra if there is really a need for HDMI connector, M.2, or you have equipment connected via outdated COM or LPT interfaces.
Many board models, in fact, have several modifications that differ in the installed interfaces, primarily for connecting a monitor. So, ASRock's simplest H110M-DGS R3.0 has only DVI, and H110M-DVS R3.0 also has VGA. True, it already costs 400 rubles more. ASRock H110M-HDV is already equipped with HDMI, and for this you will have to pay another 100 rubles compared to the previous version.
 Boards such as Gigabyte GA-H110-D3A, ASRock H110 Pro BTC+ and the like stand somewhat apart. Their cost is 7500 for the first and about 12700 for the second. Both of them are full-fledged ATX, and such a characteristic as the number of PCI-E x1 ports speaks about the scope of application. Gigabyte has 5 of them, and ASRock has 12. It is probably already clear that these boards are designed specifically for cryptocurrency mining.
Boards such as Gigabyte GA-H110-D3A, ASRock H110 Pro BTC+ and the like stand somewhat apart. Their cost is 7500 for the first and about 12700 for the second. Both of them are full-fledged ATX, and such a characteristic as the number of PCI-E x1 ports speaks about the scope of application. Gigabyte has 5 of them, and ASRock has 12. It is probably already clear that these boards are designed specifically for cryptocurrency mining.
To summarize, there is no fundamental difference between the boards. You can take any minimum price with the necessary set of installed interfaces, the choice of which, in other matters, is not so wide. They differ in the presence and quantity of USB 3.0 / 3.1, USB Type-C, M.2 connector. There are differences in the way the monitor is connected. Even the cheapest motherboard can be connected via DVI. Yes, and with HDMI, the model is only 300 rubles more expensive.
I would not pay much attention to the difference in the processor power system. Someone has only 4 phases, someone has 6. It is clear that the more of them, the better. Especially ASRock likes to save on the number of power phases. On the other hand, only she has radiators to cool these circuits. Considering that overclocking of processors is impossible, this is quite enough.
Perhaps, Mini-ITX, Mini-STX form factor models have their own specifics, but when choosing such motherboards, you most likely know why such options are needed.
Mid-Range Motherboards
Here, boards based on the B150/250, H170/270, Q170/270 chipsets will be accepted for consideration. Let me remind you that they differ from the H110 in a larger number of PCI-E lines, the use of the 3rd generation of this interface, unlike the 2nd in the 110th chipset, a larger number of USB ports, and the ability to use already 4 DIMM slots instead of two .
The 2xx generation is not much different from the 1xx chipset generation. One of the main differences is drive support. Overclocking on these chipsets is not provided. This can only be done by increasing the frequency of the processor or memory. The use of processors with an unlocked multiplier (with the letter "K" in the marking) is not justified, since this feature cannot be used.
B150/250 chipsets are famous for office solutions, although the number of offered models is large, Q170/270 are specific products, more focused on the corporate segment, and the number of board models based on them is very small. The most popular one is the H170/270, which lacks only the ability to overclock the processor by a multiplier. In the rest - one of the most functional options.
Considering all the proposed models is a thankless task. There are quite a few of them, and most of them are not much different from each other. I will focus on the most attractive options.
ASRock B150M-HDS
In fact, it is a complete analog of the ASRock B110M-HDS board, differing only in a different chipset (B150) and a price of about 250-300 rubles higher. I don’t see much point in buying, given the minimum of connectors, the lack of M.2, and even the not very good location of SATA connectors. It will be difficult to lay cables nicely and neatly.
Gigabyte GA-B150M-D2V
One of the cheapest, which already has 6 SATA connectors. The cost is about 4200 rubles. In the pros - 4 USB 3.0 on the rear wall, the presence of VGA and DVI for connecting a monitor. Of the minuses - only 2 DIMM DDR4, lack of HDMI and M.2 (although this minus is rather controversial).
For your money - a good option.
Gigabyte GA-H170M-HD3 DDR3
 Pretty controversial model. Chipset - H170. On the one hand, the price is about 4200 rubles, which includes 6 SATA3, 2 SATA Express (outdated connector), support for RAID 0,1,5,10, the presence of PCI-E M.2, VGA, DVI, HDMI. On the other hand, it works with memory of the already outdated DDR3 generation, and only 2 such modules can be installed. In our times, this is rather a minus, although if other characteristics suit you, then you can take it. There will be no noticeable difference between DDR3 and DDR4. The problem is with the upgrade. The next time you replace the motherboard, this memory will no longer be usable.
Pretty controversial model. Chipset - H170. On the one hand, the price is about 4200 rubles, which includes 6 SATA3, 2 SATA Express (outdated connector), support for RAID 0,1,5,10, the presence of PCI-E M.2, VGA, DVI, HDMI. On the other hand, it works with memory of the already outdated DDR3 generation, and only 2 such modules can be installed. In our times, this is rather a minus, although if other characteristics suit you, then you can take it. There will be no noticeable difference between DDR3 and DDR4. The problem is with the upgrade. The next time you replace the motherboard, this memory will no longer be usable.
If memory modules of this particular generation remain, then you can save money and use them by updating the motherboard and processor, postponing the transition to a new generation of memory for another time.
The presence of a PCI slot is also debatable. One more PCI-E would be better. In general, I would not take this motherboard, precisely because of the futility of memory.
MSI B250M PRO-VD
A motherboard based on a fresh B250 chipset for 4400 rubles, and one of the cheapest on it. The asset is a PCIe M.2 connector, 4 USB 3.1 on the rear wall, the ability to connect 6 SATA drives. The lack of HDMI (there are only VGA and DVI), and there are only two memory slots can be disappointing. Otherwise, it's a good option at an attractive price on a good chipset.
ASRock B250M-HDV
Direct competitor of the previous model. It differs by a slightly higher price (about 4500 rubles), the presence of HDMI and a gigabit network card based on an Intel chip. True, USB is only version 3.0, no 3.1 and Type-C. In my opinion, the option is slightly preferable than the MSI model, if there are no complaints about the lack of the newfangled Type-C and USB 3.0 is quite enough.
A decent motherboard for the money.
ASUS H170M-E D3
 An even more controversial option than the Gigabyte GA-H170M-HD3 DDR3. The cost is about 4600 rubles. The same DDR3 memory, although there are 4 slots for installing RAM modules. At the same time, only 4 SATA3, although with support for RAID 0,1,5,10, there is M.2.
An even more controversial option than the Gigabyte GA-H170M-HD3 DDR3. The cost is about 4600 rubles. The same DDR3 memory, although there are 4 slots for installing RAM modules. At the same time, only 4 SATA3, although with support for RAID 0,1,5,10, there is M.2.
I have no arguments in favor of this model. If you definitely need RAID, then there is a slightly cheaper Gigabyte, in which you can also connect more drives for 2 drives. The only, although controversial, plus is 4 memory slots, and even then, there is a Gigabyte GA-H170M-D3H DDR3, which also has 4 DIMMs and the same price. The model has become obsolete and is not interesting for purchase.
ASUS B150M-A/M.2
 Quite a controversial option, primarily due to not the most recent chipset. Judge for yourself. After all, for 4800 rubles. there are 4 connectors for DDR4, and HDMI, and 6 SATA, and M.2, and USB 3.1 Type-C. In the minuses - the lack of RAID, the limitation of the memory frequency to 2133 MHz. If you need M.2 and Type-C is useful, then it makes sense to include this board in the list of candidates for purchase. It's not expensive, but it has everything you need. At the same time, almost everything the same can be found on a more recent chipset and for about the same money.
Quite a controversial option, primarily due to not the most recent chipset. Judge for yourself. After all, for 4800 rubles. there are 4 connectors for DDR4, and HDMI, and 6 SATA, and M.2, and USB 3.1 Type-C. In the minuses - the lack of RAID, the limitation of the memory frequency to 2133 MHz. If you need M.2 and Type-C is useful, then it makes sense to include this board in the list of candidates for purchase. It's not expensive, but it has everything you need. At the same time, almost everything the same can be found on a more recent chipset and for about the same money.
An alternative is the Gigabyte GA-B250M-DS3H, which costs about 200 rubles. larger, offers a more recent chipset, but no Type-C. The ASUS PRIME B250M-A costs about the same with the same specifications and the same price.
There is also the already mentioned ASRock B250M-HDV, which has everything that this model has, but with a more recent chipset. True, this ASUS has 4 slots for installing memory, unlike the B250M-HDV, but the price is slightly higher.
Another alternative is MSI B250M PRO-VDH, which has everything the same as this Asus, but the chipset is more recent.
MSI B250M BAZOOKA (PRO)
The cost is about 5300 rubles, the chipset is B250. What advantages does it have over ASUS PRIME B250M-A? None. All the same. In this case, the determining factor is the cost of one or another model at the moment. Whichever is cheaper, take it.
The PRO version differs from the usual one by the installed heatsink on the processor batteries.
MSI B150M NIGHT ELF
 The cost is about 5500 rubles. A similarly equipped board can be found cheaper. What is the overpayment for then? For backlighting, an Intel network card and beautiful heatsinks.
The cost is about 5500 rubles. A similarly equipped board can be found cheaper. What is the overpayment for then? For backlighting, an Intel network card and beautiful heatsinks.
With the characteristics, however, everything is in order. There are also 6 SATA, 4 slots for memory modules, and 2 PCI-E x16, and an Intel network chip. DVI is installed for monitor connection.
For aesthetics, if the case has a glass wall, a very good option. For those who are more concerned not with how the board looks, but with how it works, spending money is not justified.
ASUS STRIX B250G GAMING
Prepare 6200 rubles. For what? For beautiful heatsinks, an Intel network card, 2 M.2 connectors, HDMI, the SupremeFX audio chip, which is used in more advanced motherboards from this manufacturer. Is the sound better than when using a Realtek audio chip? Don't think.
Otherwise, it is much more attractive than the previous model, at least thanks to a newer chipset, the presence of M.2.
ASRock H270M Pro4
 One of the cheapest motherboards based on the H270 chipset. The cost is about 6200 rubles. There are 6 SATA3 with support for RAID 0, 1, 5, 10, 2 M.2 connectors, both running on the PCIe bus, with one M.2 supporting SSDs of this form factor running on the SATA bus. The second M.2 is PCIe drives only.
One of the cheapest motherboards based on the H270 chipset. The cost is about 6200 rubles. There are 6 SATA3 with support for RAID 0, 1, 5, 10, 2 M.2 connectors, both running on the PCIe bus, with one M.2 supporting SSDs of this form factor running on the SATA bus. The second M.2 is PCIe drives only.
There is also HDMI c DVI, USB Type-C is also installed. Processor power supply - 6-phase. In general, a very "packed" model on a fresh chipset and for reasonable money. It can be compared with the previous model. Although there are no beautiful heatsinks and the word "GAMING" in the name, the performance is by no means worse, and even better.
I advise you to take a look. If multiplier overclocking is not needed, this is probably one of the best options. Similar in characteristics to the MSI H270M BAZOOKA for about 300 rubles. expensive. In this case, only one M.2.
There is a modification of this board with a slightly different layout - the H270 Pro4 model, although it is already about 400 rubles more expensive. But there is also ASRock B250M Pro4, a slightly simplified version based on a simpler chipset, devoid of RAID. But it costs 800-1000 rubles. cheaper.
ASRock Fatal1ty B250M Performance
 The cost is about 6350 rubles. The board is beautiful, made in red and black colors, in which the memory slots and heatsinks are painted. Metal connector for video card.
The cost is about 6350 rubles. The board is beautiful, made in red and black colors, in which the memory slots and heatsinks are painted. Metal connector for video card.
There is everything that should be in such boards - HDMI, Type-C, M.2, a network card from Intel, 6 SATA, DVI-D, HDMI, VGA, 4 slots for memory modules.
Well, the big name in the title. Whether all this is worth the overpayment is up to you. (Hint: the ASRock B250M Pro4 has everything the same, but without prettiness, for about 5200 rubles).
MSI B250M MORTAR ARCTIC
The cost is about 6600 rubles. The board is of interest primarily to modders who assemble a system unit in white colors. According to the characteristics - no difference with cheaper competitors.
Gigabyte GA-H270-HD3
 A full-fledged ATX board with three PCI-E x16 slots, two PCI-E x1 and two PCI, since the chipset has enough lanes to install such a number of expansion slots. And for all this you will have to pay about 6700 rubles.
A full-fledged ATX board with three PCI-E x16 slots, two PCI-E x1 and two PCI, since the chipset has enough lanes to install such a number of expansion slots. And for all this you will have to pay about 6700 rubles.
Among other characteristics - 4 slots for DDR4 memory, 6 SATA, which can be combined into RAID 0, 1, 5, 10, there is PCI-E M.2, Network Controller Intel. You can use VGA, DVI, or HDMI to connect a monitor. No, except perhaps Type-C. The rest is a very sophisticated model. It will come in handy for those who really need all these features.
Against its background, the ASUS H170-PLUS D3 chamber looks strange, which at the same cost has DDR3 memory, only 4 SATA, USB 3.0 instead of version 3.1 from Gigabyte. Do you have any arguments in favor of this Asus? I have no.
ASUS B150 PRO GAMING/AURA
 The cost is about 7500 rubles. Compared to the Gigabyte GA-H270-HD3 does not offer anything new. Moreover, it lacks RAID support, there is no USB 3.1, and the chipset of the old series.
The cost is about 7500 rubles. Compared to the Gigabyte GA-H270-HD3 does not offer anything new. Moreover, it lacks RAID support, there is no USB 3.1, and the chipset of the old series.
True, beautiful lighting and painted radiators. The SupremeFX sound subsystem is used, there are 6 SATA, M.2, an Intel network controller, there is USB Type-C. For modders - it's the most, and the proprietary Aura lighting system is just to help. For boring pragmatists - unnecessary buns, for which it is not clear why they have to pay.
Gigabyte GA-H270-Gaming 3
 Estimated price - about 9000 rubles. Belongs to the game series of boards, which, in fact, follows from the name. It has everything that should be to build a very productive gaming computer.
Estimated price - about 9000 rubles. Belongs to the game series of boards, which, in fact, follows from the name. It has everything that should be to build a very productive gaming computer.
There are 6 SATA3 with support for RAID 0, 1, 10, 5, and 2 M.2 connectors, and 4 slots for DDR4-2400 memory, and USB 3.1, and Type-C, and DVI with HDMI. By the way, there is also support for RAID 0, 1, 5, 10. Among the features is the use of a network gigabit controller Killer E2500 from Rivet Networks. Naturally, everything is in newfangled lighting. Form factor - full ATX.
MSI H270 GAMING PRO CARBON
 This is one of the most expensive boards. Its cost is about 9300 rubles. The H270 chipset provides support for DDR4-2400 memory, 4 memory slots, 6 SATA3 installed, 2 M.2 connectors. There are all modern interface connectors, including USB Type-C. An Intel based network card is used.
This is one of the most expensive boards. Its cost is about 9300 rubles. The H270 chipset provides support for DDR4-2400 memory, 4 memory slots, 6 SATA3 installed, 2 M.2 connectors. There are all modern interface connectors, including USB Type-C. An Intel based network card is used.
Naturally, it was not without customizable backlighting, installing a metal connector for the first PCI-E x16. The radiators are marked with logos and inscriptions.
This board is fundamentally no different from cheaper analogues. In this case, the choice is based more on the aesthetic qualities of the product, rather than on the characteristics that can be found in motherboards at a lower price.
MSI B250M PRO OPT BOOST
 The characteristics of the board practically do not differ from the MSI B250M BAZOOKA described above, and unlike the latter, there is no Type-C port, and a combined PS / 2 is also installed. At the same time, the price of the board is about 7900 rubles. The difference with a bazooka is about 2500 rubles. For what? And for the 16 GB Intel Optane module that comes with the kit (the letters OPT in the name are for a reason).
The characteristics of the board practically do not differ from the MSI B250M BAZOOKA described above, and unlike the latter, there is no Type-C port, and a combined PS / 2 is also installed. At the same time, the price of the board is about 7900 rubles. The difference with a bazooka is about 2500 rubles. For what? And for the 16 GB Intel Optane module that comes with the kit (the letters OPT in the name are for a reason).
Moreover, the cost of such a caching module, if you buy it separately, is about 1000 more than the difference in the cost of these two boards. What is not a reason to “one-shot” buy a motherboard and, in addition to it, a completely fresh Intel Optane, which will allow you to do without purchasing an SSD, but get the speed of work hard drive almost like a solid state?
Other options
As in the case of budget motherboards, a large number of other models remain behind the scenes, which literally do not differ from those listed, but have a higher price. There are sure to be a number of motherboards that will meet the required specifications, and choose the one that is simply cheaper.
For example, the ASRock B250M-HDV has HDMI, which is not available in the similar ASUS PRIME B250M-K, while it is also slightly cheaper. Sense then in purchase of this ASUS model?
So, the above MSI H270 GAMING PRO CARBON is far from the only one oriented to use in gaming computers. Moreover, it is one of the most expensive in this segment. There are ASRock B250 Gaming K4 (8200 rubles), ASUS ROG STRIX B250I GAMING (8200 rubles), ASUS STRIX H270F GAMING (9100 rubles) and a number of others. Which one to choose is a matter of taste and financial capabilities.
On the other hand, if we compare the top (in this collection) MSI H270 GAMING PRO CARBON and the cheapest on the same ASRock H270M Pro4 chipset, which is about 3000 rubles. cheaper, then we'll see what, in fact, is included in this difference. The boards are identical in terms of functionality, except for the lack of RAID in MSI and the presence of 2 more USB 3.0 on the rear wall, as well as an S/PDIF output.
On the other hand, MSI is equipped with a backlight (where would it be without it now), beautiful heatsinks, a rather spectacular appearance in general, and gold-plated audio connectors. It turns out that the increase in cost includes only all this beauty. Is she worth it?
Conclusion. How to choose the right motherboard
How to choose the best option from all the variety of offers? It's hard to give a definitive answer. For starters - I would not "bother" about the manufacturer. Only a few companies are engaged in the release, they are trustworthy and, frankly, the products of which differ little from each other. I would not consider exotics like Biostar or Colorful.
The next step is to decide on the main characteristics. What processor are you planning to use? If from the latest (at the moment) generation of Kaby Lake, then I see no reason to save money and consider models based on 100-family chipsets. With the exception of H110, if a budget system is being assembled and the goal is maximum savings. The 200 chipset family supports DDR4-2400 memory, has more PCI-Express lanes, which gives more options for system expansion.
Moreover, the savings may turn out to be minimal, and the chosen mother on the old chipset may no longer have any prospects. Likewise with memory. Even if there are DDR3 sticks left, it is not entirely reasonable to save and continue using them with a new one. system board. Since we are talking about an upgrade, you will have to part with DDR3 that has honestly served its purpose and switch to DDR4.
Naturally, when buying a motherboard based on chipsets without the letter "Z", i.e. without the possibility of overclocking by changing the multiplier, the use of processors with an unlocked multiplier (for example, I7-7700K) is not implied. Such a bundle, of course, will work, but why overpay for an “unlocked” processor if you can’t use it?
As you can see, there are models that may differ from each other by the presence or absence of just one connector, for example, HDMI. Do you need it, do you plan to use it? If yes, then there are no questions, if your monitor works fine from DVI, then is it really so important that the selected “mother” also has HDMI?
Now about the interfaces for connecting external devices. All models have USB 2.0 and 3.0, some have more connectors with old version USB, someone has more USB 3.0. Many offer USB 3.1, and sometimes Type-C is also present. You need it - look for a model with such a connector, no - well, do not pay attention.
Having determined the list of required characteristics, select suitable models. Is it worth taking the most expensive one? Well, if only for the sake of having a backlight, an unusual color of the textolite, metal connectors for a memory / video card, or some similar “buns”. It will work exactly the same as a cheaper analogue.
For that matter, it is better to pay attention to the processor power supply, how many phases are used in the selected board model, and whether they have heatsinks. This is especially true if you are not going to trade on trifles and plan to install a powerful processor.
The main thing is that there is plenty to choose from, and there is something to choose from. As usual, in all the variety of motherboards there are those that will fully meet your requirements, and among them it is quite possible to choose the most affordable one.
Next time, let's look at motherboards that involve overclocking and which have a place in gaming computers.

The question is very acute, given that professional electronics engineers recommend building a system unit around it.
The motherboard is the most important part of any computer. The stability of the entire computer as a whole depends on its quality and stable operation. Do not forget that all other components are connected to it in one way or another, and the motherboard coordinates their work. And if we compare the system unit with the house, then it is advisable to compare the motherboard with its foundation.
In total, there are three dozen parameters that can characterize this board, but this article will focus on the most significant of them that really affect the performance and stability of a computer device.

Component manufacturer.
Despite the fact that there are quite a number of manufacturers of computer components in the world, only a few of them make worthy motherboards. And so the question which company is better buy a motherboard answer is quite simple. Your choice should be stopped at the following four manufacturers:
- asus.
- AsRock (Subsidiary of Asus. The developments of this company are used with minor changes.).
- gigabyte.
- MSI.
It is better not to pay attention to such exotic manufacturers as Zotac and Biostar, as they are inferior to the main companies both in quality and functionality. If you need to assemble a server or workstation, then you can look at Intel products. There is nothing superfluous in such boards and they are optimally suited for long-term and uninterrupted operation in 24/7 mode.
Important! By and large, there is no difference between the four main manufacturers, and at home the difference is completely invisible. For the server and workstation, the company's products will be the best choice.Intel.
Processor socket.
Each motherboard has a socket for installing a central processor, which is called socket . This is the most important selection criterion, since only one type of processor can be installed in the selected socket.
How to choose the right processor for the motherboard? First of all, you should decide on the manufacturer of the processor. Only two companies in the world produce decent processors: Intel and AMD. The sockets of these companies are incompatible in principle.
- Intel Sockets.
Leading manufacturer of processors and chipsets. It holds about 75% of the market, and only new processors from AMD could improve the situation somewhat. The following Intel socket models are relevant:
- LGA 2066.
The newest and most modern socket of an American company. Supports the most productive processors and will be in demand for a long time. The only disadvantage of motherboards on such a socket is the high price.
- LGA 2011-3.
The platform of the previous generation, but still the performance of such processors is more than enough to solve all household tasks.
- LGA 1151-v2.
A mass segment of processors that perfectly combines an affordable price and acceptable performance. The perfect choice for modern home computer. It should not be confused with the previous LGA 1151 platform, as their sockets are incompatible.
Important! If you need to build a mid-range computer for the home, then you should opt for a motherboard with a socketLGA 1151-v2. This the best option in all respects.
- AMD sockets.
The Canadian manufacturer makes affordable, but not as powerful processors as Intel's eternal competitor. However, thanks to affordable price and wide overclocking capabilities, AMD processors are quite popular.
The most common sockets are:
- Socket TR4.
The most powerful processors of the company are built on this socket. Supports up to 16 (!!) cores and a four-channel memory controller. Perfectly suited as an extremely productive home computer, and for a workstation.
- socket AM3+.
Socket for budget mothers. Low performance and very low price. Suitable only for an office computer.
- socket AM1.
Bulk socket segment from AMD. Direct competitor to Intel's LGA 1151-v2. Has similar characteristics. Perfect for building a home system unit.
Important! If you decide to assemble a computer based on processorsAMD then the question How choose motherboard processor solved very simply. The ideal choice would be a board with an AM1 socket.
Motherboard chipsets.
A chipset is a set of chips that provides the functionality of the motherboard as a whole. It depends on how many hard drives or video cards can be connected and how fast they will work. The socket and chipset determine the final cost of the motherboard by 80%.
By and large, chipsets differ from each other only in the type and number of supported interfaces. All existing chipsets can be divided into three large groups:
- First level.
Motherboards based on such a chipset can only be used in office computers or in extremely cheap entry-level system units. For AMD, such chipsets include AMD 760G or NVidia 7025. For Intel, the H110 or H170 (270) chipset can be distinguished.
- Average level.
Golden mean. Completely suitable for the formation of home system units. Allows you to connect the required number of hard drives and USB devices. How to choose a motherboardAMD with sufficient functionality? Just choose devices with chipset and B350 or X370. For mothers with Intel processors, these chipsets will be Intel B350 or Intel Z350.
- High performance chipsets.
Maximum functionality for big money. It will be possible to connect an almost unlimited number of hard drives, USB devices and at least 2 video cards to such a motherboard. Some models contain Wi-Fi or Bluetooth modules.
For Intel mothers, this chipset is the X299. For AMD, maximum functionality can be obtained on AMD X399.
Important! For a computer worth up to a thousand dollars (about 60,000 rubles), a chipset is more than enoughZ350(Intel) orX370(AMD).
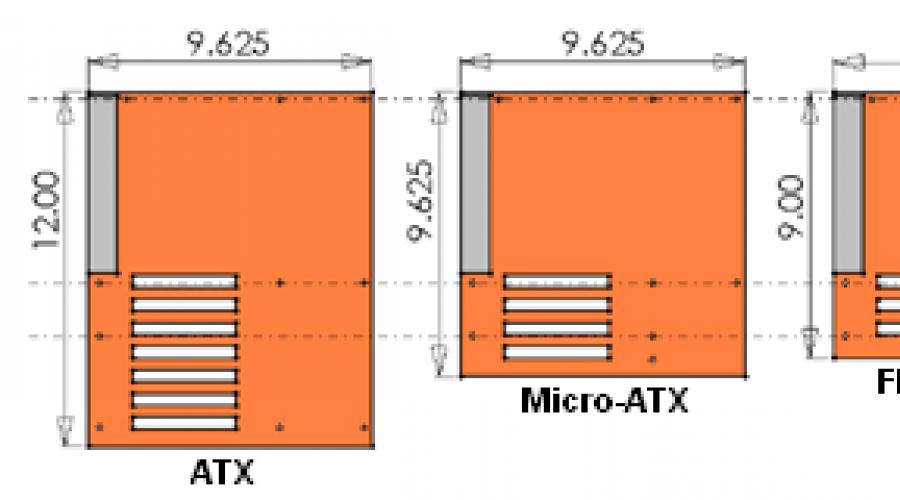
Motherboard dimensions.
Modern motherboards differ from each other not only in functionality, but also in size. This is also worth considering when assembling computers. There are five sizes in total:
- E-ATX.
The largest items. As a rule, this size is used for the most advanced mothers with flagship processors and elite chipsets. Size - 30.5 * 33 centimeters. Assembly requires an expensive large-sized case.
- ATX.
The classic size, most motherboards have it. Dimensions 30.5*24.4 cm. The smartest choice for building a computer as most cases come in this size.
- Micro-ATX.
A smaller version of the ATX mother. In most cases, it has reduced functionality and is created on simplified mid-level chipsets. Dimensions 24.4 * 24.4 centimeters. Considered a budget option.
- Mini-ATX.
Such a mother is intended for assembling compact systems with small video cards or without them at all. The functionality of the chipset has been cut. Most budget system units are built on mothers of this size. The physical size of the board is 17*17 centimeters.
- Mini-STX.
Very petite printed circuit board, having a size of 14 * 14 centimeters. Designed specifically for creating multimedia centers and ultra-compact computers for video playback. Used where maximum compactness is required.
Important! ATX andMicro -ATX - the most suitable motherboard sizes for a universal home computer.
The number of slots for RAM.
In most cases, the motherboard has either 2 or 4 RAM slots. There is a very small group of elite mothers that boast 8 memory slots, but such devices are few and far between and very expensive.
Important! It is most profitable to buy boards with 4 memory slots. This will make it possible to quickly add RAM and not change the entire device.
Connection interfaces on the rear panel.
A wide variety of connectors can be located on the rear panel, including such unusual ones as S / PDIF or a Wi-Fi antenna. Modern boards are equipped with several USB ports, audio jacks, and a PS / 2 port, which is used to connect a keyboard or mouse. RJ-45 is mandatory for Internet connection.
Important! NumberUSB ports on the rear panel should not be less than 6, and 2 of them should beUSB 3.0 In addition, it will not be superfluous to have a portUSB -C (all modern phones are equipped with it) andHDMI (it will be convenient to connect a TV or monitor).
Particular attention should be paid to audio connectors. It is best if the motherboard will natively support 5.1 or 7.1 sound. This eliminates the need to buy an additional audio card.
Connecting hard drives (HDD and SSD).
To date, even budget motherboards have at least 4 SATA connectors, where you can connect any hard disks(including solid state) and DVD drives, if they are still needed.
An average budget device can have 8-10 SATA connectors, which will not be superfluous if you plan to store a large amount of information.
Important! The connector will not be superfluousSATA Express required for connectionSSD drives and allowing them to run at full speed.
Connectors for expansion cards.
The motherboard must have at least one PCI -x16 slot to connect a modern video card. Several PCI -x1 slots will also come in handy, where you can connect additional sound cards, video capture cards, TV tuners and much more.
Important! If you plan to play games a lot and actively, then you should think about purchasing a device with twoPCI-x16 connectors. This will allow you to connect two video cards at once.
Choice results.
Summarizing all of the above, the following conclusions can be drawn.
For an office computer, a motherboard with an AMD AM3 + socket with an integrated video card, two lines of RAM and a minimum number of connectors and interfaces will be quite enough.
In the event that you need a universal home computer, then the best choice would be a motherboard with an LGA 1151-v2 socket, with four lines of RAM and with all common interfaces.
If you want to play at maximum performance or do video processing, you should pay close attention to the LGA 2066 socket, which will provide maximum performance and functionality.
Introduction
It's no secret that a computer is a complex device, consisting of a huge number of parts. But what is its main part - the motherboard - responsible for? At the dawn of time, its function was utilitarian - a platform for other computer components that has a dozen elementary settings - and nothing more. Over time, the motherboard took on more and more more features, and now you will not surprise anyone with the built-in sound card and graphics card, USB and FireWire controllers. It would seem that since there is nothing more to integrate (after all, it is now rare to find expansion cards in a regular computer), then progress should have stopped. No matter how! We will prove the reliability of the last statement on the example of the motherboard of one of the patriarchs of the IT industry - Micro-Star International Co., Ltd.
We will talk about the configuration and diagnostic application software of modern boards, about the element base that affects reliability during intensive use, about proprietary technologies that simplify the setup and operation of a computer, about the fact that plug-ins for the VKontakte social network are by no means only for communicators and smartphones, but also for operating systems built into the BIOS, about overclocking the processor and modern means overclocking, about related features that help other computer components work more reliably and efficiently - in a word, about everything that the manufacturer has invested in his offspring and which sometimes buyers are completely unaware of.
The motherboard is big, but what can it do?
Can a new generation motherboard deliver significantly more than previous generations? Yes!
The motherboard is the largest board in the computer, and various functions of the future computer depend on it - both basic and additional. So, with the main function - to combine all computer devices into a finished system that can perform the tasks assigned to it - all motherboards do an excellent job. Let's start with additional features, which will facilitate the work with the computer, making it as comfortable as possible. Usually such technologies have a name that does not always reveal their essence. For example, what is “APS” and what is it for? Let's try to consider some of the most interesting features using the MSI MS-7760 X79A-GD65-8D as an example. For clarity, we will make the following table:
| Description | MSI MS-7760 X79A-GD65-8D |
| Increased current in USB ports for charging smartphones and tablets | Super Charger |
| A utility that makes it easy BIOS settings | ClickBIOS II |
| Automatic overclocking | OC Genie II |
| BIOS update utility | M Flash |
| Energy Reduction Technology | APS |
| Component base with increased resource | Military Class III |
| Mini OS for quick access to global network Internet | Winki 3 |
| Software for updating firmware and drivers from under Windows | Live Update 5 |
| Ability to use disks larger than 2.2 TB | 3TB+ Infinity |
| Surround Sound Compliance | THX, HD Audio |
Although the above list, of course, does not claim to be complete, the listed technologies alone already allow us to conclude that a high-quality motherboard satisfies most of the needs of both ordinary users and specialists.

VKontakte can't wait!
Can the motherboard make it so that downloading the necessary applications from the HDD takes less time compared to the state-of-the-art SSD?
Typically, the startup time of the computer is associated with the drive installed in the system. At 75%, this is true: Windows starts many times faster from a modern SSD drive compared to a system installed on a hard drive. It should be noted that before running the installed operating system the computer conducts self-diagnostics, the duration of which, sometimes reaching 10-15 seconds, sometimes is half (or even more) of the total time the computer starts up. With the introduction of the latest generation of UEFI BIOS into motherboards, the time from pressing the power button to transferring control to the operating system has been significantly reduced, so when choosing a new motherboard, you should pay attention to this parameter. In addition to reducing startup time, the UEFI BIOS allowed the introduction of a graphical interface into the program. initial setup BIOS setup. In addition, it became possible to change the interface language, and some manufacturers, for example, have Russian in the extensive list of languages.

However, this is not all. Quite often, a computer is turned on simply to check mail or communicate in popular in social networks, such as VKontakte or Facebook, for which you have to wait for the operating system to load and the browser to start - when using classic hard drives, this procedure takes quite a long time. To reduce latency, MSI motherboards support Winki 3 mini operating system, which has minimal functionality but starts up in just a few seconds. When using it, you will have access to an Internet browser, a photo viewer, an Internet pager and an office suite. It is worth noting that such an opportunity is currently unique, and no other motherboard manufacturer offers such a set of applications, which increases the attractiveness in the eyes of potential buyers.

ATX, ITX, or maybe DTX? What are these abbreviations?
Does size matter? Is the functionality of the board related to its format? In "supercomputer" motherboards, "bigger" always means "better"!
. When choosing a motherboard, you should remember that modern cases have different sizes, and not every motherboard will fit in the selected case. In order to simplify the selection of the motherboard, standards have been developed indicating the size of the board, the location of mounting holes and expansion slots. These standards are called the motherboard form factor. For desktop computers the most common sizes are XL-ATX, ATX, microATX, mini-ITX. In the above list, the formats are presented in decreasing order of size. Keep in mind that a small board can be installed in a large case: all fasteners and expansion slots will be in the right places, but this should only be done as a last resort. For example, when upgrading, you have an ATX case, and you liked the microATX board. When buying a new computer, it is better to select components of the appropriate size. The photos below show boards with different sizes.

Please note: a computer built on a board of the smallest format (mini-ITX) is usually designed to work in office computers or media centers, so these models do not have a PCI-E 16x slot for installing discrete video cards, as a result of which modern games will not be available .
In general, when miniaturizing a motherboard, additional slots for video cards are removed from it first of all, the cooling system is simplified, and sometimes the number of SATA connectors is reduced. When choosing a board, you should think about whether any components will be added to the system unit - if not, then microATX will be an excellent choice, because computers assembled on such boards take up much less space, but they are not suitable for a serious gaming computer.
"Chipset" - just a buzzword or something more?
What do manufacturers ask for money for when they offer more or less expensive boards based on one chipset: for marketing or for really useful things that make the computer more convenient to use?
When choosing a motherboard, you need to pay attention to such a component of the motherboard as the chipset. For a long time, this complex semiconductor device was practically the second processor of any home computer. Its functionality included a memory controller, a PCI-E or, even earlier, AGP controller, an integrated graphics adapter, USB and hard drive controllers, and more. As a result, computers assembled from the same components, but differing in motherboards and, accordingly, chipsets, had different performance.
Today, the situation has changed: the functions that are critical to performance have moved to the processor, so the impact on computer performance has been significantly reduced. Computers built on different chipsets of the same generation have the same performance, differing in such parameters as support for the video core built into the processor, overclocking capability, the number of SATA II/SATA 6 Gb/s and USB/USB 3.0 ports. Despite this, manufacturers quite often in their model range have several boards based on the same system logic. This is done to expand the functionality of the product by adding additional controllers or disabling functions that are not critical in terms of reducing the final cost of the product. A good example is the line based on the Intel Z68 chipset.
| Z68A-G45(B3) | Z68A-GD65 (B3) | Z68A-GD80 (B3) | |
| Intel Smart Response | + | + | + |
| Lucidlogix Virtu Switchable Graphics | + | + | + |
| Charger USB devices(iPod, iPhone, etc.), | + | + | + |
| Uses 100% solid polymer capacitors | + | + | + |
| Automatic overclocking | + | + | + |
| Heat pipe cooling system | - | + | + |
| Increased power USB ports | - | + | + |
| Driver-MOSFET (DrMOS) | - | + | + |
| Tantalum Capacitors | - | + | + |
| IEEE-1394 controller | - | - | + |
| Availability of two network cards 10/100/1000 Mbps | - | - | + |
| 3 PCI-E 16x slots | - | - | + |

If you look at the price list of the NIKS Computer Supermarket, it becomes obvious that the most functional motherboard has the highest price. Three computers assembled on the basis of the same components, but having three motherboards from the above example, will have the same performance, however, the functionality and reliability in this case will differ due to the use of high-quality military-grade components in expensive models.
"I want Japanese capacitors." Is such a desire justified?
Stability in everything is the desire of most of humanity, and if in life its implementation largely depends on the state, then in a computer this role is assigned to the motherboard. But do all "computer governments" care about their "inhabitants" in the same way?
All motherboard manufacturers strive to increase the resource of their products using advanced scientific achievements, and the only limitation in this case is the promptness of engineers. Quite a long time ago, two or three years ago, many companies began to use expensive solid capacitors. This step made it possible to significantly increase the reliability of the boards, since swollen electrolytic capacitors in the power supply circuit of the central processor were a fairly common cause of the failure of the entire computer.
Then ferrite coils and low resistance transistors began to appear, but progress did not stand still, and over time, components previously used only in the aerospace industry began to appear in desktop computer boards, which allowed reliability to be taken to a new level. Leading the way is MSI, which is the industry's first to use Hi-c polymer capacitors based on the rare earth tantalum.

Unlike conventional solid capacitors, which cannot operate when damaged, MSI HI-c capacitors can self-heal thanks to the Nobel Prize-winning polymers.
In addition, the low height of such capacitors minimizes the likelihood of damage when installing a bulky processor cooling system. The only drawback of these devices is a rather high price, therefore, Japanese solid capacitors are used in less critical areas of the board, which have a very long service life. To confirm the reliability of its motherboards, MSI independently tests components to MIL-STD-810G, which is a testament to the highest quality and reliability. It is not for nothing that all US Army equipment is subject to such certification. To obtain the appropriate certificate, components must pass 7 tests:
- temperature fluctuations
- Can be used in high humidity
- Vibrotest
- Low pressure operation
- High temperature operation
- Low temperature operation
- Test for resistance to physical impacts
Overclock the processor? Easily!
Everyone knows that Russians love to drive fast. And what in motherboards is allied to this feeling?
There are situations when the performance of the processor used is not high enough. How to proceed in such a case? There are two options:
- Buy a faster processor
- Overclock existing

We use the word "usually" for a reason. Most modern boards provide the ability to automatically overclock, which makes this task quite simple and safe, but not everything is perfect here.
The most common way to automatically overclock is to run a specialized utility that gradually increases the processor frequency. In the future, there is a reboot and a subsequent increase in frequency - and so on until a certain safe level, according to the electronics of the board, is reached. Although this way, of course, is effective, the overclocking process takes quite a long time, while not everyone is satisfied with the need to install an additional software. MSI took a different path with the development of OC Genie technology and its further development, OC Genie II.

To overclock the processor on the MSI board, just before turning on the computer, press the button on the motherboard that says "OC Genie" and turn on the computer. Immediately after turning on, the frequencies will be increased and the computer will be ready to work, and the stability of the system will not be affected due to the use of high-quality components.
And if you need to install more than one video card?
Since we are talking about performance, the mention of the computer's graphics subsystem will be a completely logical development of this topic. When choosing a high-performance gaming computer, first of all, you should pay attention to the video card, because the performance in games mainly depends on it. "What's with the motherboard?" - you ask. Let's figure it out.
Since modern gaming graphics cards installed in a PCI-E 16x slot, Mini-ITX motherboards are the most suboptimal choice for a gaming computer due to the lack of such a slot. Quite often, motherboards have two or more PCI-E 16x slots. This configuration will be of interest to hardcore gamers and enthusiasts, since it will allow you to assemble a multi-GPU system, increasing the performance of the computer's graphics subsystem by a multiple of the number of video cards.
To implement such a scenario, just having the right connectors is not enough - you need to support Crossfire technologies for AMD Radeon video cards or SLI for nVidia graphics cards Geforce. Information about the support of these technologies can be found in the description of the motherboard you like on the website or on the manufacturer's website. If games as a class of software are not of interest to you, in this case it is quite possible to get by with a video card integrated into the motherboard or processor, the capabilities of which in most cases will be enough for office work and watching any movies, and this solution will save energy.
|
|
"Hybrid graphics". Did not hear? Let's tell!
 Your new computer can become noticeably quieter and more economical than before!
Your new computer can become noticeably quieter and more economical than before!If you want to not only play modern games, but also save electricity, then a motherboard with hybrid graphics is the best option. For the first time, such technologies appeared in laptops - the most critical devices in terms of power consumption, because battery life directly depends on this parameter. Over time, the turn came to desktop computers. The operation in this mode is quite simple to explain. In idle (for a video card, idle is any mode other than a game), the built-in video adapter works, and when a game or other application that actively uses the resources of the graphics adapter is launched, a discrete video card is turned on.
Energy savings come from the fact that any discrete graphics card consumes more power when idle than integrated graphics, and the difference is quite significant. If you plan to use such a bundle, you should choose boards that support Lucidlogix Virtu Switchable Graphics technology, such as . You can find out about the board's support for this technology on our website in the description or by looking at the box, where the corresponding logo should be present.
If saving energy is not a priority, but when working with a computer you have to convert video materials, in this case, purchasing a board that supports Lucidlogix Virtu also has one very significant plus. The fact is that the graphics core built into Intel Sandy Bridge processors supports Intel technology Quick Sync, thanks to which the time required to convert a video is reduced by several times. Thus, by configuring discrete graphics for continuous operation, and the integrated video core for the video converter, you will get both the highest performance in games and the ability to encode video in minimal time.
What to choose?
So what do you end up choosing? Quality? It is at the proper level for all major manufacturers. Extended functionality? As we pointed out in the first part, the variety of features eventually translates into different names for the same features. Price? Perhaps this is indeed the right factor - however, you should not take the most expensive one, since for the most part this is a payment for a bigger name and the active work of marketers.
Founded more than a quarter of a century ago, MSI independently manufactures motherboards and components, so the prices for MSI products are among the most affordable, and we are talking about full-fledged products. highest quality. Another important advantage of MSI solutions is a long warranty period and excellent support. For fans of online battles, the unique promotions held by MSI together with the developers of popular games will be a pleasant surprise. If you are a fan of the most popular MMO World of Tanks, then by purchasing you will receive some in-game gold and a premium account.

