Connection problems. Possible causes of problems with Internet communication: secrets of the system engineer
Read also
find out , How to Troubleshoot Connections To Internet
Are you unable to connect to the Internet? Well let's take a look at possible reasons and show you how to eliminate them.
To make things easier, we will follow a 3 step process to fix the problem you are facing.
Step 1: Modem and Internet Service Provider (your Internet Service Provider)
We have to start right from the source, you are connecting to your ISP.
1. Contact your ISP and check your internet service is activated, if so, are they experiencing downtime/line cuts or other issues? If they are experiencing problems, you will not be alone and they will probably work overtime to fix it and you will be connected right away!
2. The connection is good, but what's next? Well, whatever modem/router you are using with the connection. Make sure the cables; data and power are connected correctly. Also, check with your modem/router's instruction manual if you've configured your connections. If you purchased the modem separately, you will most likely need to set it up as opposed to the pre-configured ones supplied by your ISP. So once your done checking the status of your modem/router, you should be able to send your modem data/receive lights flashing off of the connection!
Step 2: Configuring Internet settings
This step includes configuring your Internet settings operating system to detect internet connection successfully and share it with applications that need them.
1. Check the details against the following information provided to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and your Internet Protocol (IP):
- IP address
- Subnet mask
– Default gateway
– DNS servers
After receiving the above details from your ISP, you need to view the current IP details on your computer by doing the following:
– Jump to: Start > Run > CMD > Type IPCONFIG / ALL to the command line window. (Note, What on Windows Vista and 7 you need to search for 'Run' in the search bar on the start menu)
– By doing this, you will see the current details for the above four requirements. You will need to share these details with your ISP to help fix this issue. Please note that, inappropriate parts on this stage may be caused by defective hardware component or due to incorrect modem configuration.
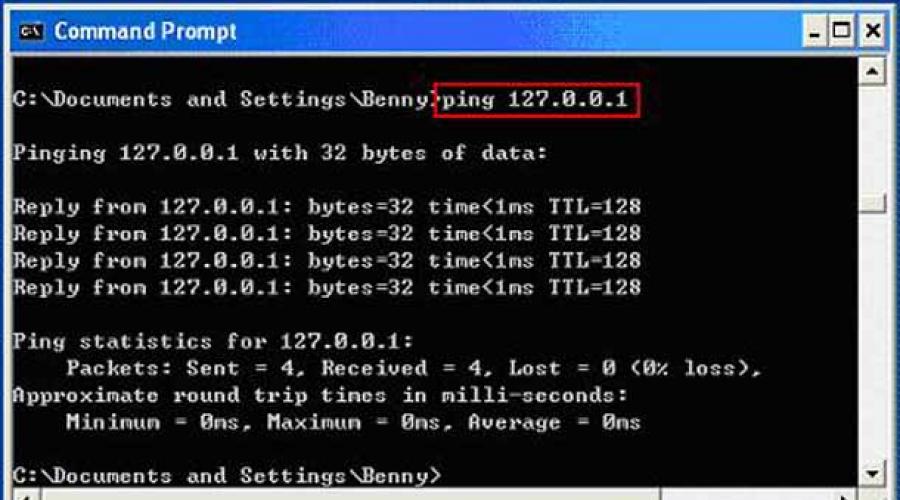
2. Checking whether the Internet protocol suite (otherwise known as TCP / IP) is configured correctly by performing a PING test.
– Jump to: Start > Run > CMD > and type ‘ ping (router address) ‘
In most cases, the address will be “192.168.1.1”. You can also PING an external address for further verification.
You should see several hours of replies followed by ping statistics, indicating that all is well.
3. You can also use windows tool Network Diagnostics to collect information about your Internet / network connection.
Start > Help and Support > Type Network Diagnostics and it should give you the option to run network diagnostics.
Trying to restore your network connection may or may not help, depending on the type of task. Here is how you do it:
Start > Settings > Network connections> Select your network adapter > Click right click mouse and select Restore.
Once the process is complete, it should tell you if the repair was successful or not.
Step 3: Browser/App Setup
Once Step 1 & Step 2 have been sorted out, it's safe to say that your internet connection is perfectly fine. The problem is the application is trying to use it, in most cases your browser, Internet Explorer, For example.
– Open Internet Explorer and get to the options:
Internet Explorer > Tools > Properties Browser > Connections > LAN Setup > Uncheck Automatic detection parameters And Use proxy – server for your options LAN> OK> Apply and OK.
Now trying to open a web page should bring a smile to your face.
– Similar settings available in other browsers must also be disabled for them to successfully use the Internet connection.
So there you go, all geared towards an enriching Internet experience and nothing will stop you now.
To troubleshoot network issues, it's important to have a basic understanding of your network setup. There are three categories network problems: physical, configuration problem and software problems. The first step to take when you are going to troubleshoot network problems is to determine what type of problem you have. This solution is the first of many that will help you solve the problem. There are two simple rules that are critical if you want to successfully troubleshoot network problems. The first rule is to change only one at a time and then test it. The logical, methodical approach is the only effective method troubleshooting a technology problem.
There are often multiple causes of network problems. If you can't determine the action and associated result, you have no idea if you're on the right track or not. A number of changes can also lead to unexpected results. One step after another is the best way to continue searching for network problems.
Top-down troubleshooting is the second rule for troubleshooting. Make clear notes about the form that explain the steps you took and the result. These notes are invaluable and will help you build a knowledge base you can rely on when you're trying to troubleshoot.
If you encounter network problems, always start with the physical network first. Check devices, connections and power. Make no assumptions and check each connector carefully. These problems are the easiest to fix and are the most common. Follow the cable to make sure everything is properly connected.
If the problem is not hardware, look at the configuration. The first step is to create a system restore point in the software configuration. This will allow you to start from the same moment if it becomes necessary. Look at your notes from the installation and don't forget to make new notes.

To start troubleshooting, you should check the configuration of each computer on the network. This information can be accessed by entering "ipconfig" in command line for each computer. To obtain full level details, enter "ipconfig /all". Review the information and compare it with initial setting. Errors or inconsistencies will cause most problems.
The most common software problems are related to firewall installation. Check your antivirus software, as it is often associated with a firewall. Installing multiple firewalls will create a cascading series of network problems. Look for any settings that can be changed.
Read how to fix internet connection problems at home. A few mandatory steps before contacting a specialist or provider. Internet connection problems are very frustrating for us. Rather than uselessly flicking F5 and desperately trying to reload your favorite website, we suggest trying a few troubleshooting methods and determining the reasons for the connection failure.
Ping Command
The first thing to do when you have connection problems is to run the command "ping". Launch the Windows command prompt (how to run the Windows command prompt as an administrator, see the video on our channel how to run the Windows command prompt) and enter, for example, or "ping site".
This command will send multiple packets to the address you specify, and the web server will respond to each one. In the screenshot below, we will see that everything is working fine. Packet loss is 0% and the time taken by each packet to move along the route is minimal.

If you find packet loss (in other words, if the web server has not responded to one or more of the requests sent), then this definitely indicates a problem with the network. If the response time of the web server for different packets varies greatly, this indicates a high load on the Internet channel. Also, the problem may be related to the website itself (unlikely if the same problem occurs on several web resources), with your Internet service provider or in your local network(for example, with a router).
Please note that packets cannot be exchanged with some web servers. For example, the command "ping microsoft.com" will result in 100% packet loss.
Problems with a specific website
If only a certain website has access problems, and it shows that everything is in order, then most likely the problems occurred on the server where the website is physically located.
To check if this site is working properly, we can use a special tool on the web - www.downforeveryoneorjustme.com. It allows you to poll websites from different IP addresses and determine if they are actually working or not. If you get an answer that the site does not work for everyone, then the problem is definitely on the server.

The response of the site that this web resource does not work only for you indicates errors with the connection on your part. And there may be at least a dozen options. Perhaps there is a mismatch in the routing between your computer and the server on the Internet. To troubleshoot these issues, use the command "tracert", for example, enter "tracert google.com" at the Windows command line. The utility will send a trace packet and display the IP addresses and names of all hosts that the packet interacts with as it travels along the route. If a bug is found after your ISP's server, then there's basically nothing you can do but wait for it to be fixed.
Problems with the modem or router (router)
The lack of access to various websites may be caused by the modem or router (router).
Many people use a modem to connect to the Internet, that is physical device, which transmits digital data through analog channels. The modem converts the analog signal to digital, and vice versa. For such interaction, he has two interfaces, digital for a computer and analog for telephone line. A modem is a device that communicates with your Internet Service Provider.
A router is also a physical device that, via wired, wireless, or mobile network connects to the internet. In addition, it can combine all devices that are equipped with Ethernet network ports and WiFi adapters, to one local network. With its help, local network members can freely exchange files and remotely control other devices (for example: printers, TVs, etc.).
In some cases, the modem and router may be the same device.
Take a look at the router. If it has blue or green lights flashing ( different manufacturers may use different colors), this is normal and indicates a stable internet and LAN connection. But if you see a steady blinking orange (or red) indicator light, then this usually indicates that there are none. The same applies to the modem - a flashing orange light usually indicates a problem.

If the lights indicate that both devices have a problem, try turning them off and on again. That is, restart the devices, just like restarting a computer. You can perform this action even if the lights are flashing normally - there are some routers that sometimes need to be rebooted for them to work properly. After a few minutes, your modem or router should reconnect to your ISP. The error may be related to updating servers from the provider itself.
If this does not solve the problem, then you can perform a factory reset on your router or update the firmware. To check if the problem is indeed with your router, you can connect your computer's Ethernet cable directly to the modem, bypassing the router. If the connection is restored, then it is clear which device is causing problems.
Possible problems on the computer
If you're only experiencing network issues on one computer on your local network, then it's most likely a software-related bug. It can be caused by a virus malware or a bug in the browser.
Check your system with anti-virus software and try to install another browser, then try to open this site in new program. Other errors may also occur, such as incorrect firewall configuration.
Problems with DNS servers
When you download a Google.com resource, your computer contacts its DNS server and requests the web resource's IP address. The default DNS servers used by your network are provided by your ISP, and if they are not up to date, problems may arise.
You can try to access the website by IP address directly, bypassing the DNS server. For example, copy the address "http://216.58.197.78" into the address bar of your web browser to visit Google.com directly.

If you manage to access the IP address but still can't open the site by simply typing Google.com in the address bar, then it's a problem with the DNS servers. Instead of waiting for your ISP to update their server, you can try using a third party DNS server such as OpenDNS or Google Public DNS.
Ultimately, most connection problems you encounter are someone else's glitches or bugs - you can't fix them yourself. Often, the only thing you can do is wait for your ISP or specific website to fix the problem.
And of course, you can always call your Internet Service Provider for support by phone. Support can check the connection to your computer (router or modem) to see if there are any problems. They will tell you if there is a server error, or if the problem is still on your end. Also see what can be done to speed up the Internet connection.
Whenever you encounter a network problem, the most common solution is to run a diagnostic program to detect and fix the errors. However, the most common network problems can be solved with simple commands like ping, tracert, ipconfig, etc.
Do you know that?
Team "ipconfig" can be used to find a computer by IP address on both Windows and Linux/Unix machines.
All of the following commands must be entered on the command line. To open a command prompt in Windows, do any of the following:
- Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Command Prompt.
- Start -> Run and enter the name of the program cmd.exe
- Press keys Win +R and enter the name of the program cmd.exe
Anyone with a basic knowledge of networking knows about the ipconfig command. This command gives information about the computer's IP address, along with DNS, DHCP, gateway, and subnet mask. The IP address is required for further troubleshooting commands. If this command returns a default gateway of 0.0.0.0, then you have a problem with your router. You can try another variation of this command to solve your network problems. Another extension of this command is the ipconfig/flushdns command. She cleans DNS cache upon any unauthorized IP address or technical failure.
Team "ping"

Ping is one of the most important commands used on the web. This command is used to test connectivity between a host and a destination. The main advantage of using this command is to find out the problem area in the network. If you ping from any computer on the network, you will get the status of the router. You will also receive four responses to the ping request. If you do not receive responses, then this indicates problems with the network card.

Another benefit of using the ping command is the ability to test connectivity to any website/internet. In order to do this, you need to enter the website name after the ping command. If you are getting responses from a website, then there is little to no problem. But if you don't get a response, chances are you have a bad cable, DSL modem, or ISP connection problem. To further narrow down the likelihood and find the root cause of the problem, type ping 4.2.2.1. If you get responses on the command line, but still can't access the website, then you have a problem with your DNS configuration.

The tracert command returns the entire data path that is required to get to the destination. The response will be a list of transit points that the data passes through to reach its destination. If you look closely, you will see that with each point there is a change in the network. This means that each network transmits data to the other network until it reaches its destination. However, you can see asterisks at some points, these asterisks represent a network that has problems.

The Domain Name System (DNS addresses) is basically the root cause of many network problems. These IP addresses are required for the operation of network devices to connect to the internet or network. In the event that there are problems with these addresses, the functions of the entire network are hindered. The nslookup command lists the IP addresses associated with domain name. If you cannot get any information regarding the IP address, there is a DNS problem.

In the case of networks a large number of hosts are connected to the same router. Thus, there is the most difficult task to check the connectivity of each node in case of network problems. However, at the same time, it is important to check if the connections (TCP, UDP ports) are active or not. Netstat command returns a list of all computers connected to the router, along with their status. Knowing this state, you will know the port number (and IP address) of a TCP/udp connection that is in a failed state or is in a closed or idle state.

The "arp" command is an external command that is used to identify problems related to resolving IP to local network addresses. The most common problem that can be found in the "arp" table is sharing one IP address by two systems. Two hosts (one of which is definitely not the same) use the same IP address, and the chances of the wrong host responding to the IP in this case are high. This will affect your entire network. You should check if there are paired local networks and if the correct IP addresses are registered. To do this, you must make a list of the network addresses of each host. By comparing your list and the "arp" command table, you can easily identify the problematic host.
Diagnostics is carried out for all networks without exception. The Internet connection process is complex, as it depends on the reliable operation of many internal devices PC, home network equipment And external elements network provider. Therefore, the cause of failures can be not one, but several sources.
User assistants in this case are utilities built into Win. For example, Ping helps identify problems with your home network and ISP. The ping tool is used to constantly call the IP address and check for connection problems.
Diagnostics Windows networks needed to solve common network problems such as DNS or proxy troubleshooting. And if the user does not find ways to solve the problem on his own, you can use third-party tools. Tracert is useful in that it will scan the route and measure packet transit delays.
Procedure:
- To start diagnosing, click the "Start" button and enter the patch network in the search field. The user will find possible options.
- Next, click the "Find" button and fix network and connection problems.
- After the troubleshooting window appears, click the "Advanced" button and run the program again as an administrator.
- The user can automatically perform repairs if he wants to solve the problem without interruption.
- Select the type of connection that needs Internet network diagnostics for subsequent troubleshooting, and click next.
- Win will find and fix the problem with the network connection.
If the tool does not determine the cause of the failure, the user can contact the Microsoft online service or consult the provider.

People set up home networks to automatically obtain DNS server addresses from their ISP. When servers or a provider's network suffer from failures or are heavily loaded with traffic, they DNS services may suddenly stop working. Customers are forced to wait until the provider fixes the problem.
On the Internet, there is an alternative to private DNS servers - free public services such as Google and OpenDNS. This allows router administrators to switch the DNS setting home network from private configuration to public DNS by manually entering public DNS IP addresses in the router's configuration settings.
Administrators create this connection temporarily only in emergency situations. However, the DNS settings can also be applied on the Win device through the Network and Sharing Center. This will also not work on a permanent basis as devices receive and determine local settings using router settings via DHCP.

There may be no internet connection for several reasons. The most common failure is related to the Domain Name System (DNS), a distributed name resolution service used by providers. PCs running Win 7, 8.1 and 10 report errors and problems found in the window. For example, that the DNS server is not functioning, the PC is working correctly, but the resource server is not responding.
How to fix the problem, consider below.
On Microsoft OS, network diagnostics are carried out. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open "Control Panel".
- Select "Network and Sharing Center" public access».
- Click "Troubleshoot" under "Change network settings".
- Click "Internet Connection". A new connection window will open.
- Click "Next".
- Click "Run the troubleshooter".
- Click "Troubleshoot Connections".
- Wait for the troubleshooting tests to complete and review the "Problems Found in Window" section of Windows Network Diagnostics for error messages.

Most wireless broadband routers available today have their wireless security features disabled. This makes it easy to set up wireless network for novice users in homes or offices, but it also makes the network vulnerable to unauthorized guests.
Although precise procedure security for different models routers may differ, in general, the process of accessing the relevant parameters will be similar.
For example, if the router's IP address is 192.168.1.1, then do the following:
- You must open a web browser on a system connected to the network and enter 192.168.1.1 in the address field.
- The user will be prompted to enter the required credentials to access the router's configuration menu. If such data is unknown, contact the provider for help.
- You need to turn on the necessary Wi-Fi security to prevent unwanted access to the network by guests. After logging into the router, the user will see tabs or links in the control panel.
- Go to tab " Wireless connection” or “Wireless Security”.
- An area will appear on the screen in which the security mode is set, with the necessary parameters, such as WEP, WPA, WPA2 and others.
- If there are relatively modern wireless devices Supporters of the standard recommend enabling WPA2 Personal on your home network, which offers more sophisticated encryption than other methods.
- If the devices do not support WPA2, try WPA or WEP. Then set the encryption type to TKIP or AES, and then determine the wireless password or key, and then perform LAN diagnostics.
- Create a password/key, enter letters, numbers and Special symbols.
- Save the settings and reboot the router, at least a basic level of security.
- Wi-Fi is now functional.

Some applications require working network ports to be opened and forwarded to the PC in order to perform Internet functions, such as game servers. If the required ports are not opened and requests are not forwarded to those ports, incoming traffic will not pass through the firewall to them.
A quick guide to diagnosing network and port forwarding problems:
- In this example, incoming UDP and TCP traffic on ports 8888 - 8889 will be redirected to the computer with IP address 192.168.1.115.
- Connect the computer to the network, open a web browser, and enter the router's IP address 192.168.1.1 in the address field.
- Log in with a username and password, then find the NAT (Network Address Translation), Firewall or Port Forwarding menu.
- Create a set of rules that tell the router which protocol to use UDP, TCP or both, define the range of ports to forward.
- Specify which IP address traffic will be sent to on these ports. For example, if the computer running the application finds the IP address 192.168.1.115, place this string in the IP address field.
- Save the settings to enable the rule and then reboot the router to complete the job.

Sometimes port forwarding is not enough, you have to give the system access to the Internet. In these cases, the machine is placed in a DMZ network or in a DMZ. Entering in the DMZ means that all ports will be available, this situation is dangerous, so this operation is performed only if absolutely necessary.
Placing the system in the DMZ opens access to all ports. Let's assume that the router's IP address is 192.168.1.1 and that the user is connected to the network. In this case, the sequence of operations is as follows:
- Open a web browser and enter 192.168.1.1 in the address field.
- Enter the router and open the NAT (Network Address Translation), Firewall or DMZ menu, the options will be under the menu.
- When the user is in the DMZ configuration menu, you need to enable DMZ and specify the IP address to be placed in the DMZ.
- Enter the IP address, save the settings and reboot the router.

How peripheral device on PC with OS Windows network the controller needs drivers. These drivers tell the operating system how to use the device. Sometimes an update is needed to fix problems or add new features.
Update network drivers performed in one of three ways:
- Through software windows update.
- By downloading and running the executable installer.
- By manually selecting the driver through the device manager.
When possible, use the first method of updating the driver through the Center windows updates, the method is simple and automatic. The manual method through the dispatcher is more difficult to perform. If the user has downloaded the driver for the network interface card from the manufacturer's website and the file contains only some .inf or other unused files, then it is best to manually install using the Win Device Manager.
To do this, click the "Start" button and enter "Device Manager" in the search. Next "Enter" to open "Device Manifest" find " Network adapters” in the device list, click the network controller, and update the software driver in the menu.
In the new window that opens, click on "Browse PC" for the driver software button, then click "Browse" and move to the folder with the new driver. Click "Next" - and the driver will be installed automatically.
Windows Firewall Exceptions
The built-in firewall of Win 7 constantly asks to allow or deny access of the application to the network. If the diagnosis computer network found that the application was blocked by mistake and needs to be unlocked, the user will have to manually change some settings in the control panel Windows firewall. To obtain permission to access the program through the firewall in the "Allowed Applications" panel, do the following:
- Press the "Start" button.
- Enter "Allowed Applications" in the search field and press "Enter". The window that appears will show installed apps that are marked by the firewall.
- If you want to block an application that communicates through the firewall, click the "Change settings" button at the top of the screen. Then you need to scroll through the list of programs until the desired application appears, and disable it from accessing the Internet through the "Public networks" section.
- If you need to unblock a program, find it in the list and select the appropriate box next to this entry.
Scan for connected devices
When there are many connected devices in the house, you need to scan the network to find out which devices have received IP addresses and the amount of resource consumption. The router has the ability to check the status of connected clients, you can also use third party application, which will scan a range of IP addresses to find and retrieve information about connected devices. For example, Angry IP Scanner scans the network and identifies used IP addresses within a given range.
Available on the Internet free utilities, which will scan the network, but most often users use Angry IP Scanner, download it to a PC and run the executable. The program does not even require installation. Enter the IP range to be scanned, press the "Start" button - and in a few minutes the user will have a list of active IP addresses, as well as information, what is the ping time in the device, host name and open ports.
When you right-click on active device the list will show more detailed information. The program will also allow you to determine the IP address and connect through a web browser or FTP client.

The antivirus programs that people install on their Windows PCs are designed to deter intruders, but they also provide the ability to block Internet access if they detect a bad device.
Most anti-virus programs work using special database files (dat) that software vendors update automatically on a regular basis. PC users often don't realize when these updates are installed as they run in the background and are designed to be non-disruptive.
Unfortunately, sometimes errors occur with these data updates that cause antivirus program believing that the computer is infected by transmitting a false signal. These false positives cause Win to block a DNS server that is not responding to errors.
To check if this is the cause of the device's Internet connection failure, temporarily disable the antivirus program and run the Windows Network Diagnostics program. Then contact the antivirus vendor for a new update or technical support.
The broadband router or modem initiates DNS error messages on home network devices. Restarting your router and modem will help fix problems with your router, at least temporarily.
Routers and modems must be replaced if failures continue. Poorly configured routers and modems generate errors related to the underlying network connection.
If the user connects to the router through a wired Ethernet port, you can try moving the Ethernet cable to use a different port. In order to properly fix internet connection failures, you first need to isolate the problem from its root cause.
Common reasons for these failures:
- Wrong ISP.
- Malfunction of TCP/IP or DHCP services.
- Overly aggressive antivirus software.
- Faulty router or modem.
If the user is not sure that the Internet connection problems are really DNS related, they first try to use the general troubleshooting methods:
- Diagnostics of IP networks and DHCP. The TCP/IP software inside the operating system of the client device may have malfunctioned and incorrectly set the DNS server addresses.
- Reboot Win computer often clears these temporary glitches. The right decision will start utility programs TCP/IP that perform a standard procedure to release and update Win IP address settings and network diagnostics dns probe finished.
- Similarly, most TCP/IP networks use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) service to assign IP addresses to clients. DHCP assigns not only the private IP address of the device, but also the address of the primary and secondary DNS server. If DHCP is not working correctly, you need to restart your computer to recover.
- First you need to make sure that the devices and the network router have DHCP. If DHCP is not used at the end of the connection, Internet connection errors occur.

If you carefully perform Windows network diagnostics and PC setup, then when connected to a network, a yellow icon will never appear on the monitor screen.