What is the connection point of communication networks. Rules for interconnection of telecommunication networks and their interaction
Read also
8. The connection of telecommunication networks and their interaction are carried out on the basis of agreements concluded by operators of communication networks on the connection of telecommunication networks (hereinafter - the agreement on connection) and in compliance with the requirements established by these Rules.
9. Intercity and international network operator telephone connection renders telecommunication network interconnection services (hereinafter referred to as interconnection services) to operators:
1) long-distance and international telephone networks;
2) zonal telephone networks.
10. The zonal telephone network operator provides connection services to operators:
1) zonal telephone networks;
2) local telephone networks;
3) data networks.
11. The operator of the local telephone network provides connection services to operators:
1) local telephone networks;
2) data networks.
12. The data transmission network operator provides connection services to operators:
2) zonal telephone networks;
3) local telephone networks.
13. The operator of the telegraph communication network shall render connection services to the operators of the telegraph communication networks.
14. To interconnect networks, telecommunication network operators organize interconnection points. Wherein:
1) the operator of the long-distance and international telephone network creates connection points in each subject Russian Federation;
2) the operator of the fixed zonal telephone network creates connection points in each urban settlement of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, on the territory of which this network operates;
3) the operator of the local telephone network creates connection points in each municipality in whose territory this network operates.
15. The accession agreement (in addition to other provisions) must provide for:
1) the rights and obligations of telecom operators when connecting telecommunication networks and their interaction;
2) the essential conditions for the connection of telecommunication networks and their interaction, specified in Section IV of these Rules;
3) the procedure for considering disputes between telecom operators on the issues of interconnection of telecommunication networks and their interaction.
16. The connection service provided by the communication network operator includes:
1) approval of design and estimate documentation required by another operator for the implementation of the conditions established by the connection agreement for the connection of telecommunication networks and traffic transmission;
2) installation and adjustment of communication facilities that form the connection point;
3) connection of the communication network;
4) maintenance of the means of communication that form the point of connection, during the term of the agreement on accession.
17. In the connection agreement, agreement must be reached with respect to all essential conditions for the connection of telecommunication networks provided for in Section IV of these Rules.
18. The relations of communication network operators regarding the conclusion of an agreement on connection, with the exception of cases where one of them is an operator occupying a significant position in the public communication network, are subject to the rules for sending an offer and receiving an acceptance, provided for by the civil legislation of the Russian Federation.
19. When putting into operation new means of communication, introducing new technological solutions in its telecommunication network, decommissioning or upgrading obsolete means of communication, which significantly affects the conditions for connecting other telecommunication networks and traffic, the relevant telecom operator is obliged to notify the operators in advance interacting networks.
20. The operator of the long-distance and international telephone communication network, when providing interconnection services, is obliged to ensure the possibility of passing traffic:
1) between zonal telephone communication networks operating in various constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
2) between zonal telephone communication networks and public communication networks of foreign states.
21. The operator of the zonal telephone network, when providing connection services, is obliged to ensure the possibility of passing traffic:
1) between long-distance and international telephone networks and local telephone networks operating within the territory of the same subject of the Russian Federation;
2) between zonal telephone communication networks of different numbering zones operating within the territory of the same subject of the Russian Federation;
3) between local telephone networks of the same numbering zone operating in different municipalities within the territory of the same subject of the Russian Federation, with the exception of passing traffic between local telephone networks of the same numbering zone operating in different municipalities within the territory of a federal city values;
4) between zonal telephone communication networks and data transmission networks operating within the territory of the same subject of the Russian Federation.
22. The operator of the local telephone network is obliged to ensure the possibility of passing traffic:
1) between local telephone networks operating within the territory of a municipal formation or a city of federal significance;
2) between data transmission networks and local telephone networks operating within the territory of a municipality or a city of federal significance.
23. The operator of the long-distance and international telephone network, in accordance with the choice of the operator who intends to receive interconnection services and traffic transmission services, is obliged to ensure the possibility of interaction between the long-distance and international telephone network with the network of such an operator either using circuit switching technology or packet switching technology information.
24. The operator of the telegraph communication network, when rendering interconnection services, is obliged to ensure the possibility of passing traffic between the connected telegraph communication networks.
25. The operator of the telephone network is obliged to keep records of services for passing traffic by time. The duration of each connection is taken into account from the first second of its establishment.
26. Operators of telegraph communication networks and data transmission networks independently determine the list of traffic transit services and keep records of these services based on the amount of information transmitted.
The Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications decided to make changes to some regulatory legal acts that regulate the interaction of operators in matters of interconnection, traffic transmission and payment for these services. In the published draft government decree, the attention of many was drawn to the exceptions for data operators for the purposes of voice transmission. In response to the statements "Skype offend", the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications replied that nothing was changing for IP-operators. I propose to compare the current "Rules for the connection of telecommunication networks ..." and the proposed changes.
The accompanying document "Regulation Summary Report" contains mandatory information about the problem, which can be corrected by proposed changes to existing laws and regulations. Therefore, I suggest that you first "listen" to the developers, before you get acquainted with the table, which will allow you to find out what changes to what.
In this case, the problems are summarized as follows: There are requirements for the hierarchical construction of telephone networks and the passage of traffic only between networks of the same level or through networks top level hierarchy. The current regulation leads to the use of non-optimal traffic routes between the networks of telecom operators and, as a result, the emergence of unjustified costs for telecom operators. The need to equalize the economic conditions for the interaction of fixed telephone operators and mobile radiotelephone operators".
That is, the authors of the changes are aimed at changing the situation that operators have been talking about for several years already - the redundancy and non-optimality of traffic routes due to the requirements for the interaction of local telephone networks only through connection to zonal and LD/IL networks. These requirements to connect networks and pass traffic - "only so" - allowed state telephone monopolies in the past to receive additional income from alternative operators. There was another reason for the introduction of just such connection and traffic transmission - this was the presence at that time of a more developed (in terms of geographical coverage) and more powerful backbone network for those to whom local operators joined.
Time passed, changes took place, other operators appeared who received international/international licenses and built their own backbone networks, regional/local operators expanded their business, and more and more situations arose when it was clear that there were technically feasible and cost-effective ways to organize interaction operators in which zonal networks are an "extra link".
"Lack of a solution to this problem leads to the fact that telecom operators incur additional costs for paying for the zonal call termination service or for building their own zonal networks, which is ultimately shifted to subscription rates ", — "Summary report in relation to the normative act".
What is proposed to be changed in the current regulatory legal acts:
a) allow additional options for connecting local telephone networks to mobile radiotelephone networks and long-distance and international telephone networks in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
b) introduce new services of inter-operator interaction such as "call termination in the subject", "call initiation in the subject", which combine the services of termination at the local and zonal level and initiation at the local and zonal level, respectively;
c) service bundling is introduced to introduce a single price for zonal and local termination of a call.
The proposed changes may, in one way or another, affect a large number of telecom operators - about 10 thousand telecom companies, according to the authors of the new edition of the NPA.
As an argument, they refer to how the interaction of operators in other countries is built: " In the countries of the European Union and the United States of America, a two-tier system for building telephone networks is more common.". That is, the optionality (or uselessness) of zone networks in the hierarchy of Russian communication networks is additionally confirmed.
For ease of comparison, I have prepared a table in which the additions or deletions of words (strikethrough text) are marked (in bold).
The change under the conditional number 1 really contains an "innovation" - a direct connection (connection) can be organized between the MG / IL network and the local telephone network.
In amendments numbered 2 and 3 (and further in other paragraphs of the "Rules ..."), the authors of the draft RLA propose to separate, from the point of view of this RLA, data transmission networks for the provision of communication services for data transmission and data transmission networks for the purposes of voice information transmission . In one case, the connection service is provided, for others it is excluded.
To be honest, if we take into account only these changes and in the form in which they are proposed, it is completely incomprehensible how data transmission networks should function for the purpose of transmitting voice information if they are outside the "Rules for the connection of telecommunication networks and their interaction", containing norms for networks of different levels of hierarchy, for operators of local, zonal, intercity and international communications.
Paragraphs 6-8 describe the changes related to the passage of traffic, taking into account the appearance of the connection of the local telephone operator to the operator of international/international communication. In paragraph 6, I suppose, the developers of the changes also take into account the possibility of the appearance of the "number portability" service in fixed telephony networks (similar to MNP). Or is there something else here?
Paragraphs 9 and 10 describe the interaction of mobile radiotelephone operators in the presence of a local telephone network connection.
The main changes in Appendix No. 2 that I drew attention to are related to the idea of introducing a new service "call termination in the subject", "call initiation in the subject" (by combining the termination service at the local and zonal levels and initiation at the local and zonal levels respectively). In addition, the "call transit within the constituent entity of the Russian Federation" service will replace/combine the services of zonal call transit and local call transit.
Not only the text of the "Rules..." will be updated. Changes in the list of services and change of names will also be in the text of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 19, 2005 No. 627 "On state regulation of prices for interconnection services and traffic transmission services provided by operators occupying a significant position in the public communication network".
Sources used for the comparative table: "Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 03.28.2005 N 161 (as amended on 08.08.2015)" On approval of the Rules for the connection of telecommunication networks and their interaction "" on the site "Consultant Plus" and the draft law "On amendments to some acts of the Government of the Russian Federation regarding the interaction of telecommunication networks" on the website regulation.gov.ru.
On May 20, Kommersant published an article "Skype subscribers are closed within the network", in which the author focused on the impossibility of connecting a data transmission network for the purpose of transmitting voice information after the changes come into force.
The reaction of market participants (quotes from the article):
- "It is critical for us if we cannot provide users with the opportunity to call mobile and fixed phones: this is one of the methods of monetization", - a source in one of the IP operators told Kommersant.
- The Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications refused to comment on the project in detail, only stipulating that " it does not impose any restrictions on IP operators".
- MegaFon says that the project needs to be discussed. VimpelCom and MTS declined to comment on the project.
- The proposed solutions in the field of tariff rules, according to MTT, " may significantly reshape the inter-operator and final market by providing unreasonable preferences to a significant operator, and in fact lead to monopolization of the fixed-line market".
On the evening of the same day, TASS published
1. Provisions on a public contract with regard to operators occupying a significant position in the public communications network shall apply to the agreement on the connection of telecommunication networks, which determines the conditions for the provision of connection services, as well as the obligations associated with this for the interaction of telecommunication networks and the passage of traffic. At the same time, the consumers of interconnection services and traffic transmission services for the purposes of this article are public communication network operators.
An operator occupying a significant position in a public communications network, in order to ensure non-discriminatory access to the communications services market in similar circumstances, is obliged to establish equal conditions for connecting telecommunication networks and traffic transmission for communications operators providing similar services, as well as provide information and provide these communications operators connection services and traffic transmission services on the same terms and of the same quality as for its structural divisions and (or) affiliates.
The operator, which occupies a significant position in the public communications network in the territories of several constituent entities of the Russian Federation, establishes the conditions for connecting telecommunication networks and passing traffic separately on the territory of each constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
2. The refusal of an operator occupying a significant position in a public communications network to conclude an agreement on the connection of telecommunication networks is not allowed, except in cases where the implementation of the connection of telecommunication networks and their interaction contradicts the terms of licenses issued to communication operators, or regulatory legal acts determining construction and operation single network telecommunications of the Russian Federation.
3. The procedure for connecting telecommunication networks and their interaction with the telecommunication network of an operator occupying a significant position in the public communication network, and its obligations when connecting telecommunication networks and interacting with telecommunication networks of other telecom operators, telecommunication networks of owners of special-purpose communication networks are determined in accordance with rules approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Operators occupying a significant position in the public communication network, on the basis of the rules for connecting telecommunication networks and their interaction, establish the conditions for connecting other telecommunication networks to their telecommunication network in terms of the use of network resources and traffic transmission, including general technical, economic, information conditions, as well as the conditions determining property relations.
The conditions for the connection of telecommunication networks should provide for:
technical requirements relating to the interconnection of telecommunication networks;
scope, procedure and deadlines for performing work on the connection of telecommunication networks and their distribution between interacting telecom operators;
the procedure for passing traffic through the telecommunication networks of interacting telecom operators;
location of points of connection of telecommunication networks;
a list of interconnection and traffic transmission services provided;
the cost of connection services and traffic transmission services and the procedure for paying for them;
the procedure for interaction of telecommunication network management systems.
Operators occupying a significant position in the public communications network, within seven days after the establishment of the conditions for the connection of telecommunication networks, publish these conditions and send them to the federal executive body in the field of communications.
In the event that the federal executive authority in the field of communications, on its own or at the request of telecom operators, discovers a discrepancy between the conditions for connecting other telecommunication networks to the telecommunication network of an operator occupying a significant position in the public communications network, and passing traffic through it to the rules specified in paragraph one of this paragraph, or regulatory legal acts, the said federal body sends to the operator, which occupies a significant position in the public communications network, a reasoned order to eliminate the indicated inconsistencies. This instruction must be accepted and fulfilled by the telecom operator that received it within thirty days from the date of its receipt.
(see text in previous edition)
The newly established conditions for the connection of other telecommunication networks to the telecommunication network of an operator occupying a significant position in the public communication network, and the passage of traffic through it are published by the operator occupying a significant position in the public communication network, and sent to the federal executive body in the field of communications in the manner provided for in this article.
When new communication facilities are put into operation, new technological solutions are introduced in its telecommunication network, obsolete communication facilities are decommissioned or upgraded, which significantly affects the conditions for connecting other telecommunication networks and passing traffic through the telecommunication network of an operator that occupies a significant position in the general communication network use, the said communications operator has the right to establish new conditions for the connection of other telecommunication networks to its network in the manner prescribed by this article. At the same time, the conditions for connecting telecommunication networks cannot be changed more than once a year.
4. An operator occupying a significant position in a public communications network considers the communications operator's applications for concluding an agreement on the connection of telecommunication networks within a period not exceeding thirty days from the date of receipt of such an application. An agreement on the connection of telecommunication networks is concluded in writing by drawing up, in accordance with civil law, one document signed by the parties, within a period not exceeding ninety days from the date of receipt of the application. Failure to comply with the form of such an agreement entails its invalidity.
5. The federal executive authority in the field of communications maintains and publishes a register of operators occupying a significant position in the public communications network.
6. The federal executive body in the field of communications is obliged to consider the appeals of telecom operators on the issues of connection of telecommunication networks and their interaction within sixty days from the date of receipt of these appeals and publish the decisions taken on them.
In the event that an operator occupying a significant position in a public communication network fails to comply with the instructions of the federal executive authority in the field of communications on the issues of interconnection of telecommunication networks and their interaction, as well as the operator, which occupies a significant position in a public communication network, evades from concluding an agreement on connection networks of telecommunications, the other party has the right to apply to the court with a demand for compulsion to conclude an agreement on the connection of telecommunications networks and compensation for damages.
In accordance with subparagraph 19-13) of paragraph 1 of Article 8 of the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated July 5, 2004 "On Communications" I ORDER:
It is allowed to connect to public telecommunications networks of networks of the same operator in several geographically separated points. In this case, in each of these paragraphs, all the requirements determined by these Rules must be met.
20. When issuing technical conditions for connection, the issues of increasing the power of various elements of the connected and connecting networks (interstation and switching capacities, capacities of communication lines) may be taken into account. The costs of increasing the capacity by agreement of the parties may be borne by the operators of the connecting and connected networks using given element network, in proportion to the capacity involved in the interests of a particular operator.
21. After the fulfillment of the technical conditions, an agreement is concluded between the telecom operators (owners) of the connected and connecting networks, which determines all issues of mutual settlements, the responsibility of the parties for the quality of the services provided.
22. Financing of the design and construction work carried out in the course of connecting telecommunications networks is carried out on a contractual basis.
23. The connection of telecommunications networks of telecom operators is carried out in the presence of a certificate for the equipment used.
24. The organization of connection to the network of the dominant telecommunications operator is based on the following principles:
1) providing telecom operators with information about standard points of connection (connection) and conditions for connection are determined in accordance with clause 18 of these Rules;
2) observance of equal conditions for connecting telecommunications networks and traffic transmission for all telecommunications operators, network owners, telecommunications providers providing similar services;
3) the provision of connection and traffic transmission services by the dominant telecommunications operator to other communication operators, network owners is carried out on the same conditions and traffic transmission technology as when organizing these services by the dominant telecommunications operator within its network and (or) providing these services to affiliates;
4) providing details of the invoice for payment for interconnection and traffic transmission services;
5) observance of the confidentiality regime between the parties in relation to information about competitors and customers;
6) provision of the possibility of paid use, on a contractual basis, of synchronization systems, operational support systems, billing systems, and other hardware and software required to provide new services; "undivided" network components, including subscriber lines;
7) provision of the possibility of implementation on a contractual basis of paid use of infrastructure elements (for example, buildings, poles, telephone (cable) ducts, channels, antenna-mast structures and others).
25. For dominant telecommunications operators, the Connection Agreement, on the basis of which the conditions for the provision of services for the connection of other telecommunications networks, as well as the obligations related to these networks interconnection and traffic transmission, is a public agreement.
26. When issuing technical conditions for connection, discrimination of telecom operators is not allowed. The dominant telecommunications operator sets equal conditions for interconnection and traffic transmission for the interconnected networks of operators.
27. When the merging operator fulfills all the requirements provided for by these Rules, the refusal of the dominant telecommunications operator to conclude the Contract of Accession is not allowed.
28. Local affiliation:
1) fixed networks local communications with each other, fixed communication networks with mobile communication networks (mobile radiotelephone communication and trunking communication), which are connected to public telecommunications networks, is carried out with the allocation of an appropriate local network numbering resource;
2) through the switching stations of the attached network with inclusion in the local digital telephone exchange, the connecting network on which the accounting of outgoing and incoming traffic of the attached network should be carried out;
3) by connecting the switching stations of the connected network to the local digital telephone exchange of the connecting network. The connection can be carried out by digital communication channels, using the circuit switching technology, formed by:
connecting lines;
custom-connection lines intended for the transmission of outgoing long-distance telephone messages of the local telecommunications network;
interconnecting long-distance telephone communication lines connecting the intercity telephone exchange with the station of the local telecommunications network and intended for the transmission of incoming long-distance messages;
and channels for transmitting a speech signal using the technology of switching packets of information;
4) in the event that the capacity of the connected station is at least 3500 numbers, it is allowed if there is a reserve capacity at the automatic intercity telephone exchange (hereinafter referred to as ATE), the organization of direct channels between the switching stations of the connected network and ATE of public telecommunications networks located in the same zone numbering;
5) if the capacity of the connected network creates an excess of the reserve of the current numbering of the local network, then the authorized body in the field of communications takes measures to resolve this issue.
29. Accession at the intrazonal level:
1) for connection at the intrazonal level, the connected network is switched on as a local network with the assignment of an intrazonal access code "ab" within geographical area numbering;
2) in the absence of a numbering resource for connecting telecommunications networks at the local level, a network with a capacity of at least 5000 numbers can be connected, in agreement with the operator of the connecting network, at the intrazonal level with the inclusion of switching stations of the connected network in the ATE of this numbering zone.
30. Connection at the long-distance level - the connection of one telecommunications network to another, in which the connected network of the operator (network owner) is included in the standard points of connection (connection) at an automatic long-distance telephone exchange or at an intercity transit node (MGTU) of the connecting network. At the same time, the connected network is allocated a numbering resource - the code of the geographically defined area ABC, the access code "X1X2" in ABC, the code of the non-geographically defined area DEF, the operator code in the service access code (hereinafter referred to as CDU), the prefix for selecting the long-distance and / or international operator communications (hereinafter - PoP).
31. Accession at the international level:
1) interconnection at the international level is carried out for networks of international communication operators, in which the connected telecommunications network is connected to the international switching center of the network (hereinafter referred to as the MCC) that performs the interconnection;
3) during the interaction of networks of international communication operators with each other (at the MCC-MCC level), it is envisaged to organize bypasses to pass traffic in case of accidents and in the event of emergencies on one of the networks, both within the national network and when entering foreign public telecommunications networks.
32. The connection of telecommunications networks of long-distance and (or) international communication operators is organized at the inter-city and (or) international level.
33. The connection of local telecommunications networks to the networks of long-distance and (or) international communication operators is organized as follows:
1) the connection of local telecommunications networks connected to public telecommunications networks to the networks of long-distance and (or) international communication operators is carried out through the connection points of the local level of the connecting network (transit nodes of automatic telephone exchanges - ATS TU, automatic long-distance telephone exchange AMTS) of the operator of long-distance and ( or) international communications, on which accounting of outgoing and incoming traffic should be carried out;
2) the choice by subscribers of a local telephone operator connected to public telecommunications networks, the network of an operator of long-distance and (or) international communication is carried out through the operator prefix (POP) assigned to the operator of long-distance and international communication.
34. The connection of the network of the operator of long-distance communications to the network of the operator of long-distance and international communications is organized as follows:
1) connection of the network of the long-distance communication operator to the network of the operator of long-distance and international communication is carried out at the long-distance level between the ATEs of these operators located in the same geographical numbering zone (ABC);
2) interaction between ATE of the connecting network and ATE of the connected network is carried out by organizing direct communication channels between them;
3) accounting of outgoing and incoming long-distance traffic is carried out by both operators of long-distance and (or) international communication, or, by agreement, by a single settlement center belonging to one of the interacting communication operators.
35. The connection of the network of the operator of international communications to the network of the operator of long-distance and international communications is organized as follows:
1) the connection of the network of the operator of international communications to the network of the operator of long-distance and international communications is carried out between the MCC of the networks of the connected and connecting operators;
2) interaction between the MCC connected and connecting networks is carried out by organizing communication channels between them;
3) when interacting networks of long-distance and international operators and international operators (at the MCC-MCC level), it is envisaged to organize bypasses to pass traffic in case of accidents and in the event of emergencies on one of the networks, both within the national network and during access to foreign public telecommunications networks.
36. Connecting the network of an operator of long-distance and international communications to the network of another operator of long-distance and international communications is organized respectively between ATE and ATE of one geographical area, MCC and MCC networks of the connected and connecting operators.
37. Launching into commercial operation of networks of an operator of long-distance and (or) international communications connected to the network of another communications operator is carried out after confirmation by the authorized body in the field of communications on the fulfillment of qualification requirements and criteria for determining the operator of long-distance and (or) international communications imposed on telecommunications networks operators of intercity and (or) international communication.
If the connecting operator detects a discrepancy between the information in the Act on the fulfillment of the qualification requirements by the operator and the actual situation, the connecting operator has the right to restrict the passage of traffic, as well as notify the authorized body in the field of communications about this.
38. A corporate telecommunications network may be connected to public telecommunications networks as corporate client by installing an office switching station within the administrative territory:
at the local level;
at the intercity level, if it combines network sections distributed over different administrative territories, with the allocation of an appropriate numbering resource (code "DEF");
or be directly connected to a mobile network.
If the owner intends corporate network to provide services on a reimbursable basis, connection to public telecommunications networks is carried out on the condition that:
1) the connected part of the network can be programmatically or technically separated by the owner from the rest of the network used for internal production purposes (management of technological processes in production);
2) the connected part of the network complies with the requirements for the functioning of the telecommunications network set forth in these Rules;
3) the owner of the corporate telecommunications network keeps separate records of the costs of operating the network used for management and internal production purposes (management of technological processes in production) and its part connected to telecommunications networks.
39. Connecting mobile networks:
1) public mobile radiotelephone and trunking networks can be connected to public telecommunications networks at the intercity, intrazonal and (or) local level with the allocation of an appropriate numbering resource in accordance with regulatory enactments or by agreement between telecom operators;
2) mobile radiotelephone networks and mobile satellite communications for which the DEF code of the non-geographical numbering zone is assigned, are connected to public telecommunications networks at the intercity level, to pass traffic to subscribers of other numbering zones and at the zonal level - through the ATE of the geographical numbering zone in which the switch of the mobile network is located, to pass traffic within a given geographic numbering area;
3) networks cellular communication, for which the DEF code of the non-geographic numbering area is assigned, are connected to public telecommunications networks at the intercity level, the connection of cellular networks to each other is carried out at the corresponding levels switching equipment these networks by organizing direct communication channels;
4) public mobile radiotelephone and trunking networks, which are assigned the code "ab" in the geographical numbering zone ABC, are connected to the public telecommunications networks through the ATE of the given geographical numbering zone. The numbering plan of the network to be joined is included in the numbering plan of the geographic area;
5) networks of mobile radiotelephone and trunking communications of general use, which have received the ATC index of the local network "abX / abXX", are connected through the switching stations of the local network. The numbering plan of the connected network is included in the numbering plan of the local network.
40. Connection of telegraph and telex networks:
1) connection to public telex networks is permitted for departmental telegraph and telex networks and telematic services;
2) connection to telegraph and telex networks is carried out at the level of subscriber terminals or installations;
3) connection at the level of subscriber installations means the connection of a user terminal to a telecommunications network, through which the operator transmits and receives information;
4) connection to public telegraph and telex networks with message switching is allowed for telegraph and telex networks of operators;
5) in some cases, if there are appropriate technical means in the connected network, it is allowed, on the basis of instructions from the authorized body in the field of communications, to connect to telegraph communication networks at the level of stations (substations) of channel switching or centers (concentrators) of message switching;
6) specific connection points and numbering allocated to the connected network are established by the operator of the public telegraph network.
41. Connection to public telecommunications networks of access nodes of telecommunications providers is organized in one of the following ways:
1) connection of the equipment to the ATE of the public telecommunications network using the operator's code in the CDU appointed by the authorized body in the field of communications. At the same time, access is organized only for subscribers of the numbering zone, to the ATE of which the equipment is connected;
2) connection of the equipment to the public telecommunications network at the local level via unidirectional communication channels outgoing from subscribers of the local network, included in the standard connection (connection) point.
42. To organize access to services provided by telecommunications providers, operators of local telecommunications networks provide telecommunications providers with subscriber lines with the allocation of subscriber numbers or serial numbers. The contract for the allocation of subscriber lines indicates for what purpose they are allocated.
The procedure for allocating serial numbers and the interaction of telecommunications providers with telecom operators of local telecommunications networks, issued serial number is given in Appendix 6 to these Rules.
43. Connection of access nodes of IP-telephony operators to the network of long-distance and (or) international communication operators is carried out at the intercity level using the CDU. Along with using the operator code in the CDU, the local phone number assigned as a service access number. At the same time, the level of connection of access nodes of IP-telephony operators remains long-distance.
44. KDU and operator code X1X2X3X4 are assigned by the authorized body in the field of communications.
45. Access to the services of IP-telephony operators is organized for subscribers of the ABC numbering zone, to the ATE of which the operator's access node is connected.
46. Not allowed direct connection access nodes of IP telephony operators to the equipment of mobile networks.
47. are issued in accordance with the application for accession and must contain the following:
1) a method of connecting networks (communication facilities) that allows for connection, indicating the relevant line-cable and station structures used, the affiliation of these structures, station equipment;
2) the use of existing telecommunications facilities to pass the traffic of the connected network, in the absence of such, the need to build new facilities by agreement of the parties;
3) types of equipment and its technical parameters at network connection points - signal levels, signal spectra, transmission rates and other parameters of joints;
4) alarm systems used;
5) binding to the network clock synchronization system;
6) numbering resource allocated to the affiliated operator by the authorized body in the field of communications;
7) measures necessary for the connection, a preliminary list of construction and installation works;
8) stages of work on connection;
9) validity period (at least six months).
A restrictive list of signaling protocols supported by digital stations in public telecommunications networks is given in Appendix 7 to these Rules.
48. Technical conditions for connection are specified within the time limits provided for their issuance in the following cases:
1) renumbering on the network that carried out the connection;
2) modernization, reconstruction or replacement of the technical means of the network that has carried out the connection, directly interacting with the connected network, requiring a change in signaling systems, etc.;
3) the need to upgrade equipment on the connected network and (or) expand its capacity;
4) changes in the level of connection in accordance with the regulations of the authorized body in the field of communications;
5) obtaining by the affiliated operator of other licenses for conducting entrepreneurial activities in the field of telecommunications requiring the connection of networks.
49. When modernizing public telecommunications networks, the connecting operator, after the approval of the modernization project, notifies all interested telecommunications operators, network owners, telecommunications providers about a possible change in technical conditions 4 (four) months in advance. If necessary, the acquiring operator shall issue changes to the specifications to the merged operator no later than three months before the start of modernization.
At the same time, the connected operator applies to the connecting operator for clarification of the technical conditions for connecting its network to the public telecommunications network.
Specification for connection specifications is carried out in the manner and terms determined by these Rules for the issuance of technical specifications. After the work on connection is completed in accordance with the new technical conditions, the interacting telecom operators Contract of connection and interaction must be specified.
In cases of changes or clarification of the technical conditions for connection, changes or additions must be justified, optimally necessary and not go beyond the issues regulated by these Rules.
50. If the connection is found to be inconsistent with regulatory legal or regulatory and technical acts, the connecting operator must issue technical conditions to the connected operator that comply with these Rules. The expenses arising from this are paid by both interacting operators in the amount determined by the agreement between them.
51. Telecom operator:
1) provides users of its networks with the right to choose any operator of long-distance and (or) international communication;
2) provides interconnection and traffic transmission services that meet the quality standards, technical norms, terms and conditions of the Interconnection Agreement;
3) provides on its networks the ability to connect to transferred cellular subscriber numbers using the "All Call Query" direct routing method using information on assigned routing numbers received from a centralized subscriber number database.
52. Between telecom operators and / or owners of networks participating in a single technological process for the provision of interconnection and traffic transmission services, an agreement is concluded providing for:
1) mutual responsibility for the quality of the provided connection and traffic transmission services;
2) the procedure for compensation for damage to telecom operators and / or owners of networks in case of non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of the requirements of regulatory enactments on technical operation, which led to a deterioration in the quality of services or their non-provision;
3) the powers of telecom operators and/or network owners to make payments for connection and traffic transmission services provided by other telecom operators and/or network owners, and the procedure for mutual settlements for these services;
4) the procedure for carrying out work to consider claims received from interacting telecom operators and / or network owners;
5) the procedure for passing the traffic of operators of interacting networks;
6) conditions and procedure for mutual settlements for traffic transmission;
7) issues of interaction between systems of operational and technical management of networks;
8) timely provision of information to other telecommunications operators, network owners, telecommunications providers about emergency failures of communication facilities, entailing interruptions in the provision of services, and taking a set of measures to restore communication as soon as possible;
9) timely notification of telecommunications operators, network owners, telecommunications providers about scheduled preventive work on the network, which may lead to interruptions in the provision of services;
10) ensuring the correct translation of signaling parameters in accordance with the common channel signaling of SS 7 networks or SIP-T / SIP-I protocols, including the numbers caller(subscriber number A) for local, long-distance and / or international calls, if it is present in the original records of the switching equipment of the telecom operator (detailed call record - Call Detail Record).
Footnote. Clause 52 as amended by the order of the Minister of Information and Communications of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 10/21/2016№ 21853. The telecom operator participating in the establishment of a telephone connection transmits information about the number of the calling subscriber (subscriber A number) unchanged, taking into account the recommendations of the ITU and the requirements of these Rules.
In the event of a discrepancy between the quality parameters of the services provided and the current standards, the interacting telecommunications operators, network owners, telecommunications providers must immediately find out the causes of disruptions in the operation of telecommunications networks and take measures to eliminate these causes. In this case, the costs are reimbursed by that telecommunications operator, network owner, telecommunications provider, in the operation of whose equipment a non-compliance with applicable standards is found.
54. When introducing time-based accounting of local telephone connections, telecom operators ensure that subscribers are provided with the possibility of free connections with social facilities of the settlement in agreement with local executive bodies that compensate the expenses of telecom operators for these purposes.
3. The procedure for passing traffic through the telecommunications network and
mutual settlements
55. Telecom operators carry out the traffic of their networks in accordance with these Rules, as well as in accordance with the terms of the Agreement of Accession.
56. Each telecommunications operator, network owner, telecommunications provider operating in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan independently manages the traffic flow that closes within its network and follows the instructions of the authorized body in the field of communications in case of emergency.
1) for routing traffic that closes within the national network;
2) for routing international outgoing, incoming and transit traffic;
3) for passing traffic to transferred cellular subscriber numbers;
4) for the collection, analysis and provision complete information about the technical condition and operation of their network.
57. It is not allowed to route traffic outside the Republic of Kazakhstan when making a connection at the local, intrazonal and intercity levels.
58. In order to recover the existing debt, the telecom operator may restrict incoming long-distance and / or international traffic until such debt is paid off.
The telecom operator is allowed to restrict incoming long-distance and / or international traffic from certain numbers in case of incorrect transmission of signaling parameters in accordance with the general channel signaling of SS 7 networks or SIP-T / SIP-I protocols, including the calling subscriber number (subscriber number A) for a local, long-distance and/or international call, if it is present in the original records of the switching equipment of the telecom operator receiving traffic to its network (Call Detail Record).
In other cases, restrictions on the transmission of any type of incoming / transit traffic by telecom operators without a corresponding court decision are not allowed.
Footnote. Paragraph 58 as amended by the order of the Minister of Information and Communications of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 10/21/2016№ 218 (shall be enforced upon expiration of ten calendar days after the day of its first official publication).59. Pass local, intercity, international telephone traffic, data transfer traffic (including traffic of IP-telephony operators), traffic from/to cellular networks through the technical means of networks formed as a result of connection is allowed solely on the basis of agreements concluded between the connecting and connected operators.
Telecommunications operators, network owners, telecommunications providers are not allowed to pass unauthorized traffic on local, long-distance, international and cellular networks.
60. When passing traffic to ported cellular subscriber numbers, telecom operators use the routing numbers assigned subscriber numbers when entered into the centralized database of subscriber numbers.
In this case, the passage of traffic initiated on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan is carried out by the network of the call initiator. Call routing (connection) is carried out at the network level of the recipient operator.
61. The passage of outgoing, incoming, transit international telephone traffic of public telecommunications networks and communication networks connected to the public telecommunications network is carried out through the switching field of the MCC of operators of long-distance and (or) international communication of the public telecommunications network of the Republic of Kazakhstan, in accordance with the Agreement accessions.
62. Prefixes for the choice by the subscriber of the operator of long-distance, international, cellular communications and telecommunications providers are assigned by the authorized body in the field of communications and are used only for outgoing communications from the subscriber.
In case of incoming communication, the choice of the network of the telecom operator from the incoming international (intercity) station is carried out in accordance with the agreement between the telecom operators for the direction of incoming traffic to subscribers of local telecommunications networks.
63. In order to avoid damage, creating obstacles to the use of the network by subscribers, overloads and emergency situations on communication networks, telecom operators are not allowed to take measures that stimulate an increase in the volume of incoming traffic from the networks of other operators.
64. In the event of damage, congestion and emergencies on the network, telecommunications operators and network owners should immediately take coordinated measures to restore communication and quality of service, organize bypasses to route traffic to destinations.
Traffic routing schemes along bypass routes, the order of formation of bypass routes are established by joint decisions of telecommunications operators and/or network owners.
The operational management of work to restore communication and quality of service is carried out by one of the operators of long-distance and international communications.
65. In case of passing unauthorized traffic, including traffic with the substitution of the subscriber number (number A), the telecom operator receiving the traffic immediately notifies the telecom operator from which this traffic was received. A telecom operator that has received a notification about the passage of unauthorized traffic from its network must find out the causes and take measures to eliminate such traffic within 10 calendar days.
If the passage of unauthorized traffic is not eliminated, the telecom operator that receives such traffic on its network applies to the judicial authorities.
66. The relationship of telecom operators and / or owners of networks interacting as a result of the connection of telecommunications networks, when conducting mutual settlements, is based on the following general provisions:
1) maximum use of telecommunications network resources ( bandwidth switching stations, channels and lines);
2) stimulating an increase in the quality of call service and the provision of interconnection and traffic transmission services;
3) equal partnership, including the use of symmetrical settlement rates for settlements for the same categories of traffic;
4) accounting for the contribution of each party to the construction and operation of station and linear structures of the telecommunications network.
The settlement rates for passing inter-operator traffic are determined by the parties to the agreement, unless at least one of the Parties is recognized as the dominant operator, which makes mutual settlements with all operators on the same terms.
When setting inter-operator rates, it is not allowed to use asymmetric rates for the transmission of traffic of the same category.
67. The procedure for mutual settlements between telecom operators and / or owners of networks for the provided network resources determined taking into account:
1) relations to the ownership of technical means and telecommunications facilities that provide access to public telecommunications networks;
2) the level of connection to public telecommunications networks;
3) mutual settlements for the transmission of traffic through public telecommunications networks.
68. The tariff for connection services is a one-time payment and reflects the cost of the work of the telecom operator (network owner) arising in connection with the provision of connection services, based on the reimbursement of economically justified costs and profits (no more than three times the refinancing rate established by the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan) for creation and selection of a standard attachment point (connection).
When calculating the one-time payment for connection services, the costs of renting space and premises are not included.
The expansion of the existing connection capacity is carried out on a contractual basis, taking into account the interests of both parties.
69. Mutual settlements for the passage of all types of traffic between interacting telecom operators are made on the basis of accounts generated by their own certified billing systems.
Inter-operator settlements for SMS traffic do not include technical automatic notifications mobile operators sent to subscribers (for example, about the availability or unavailability of the subscriber). The calculations include only SMS messages initiated and received by subscribers of telecommunications services.
The basis for the formation of an invoice to the subscriber by the billing system for the provided traffic transmission services is the data of the system for measuring the duration of connections and the system for measuring data transmission, which must be entered in the register state system ensure the uniformity of measurements and have a valid calibration certificate.
70. When connecting and connecting operators interact, mutual settlements between them are carried out for the actual traffic (incoming, outgoing and transit types of traffic), for connection services, for leased telecommunications facilities and facilities and other services.
In mutual settlements for the transmitted traffic, the telecom operator, for which the direction is outgoing and which receives a fee from the subscriber, settles with the telecom operator for which the traffic transmitted in this direction is incoming or transit, based on the settlement rates agreed by the interacting parties and provided for by the Accession Agreement.
If one operator provides telecommunications services to a subscriber of another operator under prepaid cards or direct agreements with them, mutual settlements between operators are made on the basis of additional agreements providing for payments to the operator providing subscriber termination during outgoing connection, based on settlement rates.
71. Mutual settlements between the connected and connecting telecom operators are made for:
1) traffic transit services:
local (incoming, outgoing, transit);
long-distance (intrazone) (incoming, outgoing, transit);
international (incoming, outgoing, transit);
to (c) networks of mobile operators;
operators of IP telephony (Internet telephony);
traffic entering the network of telecom operators of indefinite directions;
2) access services to transport network channels:
leasing a communication channel (analogue or digital) and (or) a connecting line between different points of connection with the networks of other telecom operators;
3) services for organizing access to the network of a telecom operator:
work on organizing and connecting a channel and (or) a connecting line between the connected networks (from the network of each of the connected operators to the connection point, depending on the geographical location of the connection point);
4) access to the services of the connecting telecom operator:
billing and collection of payments from subscribers;
provision for rent or use of cable ducts and technological property for the purposes of connection;
conducting Maintenance and inspection of equipment;
5) connection services.
72. Operators of long-distance and international communications and operators of international communications carry out settlements with foreign international communications operators for international traffic.
73. Mutual settlements of telecom operators for the passage of international traffic are carried out on a contractual basis and in accordance with the legislation in the field of communications and natural monopolies, and regulated markets.
74. Mutual settlements between telecom operators for communication services at the expense of the called subscriber are carried out on a contractual basis between interacting operators.
75. Mutual settlements between telecom operators of interconnected networks connected at the intra-zonal or local level include the recommendations of these Rules and the ITU recommendations (series D) on the method of paying per unit of traffic based on calculated rates, and, if necessary, on the basis of additional lease agreements for the use of connecting lines, communication channels and telecommunications facilities.
76. When carrying out mutual settlements of operators, a standard digital channel of 64 kbps, one four-wire channel with a transmission rate of 50 Baud, is accepted for one connecting line. The E1 stream is taken as 30 standard digital channels in accordance with G.704 recommendation clause 5.2 "2048 kbit/s splice carrying n*64 kbit/s channels".
The division in the flow of n*64 channels into incoming and outgoing depends on the types of services provided by the telecom operator of the connected network, and is determined at the stage of issuing and fulfilling technical conditions for connection.
The standard point of attachment (connection) is formed by the E1 digital port, providing 30 digital voice or data channels, a separate channel for synchronization and a separate channel for transmitting control signals, a total of 32 channels of 64 kbps and a speed of 2 Mbps, as well as voice channel (encapsulation of the standard digital channel 64 kbit / s) using the technology of switching packets of information via an IP network. It is recommended to connect with the organization of groups of channels with a multiplicity of 30.
77. Mutual settlements between telecom operators for traffic transmission are carried out on the basis of accession agreements and in accordance with the legislation in the field of communications and natural monopolies and regulated markets.
78. To organize and conduct settlements between telecom operators, traffic must be measured both outgoing and incoming. At the same time, each telecom operator stores primary data on the transmitted traffic on all used paths for passing the load for reconciliation with other operators in accordance with the terms of the concluded contracts for at least three years and is responsible for the reliability of the data.
79. In order to obtain reliable data on the volume of traffic transmitted in different directions, telecom operators take measures to ensure the possibility of determining its volume and the quality of call service in all used directions for establishing connections, including direct and bypass channels.
80. By agreement between telecom operators, the collection and processing of traffic data can be carried out through a single clearing center, owned by one of the interacting telecom operators.
82. Technical means, used for traffic accounting, including systems for measuring the duration of connections and transmitting data of the telecom operator, must be entered in the register of the state system for ensuring the uniformity of measurements and have a valid verification certificate.
Organization of interaction of technical personnel in
damage and emergencies, as well as routing
calls to departmental, corporate, special communication networks and
PBX of public telecommunications networks
1. Organization of interaction of technical personnel
connected PBXs in case of damage and emergencies
1. Damage may occur on station equipment, on the equipment of transmission systems and linear structures belonging to the attached or basic automatic telephone exchanges (hereinafter referred to as ATS). Damage falls into three categories:
2. Terms of elimination of accidents depending on the category of damage are regulated technological maps and are negotiated in an additional agreement when connecting.
3. The emergency state of equipment or linear structures connected to the public telecommunications network PBX is determined by the technical staff of the interacting PBX based on emergency signals.
4. The technical staff of the interacting exchanges determines the cause of the damage. Each party eliminates damage in its section of the network. After accidents are eliminated and the damaged equipment is restored to working order, control checks of this equipment are carried out.
5. Scheduled checks of the operability of the equipment of line terminations between the connected and the reference exchange are carried out in accordance with the plans for preventive checks in accordance with the relevant technical operation instructions of this type equipment.
6. In case of carrying out preventive and measuring work, which can lead to a temporary deterioration in the quality of communication between interacting exchanges, the technical staff of both exchanges informs the dispatch service of the telecom operator about this.
2. Call routing
7. The connected PBX should provide the ability to establish the following main types of communication:
1) between subscribers of the attached PBX (intra-station connections);
2) with subscribers of public telecommunications networks (local, intercity and international);
3) access to special services.
8. Outgoing external communication from the PBX connected to the public telecommunications network connected to the PBX can be made by dialing by subscribers of departmental, corporate, special and mini PBX an unambiguous exit prefix (recommended Pm = 9) and then dialing full number the required subscriber.
9. Outgoing intercity, international communication from subscribers of the connected PBX should be carried out by dialing the exit prefix further by dialing "8" (or "8-10"), in the future "0" and "00" respectively, and then dialing a long-distance (international) number.
10. Outgoing communication to the special services from the above subscribers should be carried out by dialing the exit prefix, and then the number of the special service. It is allowed to enter the special services without setting the exit index.
11. Subscribers of the attached PBX who do not have the right to external communication should be provided with the opportunity to establish a free external communications with emergency intelligence services (101, 102, 103, 104).
12. When establishing a connection between subscribers of the connected PBX, an internal abbreviated number (three-digit or four-digit, depending on the capacity of the connected PBX) can be used.
Load and connection quality standards
PBXs of any type connected to public telecommunications networks must be connected via connecting lines with a load rate per line (channel) up to 0.7 Erl.
Attached automatic telephone exchanges of any types are included in public telecommunications networks through core, combined or transit digital switching stations.
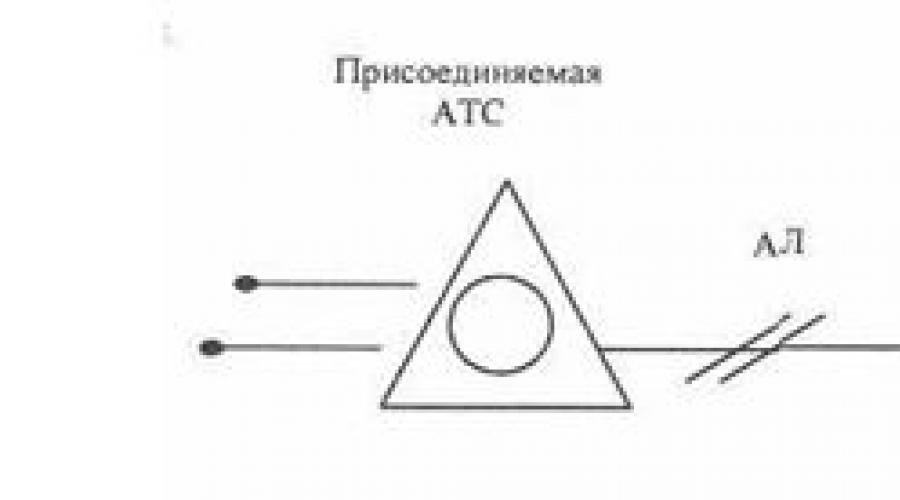
Attached automatic telephone exchanges can be connected through connecting lines with a load rate per line (channel) up to 0.7 Erl or via subscriber lines (hereinafter referred to as AL).
The average total (outgoing and incoming) telephone load per AL should not exceed 0.15 Erl.
It should be possible to limit the load on the AL. Load limitation should be carried out for each AL between the mini-ATS (capacity no more than 128 numbers) and the reference exchange. If the mini-automatic telephone exchange does not have means for limiting the load, then when this mini-automatic telephone exchange is connected to the telephone network, in agreement with the connecting party, it is rigidly fixed a certain amount of mini PBX subscribers who have access to the local network.
The quality of connection establishment is determined by the loss rates given in Table 1.
Table 1. Standards for quality indicators
Name of indicator | Norm value |
The probability of losses between the inputs of neighboring stations should not exceed: for outgoing local connection on incoming local connection for incoming long-distance, international connection | |
Control terms for troubleshooting related to: 1) with switching equipment | 45 minutes on serviced, 2 hours on unattended exchanges |
2) with line-cable equipment: in interstation communication cables, trunk and distribution cables with opening of the couplings, when the cable is not completely damaged, with a capacity of: | |
up to 200x2 inclusive | |
up to 400x2 inclusive | |
up to 600x2 inclusive | |
up to 800x2 inclusive | |
up to 1200x2 inclusive | |
3) in interstation communication cables, trunk and distribution cables, when it is required to replace the cable span, with a capacity of: | |
up to 300x2 inclusive | |
up to 400x2 inclusive | |
up to 600x2 inclusive | |
up to 800x2 inclusive | |
up to 1200x2 inclusive | |
4) in high-frequency cables of inter-office communication or inter-office VLAN | |
with replacement of cable or supports | |
5) elimination of damage in the optical cable sleeve |
Technical requirements for automatic telephone exchanges included in the network
public telecommunications
1. Options for connecting PBXs to public telecommunications networks:
1) connection of connected automatic telephone exchanges via digital connecting lines:
2048 kbit/s PCM digital trunk parameters shall comply with ITU-T Recs G.703, G.704 and G.732.
2. Options for connecting mini-ATS to public telecommunications networks:
1) connection of a mini PBX to a PBX of a telecommunications network via analog subscriber lines:

An analog subscriber set (AK) is used in a digital exchange;
Line signals are transmitted in a daisy chain;
Dialing transmission - by battery pulse or DTMF signaling;
3. Organization of access for mini-ATS:
1) mini automatic telephone exchanges are included in public telecommunications networks through subscriber sets of digital basic or combined automatic telephone exchanges via two-wire subscriber lines;
2) the use of subscriber sets of the base PBX as connecting lines for a mini-PBX should not violate the system of operation of subscriber lines (serviceability check, measurements);
3) the inclusion of a mini-automatic telephone exchange in the public telecommunications network is carried out on digital automatic telephone exchanges;
4) it is recommended to use the number "9" as a local prefix (PM) for access to telecommunications networks.
4. Connection of connected switching stations via a packet-switched network.
This type of connection is carried out through the physical connection of the Internet networks of the connected and connecting operators via 1/10 GE channels, with the organization of a virtual private network (VLAN / VPN) to pass internetwork traffic, installation of SBC equipment (session border controller) at the network edge of each operator and subsequent organization of voice signal transmission channels and call control signaling using information packet switching technology. Internet operators' networks must support technologies for ensuring the quality of transmitted speech of at least 3.5 points on the Mean Opinion Score (MOS - Mean Opinion Score) scale

5. Organization of serial search.
When organizing communication to any special service, the PBX uses subscriber sets (AK), which allow organizing a serial search. In this case, load restrictions are imposed: for each subscriber line<0,15 Эрл.
Features of accession mini automatic telephone exchange.
Parameters of subscriber sets for which
PBX
1. Parameters of subscriber sets, for which mini-automatic telephone exchanges are enabled, are the sum of the parameters: physical lines, mini-automatic telephone exchange four-terminal network, its subscriber lines and telephone sets, and should not exceed the norms established for subscriber lines. The parameters for direct current, including the mini-ATS subscriber kit, must be:
1) loop resistance, taking into account the resistance of the input interface - no more than 1800 Ohm;
2) insulation resistance between wires or between each wire and "ground" - not less than 20 kOhm;
3) capacitance between the wires or each wire and the "ground" is not more than 0.5 microfarads;
4) maximum attenuation at a frequency of 1020 Hz is not more than 35 dB for a cable with a core diameter of 0.5 mm and not more than 45 dB for a cable with a core diameter of 0.32 mm.
2. Mini PBX should receive a call coming through subscriber lines (alternating current with a voltage of 95 +/- 5 V and a frequency of 25 Hz), and imitate the response signal "Opening the subscriber line loop".
Technical conditions for connection
Technical conditions for connection
No. ____ dated "____" __________ 20__
_______________________________________________________________
(joining operator)
connects the network (of the connected operator,
network owner) on the following technical conditions:
1. Connection level
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
determined by the types of services provided by the affiliated
operator (network owner), in accordance with the rules
connection and interaction of telecommunication networks.
2. Network numbering
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
body in the field of communications.
3. Connected network capacity
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
in accordance with the relevant order of the authorized
body in the field of communications.
Type of connected equipment
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
in accordance with the application of the affiliated operator (owner
network) to connect its network to the network of the connecting operator and
Republic of Kazakhstan.
4. Signaling via connecting lines
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
in accordance with:
application of the connected operator (network owner) for
connection of its network to the network of the connecting operator;
certificate of conformity for the equipment used,
registered in the register of the State Certification System
Republic of Kazakhstan;
a restrictive list of signaling protocols,
supported by digital stations in public telecommunications networks
use.
5. Organization of inter-office communication
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
in accordance with paragraph 1 and paragraph 4 of these Specifications.
6. Synchronization
Equipment of the attached operator (network owner)
synchronized with the telecommunications network of the connecting operator
one of the following options:
1) from own synchronization source with coefficient
the stability of the clock signal is not less than 10-11. (joining operator
(network owner) attaches the Certificate to the application for connection
matches to the synchronization source registered in the registry
State Certification System of the Republic of Kazakhstan and
technical parameters of the source);
2) from the network clock network synchronization (TCS) of the connecting
operator.
7. Billing.
1) accounting of telephone traffic is made on the basis of data
equipment for time-based accounting of connections of the connecting operator and
the connected operator (network owner);
2) at the exit of subscribers of the network of the connected operator
(network owner) to intrazonal, intercity and international
communication, via the network of the connecting operator, traffic accounting
is made at AMTS (MGTU/MCC) of the connecting operator (owner
3) time-based metering equipment has a certificate of
approval of the type of measuring instruments and a verification certificate.
8. Passage of telephone traffic.
Through the switching field of the joining operator
traffic is passed from (to) network subscribers of the connected
operator (network owner) to (from) public telecommunications network(s)
use.
9. Design work.
1) the connected operator (network owner) provides
project documentation for inclusion in the telecommunications network
joining operator. Before receiving technical specifications for
organization of connecting lines and preparation of project documentation
(PD) attached operator (network owner) with a branch
connection is in progress) settle the location
terminal equipment;
2) the connecting operator is provided with a copy of the Act on
approval of the PD, for compliance with these technical conditions
and with technical conditions for the organization of connecting lines. Act
signed by authorized representatives of the acceding
operator (in the service area of which connection is carried out)
and the connected operator (network owner).
10. Construction and installation works.
1) the connected operator (network owner) receives in the branch
connecting operator (in whose service area
accession is carried out) technical conditions for the organization
connecting lines;
2) all work related to the organization of connecting lines
(rental of channels, cable laying, installation of terminal
equipment) are agreed with the branch of the connecting operator
(in the service area of which the connection is made).
11. General questions.
1) plan of construction and installation works (cable pulling scheme,
installation of terminal equipment) are agreed with the branch
connecting operator (in whose service area
connection is in progress).
2) the connected operator (network owner) provides
providing electricity to the terminal equipment, coordinating all
work and requirements for power supply with the branch of the connecting
operator (in the service area of which
accession);
3) completion of work on the implementation of these Specifications
is drawn up by an act indicating the level of connection, network numbering,
signaling type, class of connection to the TCC core network, variant
synchronization and readiness for a test connection. The act is signed
authorized representatives of the branch of the connecting operator (in
the service area of which the connection is being made) and
connected operator (network owner). Copy of act
provided to the connecting operator;
4) before joining the network of the connected operator to the network
telecommunications of the connecting operator, test
tests. With positive test results
an Act is drawn up on the results of test tests and input in order to
commercial exploitation. A copy of the act is provided to the acceding
operator. The act indicates the connection point, network numbering,
number of network resources involved, synchronization option,
testing terms, test results and connection date from
purpose of commercial exploitation. The act is signed by authorized
representatives of the branch of the connecting operator, in the zone
service of which the connection is carried out, and the connected
operator (network owner);
5) when the specific load exceeds 0.7 Erl per connecting
line it is necessary to provide an increase in the channel capacity;
6) connection to the telecommunications network of the connecting
operator is made after the implementation of these technical
7) if these Specifications are not
completed within six months from the date of issue, the data
Specifications will be cancelled;
8) connecting the network of the connected operator (network owner)
connection to the telecommunications network of the connecting operator within the framework of
of this specification is used only for services,
provided for by the Accession and Interaction Agreement;
9) in the absence of free network resources (port
capacity) at the time of fulfillment of the technical conditions by the connected
operator, this connection will be possible after retrofitting
connecting operator;
10) any changes in the network synchronization scheme of the connected
operator (network owner) are agreed with the connecting
operator.
_______________________________________________________________
Name of the branch of the connecting operator
_______________________________________________________________
Branch manager of the connecting operator (full name and
The procedure for allocating serial numbers and the interaction of providers
telecommunications with local telecom operators
telecommunications networks allocating serial numbers
1. Serial numbers may be allocated by operators of local telecommunications networks to organize user access to services provided by the owners of special, information and reference and maintenance services and on the basis of connection agreements for telecommunications service operators.
2. Serial inclusion is understood as a set of subscriber lines having the same group station number, serial inclusion number. The serial inclusion number can be a number corresponding to a station number or an abbreviated number.
3. Serial numbers can be provided to the following services:
1) special;
2) information and reference;
3) service.
4. Requirements for the recipients of the serial number:
1) the total (outgoing and incoming) intensity of the load created in the hour of the greatest load (hereinafter - NLT) for each serial connection line should not exceed 0.15 Erl;
2) the use of serial numbers allocated to the services specified in subparagraphs 1), 2) and 3) of paragraph 3 of this Appendix is carried out according to a unilateral scheme with a ban on outgoing communications to these services;
3) the conditions for connecting the equipment are negotiated in each specific case;
4) the services to which an abbreviated or ordinary subscriber number of the local telecommunications network is allocated, access is provided from any subscriber telephone number or payphone of the connecting network;
5) in all cases of obtaining serial numbers, the number of subscriber lines involved should not exceed 15 (fifteen). If the specified number of lines is exceeded, the telecom operator (recipient) submits an application to the connecting operator to connect the access node of its network to public telecommunications networks at the local level using interstation connecting lines.
5. The numbering of allocated subscriber lines of serial search is determined by the respective operators of local telecommunications networks.
6. Communication of subscribers of a local telecommunications network with subscribers having numbers with serial inclusion is provided by dialing an abbreviated number or a regular subscriber number used on this network.
7. The procedure for allocating serial numbers in the interests of telecom operators:
1) the recipient of the serial number submits an arbitrary application form to the operator of the local telecommunications network for the allocation of a serial number, which indicates:
justification for the need to use the serial number;
types and characteristics of the equipment used, for which a serial number is required to connect.
In the absence of the specified information, the application is not subject to consideration;
2) the operator of the local telecommunications network considers the application and within a month concludes an agreement (if technically possible) with the applicant for the use of serial numbers;
in the absence of free linear capacity for the organization of subscriber lines, within a month, the applicant is issued technical conditions for the organization of subscriber lines. The contract is signed after the applicant fulfills the technical conditions.
Refusal to consider the application is possible in the absence of serial numbers of the connecting operator. The refusal is given in writing within 15 working days from the date of application.
8. Accounting for the load on the serial search lines:
1) when allocating serial numbers to telecom operators, the operator of the local telecommunications network:
ensures uniform load distribution on all lines of the serial number;
determines the CNN for each telecom operator to which a serial number is allocated;
draws up and approves schedules in accordance with which the load level is measured on each subscriber line of serial search;
2) measurement data are drawn up in an act that reflects the following information:
date and time of measurements;
measurement results;
measures that need to be taken to bring the load level back to normal.
The act is the basis for making decisions on the interaction of the local network operator with the recipient of the serial number;
3) if the average load per subscriber line of the serial number in the CNN, defined as the quotient of the total load divided by the number of lines, exceeds the normal level, the telecom operator increases the number of lines.
9. Interaction of the operator of the local telecommunications network with the recipient of serial numbers:
1) in case of exceeding the load norms specified in paragraph 3 of this Appendix, the operator of the local telecommunications network sends a written notification to the recipient of the serial number with a copy of the act on carrying out load measurements, and also issues, in agreement with him, technical conditions for increasing the number of lines or technical conditions for connection via interstation connecting lines;
2) the recipient takes measures to reduce the load or to increase the number of serial search subscriber lines;
3) if the recipient of serial numbers fails to take measures to establish a normal load level, access to the serial number from public telecommunications networks may be suspended until the deficiencies are eliminated.
A restrictive list of signaling protocols,
supported by digital stations in telecommunication networks
common use
1) Table 1. Limiting list of signaling protocols
for international network
2) Table 2. Limiting list of signaling protocols
for long distance network
3) Table 3. Limiting list of signaling protocols
for SLM and ZSL
4) Table 4. Limiting list of signaling protocols
for junction of public telecommunications networks with networks
mobile communications, networks of telecom operators (network owners)
5) Table 5. Limiting list of signaling protocols
for urban and rural telecommunications network
Table 1 - Limiting list of protocols
signaling for international network
Table 2 - Limiting list of protocols
signaling for long-distance network
Table 3 - Limiting list of protocols
signaling for SLM and ZSL
Network section | Alarm system | Note |
|
|
MTP: national specification ISUP: national specification SCCP: national specification TCAP: national specification | With broadcasting of subscriber number "A" for circuit-switched networks |
||
SIP-T/SIP-I: IETF RFC 3261, 3372, 3398; ITU-T Q.1912.5. RTP/RTCP: IETF RFC 1889, RFC1890 | With translation of subscriber number "A" for packet-switched networks |
Table 4 - Limiting list of protocols
signaling for the junction of general telecommunications networks
use of the Republic of Kazakhstan with mobile networks,
networks of telecom operators (network owners)
Network section | Alarm system | Note |
|
|
MTP: national specification ISUP: national specification | With broadcasting of subscriber number "A" for circuit-switched networks |
||
SIP-T/SIP-I: IETF RFC 3261, 3372, 3398; ITU-T Q.1912.5. RTP/RTCP: IETF RFC 1889, RFC1890 | With translation of subscriber number "A" for packet-switched networks |
||
|
MTP: national specification ISUP: national specification | With broadcasting of subscriber number "A" for circuit-switched networks |
||
SIP-T/SIP-I: IETF RFC 3261, 3372, 3398; ITU-T Q.1912.5. RTP/RTCP: IETF RFC 1889, RFC1890 | With translation of subscriber number "A" for packet-switched networks |
||
Intercity |
MTP: national specification ISUP: national specification | With broadcasting of subscriber number "A" for circuit-switched networks |
|
SIP-T/SIP-I: IETF RFC 3261, 3372, 3398; ITU-T Q.1912.5. RTP/RTCP: IETF RFC 1889, RFC1890 | With translation of subscriber number "A" for packet-switched networks |
||
|
MTP: national specification ISUP: national specification | With broadcasting of subscriber number "A" for circuit-switched networks |
||
SIP-T/SIP-I: IETF RFC 3261, 3372, 3398; ITU-T Q.1912.5. RTP/RTCP: IETF RFC 1889, RFC1890 | With translation of subscriber number "A" for packet-switched networks |
||
International |
MTP: ITU-T 1988 Q.700-Q.714 SCCP: ITU-T 1988 Q.711-Q.716 TCAP: ITU-T 1988 Q.771-Q.775 (for GSM standard) | With broadcasting of subscriber number "A" for circuit-switched networks |
It is allowed to use EDSS1 signaling with PRI interface when connecting corporate and departmental networks to the public network of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Table 5 - Limiting list of protocols
signaling for urban and rural telecommunications networks
|
signaling | National grid section |
||
Joint with SKP |
|||
Line signaling |
|||
IETF RFC 3261, 3372, 3398; ITU-T Q.1912.5. RTP/RTCP: IETF RFC 1889, RFC1890 |
|||
In accordance with OTT on PS and hubs | |||
In accordance with OTT on PS and concentrators. In accordance with the national specification | |||
5. Alarm by subscriber loop | |||
In accordance with OTT on PBX with ISDN functions. In accordance with national specification | |||
7. Alarm systems at the junction with networks of telematic services and data transmission | Protocols ITU-T X series |
||
In accordance with OTT on PS and hubs. According to national specification | |||
List of symbols and abbreviations
Abbreviations | Decryption |
International Telecommunication Union, Standardization Sector telecommunications |
|
European Telecommunication Standards Institute |
|
Specifications |
|
Automatic long-distance telephone exchange |
|
International switching center |
|
Intercity transit hub |
|
Automatic telephone exchange |
|
City telephone network |
|
Rural telephone network |
|
Telecom network management (Telecommunication Management Network) |
|
Automatic number detection |
|
Order-connection lines |
|
Common channel alarm system (according to ITU-T-N 7 classification) |
|
Connecting lines |
|
Connecting lines long-distance |
|
Internet Engineering Task Force - Internet Engineering Support Task Force |
|
ISDN User Part - a call control protocol that transfers call control information between network nodes that support OKC signaling - 7 |
|
Mobile Application Part - mobile application subsystem |
|
Message Transfer Part - message transfer subsystem (MTP3) OKC - 7, level 3. |
|
Mobile User Part - user subsystem mobile communications |
|
Real-Time Transport Protocol (real-time transport protocol). |
|
Request for Comments - Working proposal |
|
Signaling Connection Control Part - OKC - 7 Signaling Connection Control Subsystem |
|
Session Initiation Protocol - protocol for establishing a communication session |
|
SIP-ISUP version of the SIP protocol developed by ITU-T and intended for interworking |
|
a version of the SIP protocol developed by a committee of the Internet Engineering Problems Group for interworking |
|
Transaction Capabilities Application Part - Subsystem transactional signaling |
|
Telephone User Part - telephony user subsystem |
Indirect connection (connection) of Subscribers to electric networks
Reference documents and terms used:
- Federal Law No. 35-FZ “On the Electric Power Industry” (hereinafter referred to as the Law).
- Rules for the technological connection of power receivers of consumers of electric energy, facilities for the production of electric energy, as well as electric grid facilities owned by grid organizations and other persons, to electric networks, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 27, 2004 N 861 (hereinafter the Connection Rules) .
- Government Decree RF dated September 30, 2015 N 1044 "On Amendments to the Rules for the Technological Connection of Power Receiving Devices of Electricity Consumers, Electricity Generation Facilities, and Electricity Grid Facilities Owned by Grid Companies and Other Persons to Electric Grids" (hereinafter referred to as the Resolution).
- Subscriber is a legal or natural person, a consumer of electrical energy, whose power plants are connected to the networks of an energy supply organization.
- Subsubscriber- this is a legal or natural person that is the third link in the chain "Energy supply organization - Subscriber - Sub-subscriber", i.e. having an indirect connection to the electrical network of the Energy Supply Organization. Thus, the Sub-subscriber enters into an agreement with the Energy Supply Organization for the transmission of electricity to him indirectly through the electrical network owned by the Subscriber with the consent of the Subscriber.
Under proper indirect accession(by connecting) understand consumer connection to the electric networks of the network organization through power plants other consumers— producers of electric energy, electric grid facilities of persons who do not provide services for the transmission of electric energy, or ownerless electric grid facilities, which are directly connected.
In accordance with Art. 26, paragraph 4 of the Law, the owner of a power receiving device or an electric power facility (hereinafter referred to as the Subscriber), previously technologically connected in accordance with the Connection Rules in agreement with the grid organization have the right to connect (connect) to their networks other owner (Sub-subscriber) of the electric power facility ( another consumer) subject to compliance with previously issued specifications.
Ways of indirect connection to networks
The methods of indirect connection to the power grid are briefly described below, depending on the technical capabilities and the status of the “Subscriber”. An indirect connection can be made as follows:
1. To the objects of persons directly connected to the networks of the network operator who do not provide services for the transmission of electrical energy (power). In this case, we talk about the flow of electricity (power).
According to clause 6 of the Access Rules, the Subscriber is not entitled to prevent the flow of electrical energy through their facilities for such a consumer and demand payment for this. However, he has the right to obtain permission to transmit electricity for a fee. To do this, he needs to apply to the relevant authority to obtain tariffs for the transmission of electricity. However, in this case, the relationship between the end consumer (Sub-subscriber) and such Intermediary (Subscriber) will be governed by the paragraphs of the Access Rules applicable to network organizations (paragraph 2, clause 6 of the Access Rules).
2. To the objects of persons directly connected to the networks of the network operator and having excess capacity, which they can redistribute in favor of another consumer. In this case, one speaks of redistribution of power.
With whom to conclude an agreement with indirect accession
If the connection is made to Subscribers that do not provide electricity transmission services, or ownerless facilities, the end consumer enters into an agreement with the grid organization to whose networks the Subscriber's power plants are connected (clause 5 of the Access Rules). The connection procedure is regulated by Federal Law No. 34, Access Rules, Accession Rules.
If the connection is made to a Subscriber who transmits electricity by overflow or redistribution of maximum power, an agreement on technical connection is concluded between him and the end consumer according to the grounds established by Federal Law No. 34, Access Rules, Connection Rules.
Restrictions on connection with redistribution and power transfer
By the Decree of the Government of September 30, 2015, a change was made to the title of Chapter IV of the Accession Rules. The change is really significant, since the removal of the phrase “between legal entities and individual entrepreneurs” from the title removes formal restrictions on the possibility of indirect technological connection to power grids if an individual acts as an Intermediary (Subscriber). Thus, the following persons can connect other consumers to their facilities on the condition of redistribution of the available maximum power:
- individuals whose power receiving devices over 15 kW and which are connected to the grid organization no later than January 1, 2009;
- legal entities and individual entrepreneurs, the power of power receiving devices of which exceeds 150 kW and which are connected to the grid organization no later than January 1, 2009;.
Intermediary subscriber can not protrude:
- companies, sole proprietorships, individuals, power energy facilities which are below;
- Subscribers, having only temporary technological connection;
- Subscribers whose power receiving devices are connected to electric grid facilities that meet the criteria for classifying objects as part of a single national (all-Russian) electric grid;
- Subscribers who have not paid or have not paid in full the fee for technological connection to the power grid.
Not allowed connection of Sub-subscribers, the power supply of which must be carried out 1 and 2, to the networks of Subscribers, which are supplied with electricity 3 each.