It is most convenient to use the information model of the following type when describing the trajectory of the movement of an object of a physical body. Computer science test on the topic "Information modeling" (Grade 10)
Read also
GBOU SPO PT No. 13 named after P.A. Ovchinnikov, teacher of computer science Makeeva E.S.
Subject " information modeling»
1. An information model of a part of the earth's surface is:
A) description of the tree;
B) globe (Earth);
C) a drawing of a house;
D) a picture of the area;
D) subway map.
2. The model reflects:
A) all existing features of the object;
B) some of all existing;
C) essential features in accordance with the purpose of modeling;
D) some essential features of the object;
D) all essential features
3. When creating a toy ship for a child of three years, it is essential:
A) appearance
B) size;
B) accuracy;
D) material
4. In the information model of a residential building, presented in the form of a drawing ( general form), reflects it:
A) structure;
B) cost
D) reliability;
D) density
5. The information model of the cloud, presented in the form of a black and white picture, reflects its:
D) density;
D) size
6. The information model of a warship, presented in the form of a children's toy, reflects its:
A) structure;
B) density;
D) size
7. In the information model of a computer, presented in the form of a diagram, it reflects:
D) structure;
D) size
8. In the information model of the car, presented in the form of such a description: “a limousine rushed along the road like the wind” reflects it:
D) size;
D) speed
9. The model of a man in the form of a child's doll was created with the aim of:
A) study;
D) sales
10. Ptolemy built a model of the world with the aim of:
B) entertainment;
D) descriptions;
D) sales
11. Recognition of an attribute of an object as significant in the construction of its information model depends on:
A) the number of signs;
B) the purpose of modeling;
C) the size of the object;
D) the cost of the object
12. It is most convenient to use an information model of the following form when describing the trajectory of an object (physical body):
A) structural;
B) tabular;
B) text
D) mathematical;
D) graphic
13. When describing appearance object, it is most convenient to use the information model of the following form:
A) structural;
B) mathematical;
B) text
D) tabular;
D) graphic
14. When describing the relationship between the elements of the system, it is most convenient to use the information model of the following form:
A) text
B) mathematical;
B) structural;
D) tabular;
D) graphic
15. The type of information model depends on:
A) the number of signs;
B) the purpose of modeling;
C) the size of the object;
D) the value of the object;
D) the appearance of the object
16. The list of countries of the world is information model:
A) the historical development of human society;
B) the device of the planet "Earth";
C) the economic structure of the world;
D) the national composition of humanity;
D) the political structure of the world
17. How many models can be created when describing the moon:
B) a lot
D) more than 10
18) How many models can be created when studying the Earth:
A) more than 9;
B) set;
19. How many models can be created when describing the solar system:
A) a lot
D) more than 12
20. The concept of a model makes sense when there are (selectfull correct answer):
A) a modeling subject and a modeled object;
B) the purpose of modeling and the object being modeled;
C) the modeling subject, the purpose of modeling and the object being modeled;
D) the purpose of modeling and two different objects;
21. Mathematical models include:
A) a police report;
B) traffic rules;
C) the formula for calculating the roots of a quadratic equation;
D) a culinary recipe;
D) instructions for assembling furniture
22. Among the documents that are an information model of government management include:
A) the Constitution of the Russian Federation;
B) a geographical map of Russia;
C) Russian dictionary of political terms;
D) the scheme of the Kremlin;
D) a list of deputies of the State Duma.
23. To information models describingorganization of the educational process at school, include:
A) class magazine
B) lesson schedule;
C) a list of school students;
D) a list of school textbooks;
D) a list of visual teaching aids
24. Drawings, maps, drawings, diagrams, diagrams, graphs are models of the following type:
A) tabular information;
B) mathematical models;
B) natural
D) graphic information;
E) hierarchical information
25. Description of the global computer network The Internet in the form of a system of interrelated concepts should be considered as a model of the following type:
A) natural
B) tabular;
B) graphic;
D) mathematical;
D) network
26. File system personal computer can be most adequately described as a model of the following form:
A) tabular;
B) graphic;
B) hierarchical;
D) natural;
D) mathematical
27. In biology, the classification of representatives of the animal world is a model of the following type:
A) hierarchical;
B) tabular;
B) graphic;
D) mathematical;
D) natural
28. Train timetables can be seen as an example of a model like this:
A) natural;
B) tabular;
B) graphic;
D) computer;
D) mathematical
29. A geographical map should rather be considered as a model of the following type:
A) mathematical;
B) verbal;
B) tabular;
D) graphic;
D) natural
30. The very first graphical information models include:
A) rock paintings
B) maps of the Earth's surface;
B) books with illustrations;
D) construction drawings;
D) church icons
31. The following sequence of human actions:
1) building a model of initial data;
2) building a model of the result;
3) development of an algorithm;
4) development of the program;
5) program debugging;
6) execution of the program;
7) analysis and interpretation of the results is:
A) algorithm for solving the problem;
B) a list of commands to the performer;
C) a plan for analyzing existing tasks;
D) stages of solving the problem with the help of a computer;
E) plan for building a mathematical model
32. As an examplebehavior patterns can be called:
a) a list of school students;
B) plan of classrooms;
C) safety regulations in the computer class;
D) fire evacuation plan;
D) drawings of the school building.
33. In the process of building a model of an object, as a rule, it involves a description of:
A) all properties of the object under study;
B) the most significant from the point of view of the purpose of modeling the properties of the object;
C) properties regardless of the goals of modeling;
D) all possible space-time characteristics;
E) three essential features of the object.
34. A toy car is:
A) real model;
B) mathematical formula;
B) tabular model;
D) text model;
D) graphic model
35. The description of the original object CANNOT be considered an information model of an object:
A) using mathematical formulas;
B) not reflecting the features of the original object;
C) in the form of a two-dimensional table;
D) on natural language;
D) in formal language
36. A mathematical model of an object is a description of the original object in the form:
A) text
B) tables;
D) formulas;
D) drawing
37. The tabular information model is a description of the modeled object in the form:
A) graphs, drawings, drawings;
B) diagrams and diagrams;
C) the totality of values placed in the table;
D) systems of mathematical formulas;
E) sequences of sentences in natural language.
38. The statement is FALSE:
A) “There are no strict rules for building a model”;
B) “The model can never replace the phenomenon itself”;
C) "An object can serve as a model of another object if it reflects its essential features";
D) "The model contains as much information as the modeled object";
E) “When solving a specific problem, the model can be a useful tool”
39. A computer simulation model of a nuclear explosion does NOT allow:
A) ensure the safety of researchers;
B) conduct a full-scale study of processes;
C) reduce the cost of research;
D) obtain data on the impact of the explosion on human health;
40. With the help of simulation it is NOT possible to study:
A) the demographic processes taking place in social systems;
B) thermal processes occurring in technical systems;
C) inflationary processes in industrial and economic systems;
D) trajectories of planets and spaceships;
E) processes of psychological interaction of people
41. The basis of modeling is:
A) communication process;
B) information transfer;
C) formalization process;
D) storage of information;
D) human interaction
42. The essence of the main thesis of formalization is the fundamental possibility:
B) transfer of information from one object to another;
D) separation of the object and its designation
43. The idea of modeling follows from the main thesis of formalization, that is, it reflects the possibility of:
A) presentation of information on a material carrier;
B) separation of the object and its name;
C) human information processing;
D) storage of information in computer memory;
E) information transmission by means of a signal
Keys to the test on the topic "Information Modeling"
Job number
Possible answer
Job number
Possible answer
Job number
Possible answer
Job number
Possible answer
The computer science test Modeling and Formalization is intended for 9th grade students. The test contains 26 questions. There are answers at the end of the test.
1. Choose the correct statement:
a) One object can have only one model
b) Different objects cannot be described by the same model
V) Wiring diagram is a model of an electrical circuit
d) The model completely repeats the object under study
2. Choose the wrong statement:
a) Full-scale models - real objects, in a reduced or enlarged form, reproducing the appearance, structure or behavior of the modeled object
b) Information models describe the original object in one of the information encoding languages
c) Dynamic models reflect the processes of change and development of objects in time
d) Only the subject area to which they belong can be taken as the basis for classifying models.
3. What features of the object should be reflected in the student's information model, which allows obtaining the following information: the age of students who are fond of swimming; the number of girls involved in dancing; surnames and names of students over 14 years old?
a) name, surname, hobby
b) first name, last name, gender, singing, swimming, age
c) name, hobby, gender, age
d) name, surname, gender, hobby, age
4. Select the element of the student's information model that is relevant to the student's grade. test in informatics:
a) having a home computer
b) the number of correctly completed tasks
c) the time spent on the performance of the control work
G) GPA for previous computer science lessons
5. Replacing a real object with its formal description is:
a) analysis
b) modeling
c) formalization
d) algorithmization
6. Select iconic model:
a) drawing
b) scheme
c) table
d) formula
7. Select figurative model:
a) photograph
b) scheme
c) text
d) formula
8. Choose mixed model:
a) photograph
b) scheme
c) text
d) formula
9. Descriptions of objects, situations, events, processes in natural languages are:
a) verbal models
b) logical models
c) geometric models
d) algebraic models
10. Models implemented using programming systems, spreadsheets, specialized mathematical packages and software tools for modeling are called:
a) mathematical models
b) computer models
c) simulation models
d) economic models
11. The file system of a personal computer can most adequately be described as:
a) mathematical model
b) tabular model
c) natural model
d) hierarchical model
12. The graphical model of a hierarchical system is:
a) chain
b) network
c) family tree
d) tree
13. The timetable for electric trains can be considered as an example:
a) tabular model
b) graphic model
c) simulation model
d) natural model
14. What is the triplet of concepts in the relationship "object - full-scale model - information model"?
a) human - anatomical skeleton - mannequin
b) person - medical record - photograph
c) car - advertising booklet with technical specifications car - atlas of roads
d) a car - a toy car - technical description car
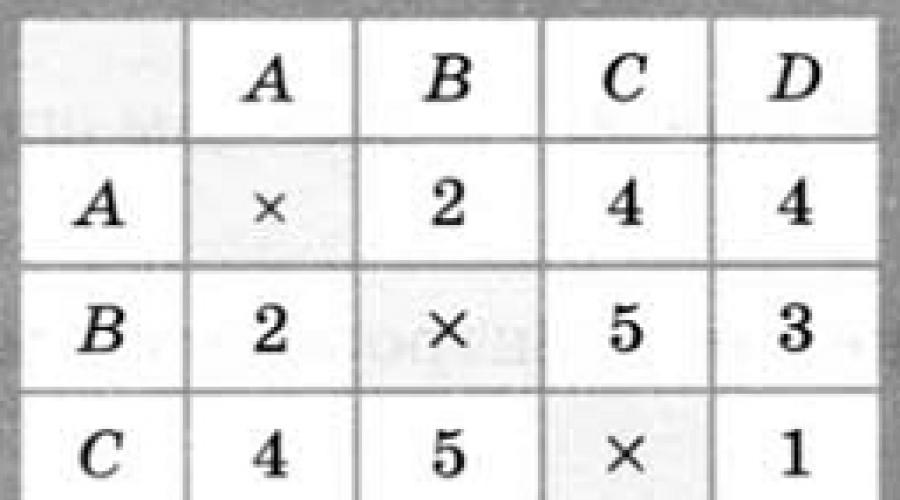
15. The diagram shows the roads between settlements A, B, C, D and the lengths of these roads are indicated.
Determine which two points are the farthest from each other. Specify the length of the shortest path between them.
a) 17
b) 15
c) 13
d) 9
16. Settlements A, B, C, D connected by roads. The travel time by car from city to city on the corresponding roads is indicated in the table:

Tourist leaving the point A wants to visit all the cities in the shortest time. Specify the appropriate route.
a) ABCD
b) ACBD
c) ADCB
d) ABDC
17.
Four students study at the school - Andreev, Ivanov, Petrov, Sidorov, who have different hobbies. One of them is fond of tennis, the other - ballroom dancing, the third - painting, the fourth - singing. Known about them:
- Ivanov and Sidorov were present at the concert of the choir when their friend sang;
- Petrov and the tennis player posed for the artist;
The tennis player is friends with Andreev and wants to meet Ivanov. What is Andreev interested in?
a) tennis
b) painting
c) dancing
d) singing
18. Two players play the following game. In front of them are three piles of stones, the first of which has 2 stones, the second - 3 stones, the third - 4 stones. Each player has an unlimited number of stones. The players take turns. The move consists in the fact that the player either doubles the number of stones in a heap, or adds two stones to each of the heaps. The player wins, after whose move either one of the piles becomes at least 15 stones, or the total number of stones in all three piles becomes at least 25. Who wins if both players play without mistakes?
a) the player making the first move
b) the player making the second move
c) each player has the same chance of winning
d) there is no winning strategy for this game
19. The database is:
a) a set of data collected on a single floppy disk
b) a table that allows you to store and process data and formulas
c) application program for processing user information
d) a set of data organized according to certain rules, intended for storage in external memory computer and continuous use
20. What database is based on a tabular representation of information about objects?
a) hierarchical
b) network
c) distributed
d) relational
21. A table row containing information about one specific object is:
a) field
b) record
c) report
d) form
22. A table column containing a certain characteristic of an object is:
a) field
b) record
c) report
d) key
23. Database management systems are used for:
a) creating databases, storing and searching for the necessary information in them
b) data sorting
c) organizing access to information in a computer network
d) creating databases
24. Which word is NOT the name of a database?
a) Microsoft Access
b) OpenOffice.org Base
c) OpenOffice.org Writer
d) FoxPro
25. Below is a fragment of the database in tabular form:
What position will the product “Scanner flatbed” be in if this table is sorted in ascending order of the QUANTITY column?
a) 5
b) 2
at 3
d) 6
26. Below in tabular form is a fragment of the database "Sale of stationery":
| Name | Price | Sales |
| Pencil | 5 | 60 |
| Ruler | 18 | 7 |
| Folder | 20 | 32 |
| Pen | 25 | 40 |
| Notebook | 15 | 500 |
How many records in this fragment satisfy the condition PRICE>20 OR SOLD
a) 1
b) 2
at 3
d) 4
Answers to the computer science test Modeling and formalization
1-c, 2-d, 3-d, 4-b, 5-c, 6-d, 7-a, 8-b, 9-a, 10-b, 11-d, 12-d, 13- a, 14-d, 15-c, 16-d, 17-b, 18-a, 19-d, 20-c, 21-b, 22-a, 23-a, 24-c, 25-c, 26-in
GBPOU of the city of Moscow "Sports and Pedagogical College" of the Department of Sports and Tourism of the City of Moscow; teacher of informatics and ICT, mathematics: Makeeva E.S.
Informatics test on the topic "Information Modeling"
1. An information model of a part of the earth's surface is:
A) description of the tree;
B) globe (Earth);
C) a drawing of a house;
D) a picture of the area;
D) subway map.
2. The model reflects:
A) all existing features of the object;
B) some of all existing;
C) essential features in accordance with the purpose of modeling;
D) some essential features of the object;
D) all essential features
3. When creating a toy ship for a child of three years, it is essential:
A) appearance
B) size;
B) accuracy;
D) material
4. The information model of a residential building, presented in the form of a drawing (general view), reflects it:
A) structure;
B) cost
D) reliability;
D) density
5. The information model of the cloud, presented in the form of a black and white picture, reflects its:
D) density;
D) size
6. The information model of a warship, presented in the form of a children's toy, reflects its:
A) structure;
B) density;
D) size
7. In the information model of a computer, presented in the form of a diagram, it reflects:
D) structure;
D) size
8. In the information model of the car, presented in the form of such a description: “a limousine rushed along the road like the wind” reflects it:
D) size;
D) speed
9. The model of a man in the form of a child's doll was created with the aim of:
A) study;
D) sales
10. Ptolemy built a model of the world with the aim of:
B) entertainment;
D) descriptions;
D) sales
11. Recognition of an attribute of an object as significant in the construction of its information model depends on:
A) the number of signs;
B) the purpose of modeling;
C) the size of the object;
D) the cost of the object
12. It is most convenient to use an information model of the following form when describing the trajectory of an object (physical body):
A) structural;
B) tabular;
B) text
D) mathematical;
D) graphic
13. When describing the appearance of an object, it is most convenient to use the information model of the following form:
A) structural;
B) mathematical;
B) text
D) tabular;
D) graphic
14. When describing the relationship between the elements of the system, it is most convenient to use the information model of the following form:
A) text
B) mathematical;
B) structural;
D) tabular;
D) graphic
15. The type of information model depends on:
A) the number of signs;
B) the purpose of modeling;
C) the size of the object;
D) the value of the object;
D) the appearance of the object
16. The list of countries of the world is an information model:
A) the historical development of human society;
B) the device of the planet "Earth";
C) the economic structure of the world;
D) the national composition of humanity;
D) the political structure of the world
17. How many models can be created when describing the moon:
B) a lot
D) more than 10
18) How many models can be created when studying the Earth:
A) more than 9;
B) set;
19. How many models can be created when describing the solar system:
A) a lot
D) more than 12
20. The concept of a model makes sense when there are (selectfullcorrect answer):
A) a modeling subject and a modeled object;
B) the purpose of modeling and the object being modeled;
C) the modeling subject, the purpose of modeling and the object being modeled;
D) the purpose of modeling and two different objects;
21. Mathematical models include:
A) a police report;
B) traffic rules;
C) the formula for calculating the roots of a quadratic equation;
D) a culinary recipe;
D) instructions for assembling furniture
22. Among the documents that are an information model of government management include:
A) the Constitution of the Russian Federation;
B) a geographical map of Russia;
C) Russian dictionary of political terms;
D) the scheme of the Kremlin;
D) a list of deputies of the State Duma.
23. To information models describingorganization of the educational processat school, include:
A) class magazine
B) lesson schedule;
C) a list of school students;
D) a list of school textbooks;
E) a list of visual teaching aids
24. Drawings, maps, drawings, diagrams, diagrams, graphs are models of the following type:
A) tabular information;
B) mathematical models;
B) natural
D) graphic information;
E) hierarchical information
25. The description of the global computer network Internet in the form of a system of interconnected concepts should be considered as a model of the following type:
A) natural
B) tabular;
B) graphic;
D) mathematical;
D) network
26. The file system of a personal computer can most adequately be described as a model of the following form:
A) tabular;
B) graphic;
B) hierarchical;
D) natural;
D) mathematical
27. In biology, the classification of representatives of the animal world is a model of the following type:
A) hierarchical;
B) tabular;
B) graphic;
D) mathematical;
D) natural
28. Train timetables can be seen as an example of a model like this:
A) natural;
B) tabular;
B) graphic;
D) computer;
D) mathematical
29. A geographical map should rather be considered as a model of the following type:
A) mathematical;
B) verbal;
B) tabular;
D) graphic;
D) natural
30. The very first graphical information models include:
A) rock paintings
B) maps of the Earth's surface;
B) books with illustrations;
D) construction drawings;
D) church icons
31. The following sequence of human actions:
1) building a model of initial data;
2) building a model of the result;
3) development of an algorithm;
4) development of the program;
5) program debugging;
6) execution of the program;
7) analysis and interpretation of the results is:
A) algorithm for solving the problem;
B) a list of commands to the performer;
C) a plan for analyzing existing tasks;
D) stages of solving the problem with the help of a computer;
E) plan for building a mathematical model
32. As an examplebehavior patternscan be called:
a) a list of school students;
B) plan of classrooms;
C) safety regulations in the computer class;
D) fire evacuation plan;
D) drawings of the school building.
33. In the process of building a model of an object, as a rule, it involves a description of:
A) all properties of the object under study;
B) the most significant from the point of view of the purpose of modeling the properties of the object;
C) properties regardless of the goals of modeling;
D) all possible space-time characteristics;
E) three essential features of the object.
34. A toy car is:
A) real model;
B) mathematical formula;
B) tabular model;
D) text model;
D) graphic model
35. The description of the original object CANNOT be considered an information model of an object:
A) using mathematical formulas;
B) not reflecting the features of the original object;
C) in the form of a two-dimensional table;
D) in natural language;
D) in formal language
36. The mathematical model of an object is a description of the original object in the form:
A) text
B) tables;
D) formulas;
D) drawing
37. The tabular information model is a description of the modeled object in the form:
A) graphs, drawings, drawings;
B) diagrams and diagrams;
C) the totality of values placed in the table;
D) systems of mathematical formulas;
E) sequences of sentences in natural language.
38. The statement is FALSE:
A) “There are no strict rules for building a model”;
B) “The model can never replace the phenomenon itself”;
C) "An object can serve as a model of another object if it reflects its essential features";
D) "The model contains as much information as the modeled object";
E) “When solving a specific problem, the model can be a useful tool”
39. A computer simulation model of a nuclear explosion does NOT allow:
A) ensure the safety of researchers;
B) conduct a full-scale study of processes;
C) reduce the cost of research;
D) obtain data on the impact of the explosion on human health;
40. With the help of simulation it is NOT possible to study:
A) demographic processes occurring in social systems;
B) thermal processes occurring in technical systems;
C) inflationary processes in industrial and economic systems;
D) trajectories of planets and spaceships;
E) processes of psychological interaction of people
41. The basis of modeling is:
A) communication process;
B) information transfer;
C) formalization process;
D) storage of information;
D) human interaction
42. The essence of the main thesis of formalization is the fundamental possibility:
B) transfer of information from one object to another;
D) separation of the object and its designation
43. The idea of modeling follows from the main thesis of formalization, that is, it reflects the possibility of:
A) presentation of information on a material carrier;
B) separation of the object and its name;
C) human information processing;
D) storage of information in computer memory;
E) information transmission by means of a signal
Keys to the test on the topic "Information Modeling"
| Job number | |||||||||||
| Possible answer | |||||||||||
| Job number | |||||||||||
| Possible answer | |||||||||||
| Job number | |||||||||||
| Possible answer | |||||||||||
| Job number | |||||||||||
| Possible answer |
1. Modeling is:
+ the process of replacing a real object (process, phenomenon) with a model that reflects it
essential features in terms of achieving a specific goal;
- the process of demonstrating clothing models in a fashion salon;
- the process of informal setting a specific problem;
- the process of replacing a real object (process, phenomenon) with another material or ideal object;
- the process of identifying the essential features of the object under consideration.
2. Model is:
- a fantastic image of reality;
- a material or abstract substitute for an object, reflecting its spatial and temporal characteristics;
+ a material or abstract substitute for an object, reflecting its essential
characteristics;
- description of the object under study by means of fine arts;
- information about non-essential properties of the object.
3. When studying the object of reality, you can create:
- one single model;
+ several different types of models, each of which reflects one or another essential
features of the object;
- one model reflecting the set of features of the object;
- exact copy object in all manifestations of its properties and behavior;
- the question does not make sense.
4. The process of building a model, as a rule, involves:
- description of all properties of the object under study;
+ selection of the most essential properties of the object from the point of view of the problem being solved;
- selection of object properties irrespective of the objectives of the problem being solved;
- description of all spatio-temporal characteristics of the object under study;
- selection of no more than three essential features of the object.
5. Full-scale modeling is:
+ modeling, in which the modeled object is recognized in the model, that is, full-scale
the model always has a visual similarity with the original object;
- creation of mathematical formulas describing the shape or behavior of the original object;
- modeling, in which any individual feature of the original object is recognized in the model;
- a set of data containing text information about the original object;
- creation of a table containing information about the original object.
6. An information model of an object cannot be considered:
- description of the original object using mathematical formulas;
+ another object that does not reflect the essential features and properties of the original object;
- a set of data in the form of a table containing information about the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the original object;
- description of the original object in natural or formal language;
- a set of formulas written in the language of mathematics that describe the behavior of the original object.
7. The mathematical model of an object is:
- a model created from any material that accurately reflects the external features of the original object;
- description in the form of a diagram of the internal structure of the object under study;
- a set of data containing information about the quantitative characteristics of the object and its behavior in the form of a table;
+ a set of formulas written in the language of mathematics that reflect certain properties
the original object or its behavior;
- the sequence of electrical signals.
8. Mathematical models include:
- police report;
- traffic rules;¬¬¬
+ formula for finding the roots of a quadratic equation;
- recipe;
- instructions for assembling furniture.
9. Among the documents that are an information model of government management include:
+ the Constitution of the Russian Federation;
- a geographical map of Russia;
- Russian dictionary of political terms;
- scheme of the Kremlin;
- list of deputies of the State Duma.
10. Information models that describe the organization of the educational process at school include:
- cool magazine;
+ lesson schedule;
- a list of school students;
- list of school textbooks;
- a list of visual teaching aids.
11. The tabular information model is:
- a set of graphs, drawings, drawings, charts, diagrams;
- description of the hierarchical structure of the structure of the modeled object;
+ description of objects (or their properties) in the form of a set of values placed in the table;
- a system of mathematical formulas;
- a sequence of sentences in natural language.
12. Mark the FALSE continuation to the statement: “To information process search for information can be attributed to ... ":
- direct observation;
+ reading reference literature;
- request to information systems;
- building a graphical model of the phenomenon;
- listening to radio broadcasts.
13. Mark the TRUE statement:
- direct observation is the storage of information;
+ reading reference literature is a search for information;
- a request to information systems is the protection of information;
- building a graphical model of the phenomenon is the transfer of information;
Listening to a radio broadcast is a process of information processing.
14. Drawings, maps, drawings, diagrams, diagrams, graphs are:
- tabular information models;
- mathematical models;
- natural models;
+ graphic information models;
- hierarchical information models.
15. Description of the global computer network Internet in the form of a system of interconnected should be considered as:
- natural model;
- tabular model;
- graphic model;
- mathematical model;
+ network model.
16. The file system of a personal computer can be most adequately described as:
- tabular model;
- graphic model;
+ hierarchical model;
- natural model;
- mathematical model.
17. In biology, the classification of representatives of the animal world is:
+ hierarchical model;
- tabular model;
- graphic model;
- mathematical model;
- natural model.
18. The timetable for the movement of trains can be considered as:
- natural model;
+ tabular model;
- graphic model;
- computer model;
- mathematical model.
19. A geographical map should rather be seen as:
- mathematical information model;
- verbal information model;
- tabular information model.
+ graphic information model;
- natural model.
20. Among the very first graphical information models should be attributed
+ rock paintings;
- maps of the Earth's surface;
- books with illustrations;
- construction drawings and plans;
- icons.
21. Specify the FALSE statement:
- “It is impossible to formulate strict rules for constructing any model”;
- “No model can replace the phenomenon itself, but when solving a specific problem, it can be a very useful tool”;
- “It does not matter at all which objects are chosen as modeling objects - the main thing is that with their help it would be possible to reflect the most essential features, signs of the object under study”;
+ “The model contains as much information as the modeled object”;
- "All education is the study of certain models, as well as methods of using them."
22. Building a model of initial data; building a model of the result, developing an algorithm, developing and programs, debugging and executing a program, analyzing and interpreting results - these are:
- development of an algorithm for solving problems;
- list of commands to the performer;
- analysis of existing tasks;
+ stages of solving a problem using a computer;
- algorithm of the mathematical problem.
23. Examples of behavior patterns include:
- a list of school students;
- plan of classrooms;
+ safety rules in the computer class;
- fire evacuation plan;
- drawings of the school building.
24. Computer simulation of a nuclear explosion does NOT allow:
- experimentally check the effect of high temperature and radiation on natural objects;
- to conduct a full-scale study of the processes occurring in nature during the explosion and after the explosion;
- reduce the cost of research and ensure the safety of people;
+ obtain reliable data on the impact of the explosion on people's health;
- obtain reliable information about the impact of a nuclear explosion on plants and animals in the irradiation zone.
25. With the help of computer simulation it is NOT possible to study:
- demographic processes occurring in social systems;
- thermal processes occurring in technical systems;
- inflationary processes in industrial and economic systems;
+ processes of psychological interaction of students in the classroom;
- trajectories of planets and spaceships in airless space.
26. The term "simulation" in the current context means
+ the process of creating a formalized description of the system in the form of a set of models
- use of previously created models
- receiving reports on some question freedom
- study of the properties of some model
- application in practice of the obtained models
27. The software model is generally understood as
+ formalized description of the software system at a certain level of abstraction
- the software itself and everything connected with it
- terms of use of this software
- a set of properties of this software
- an introductory analogue of the considered software
28. Each model defines
+ specific aspect of the system
- general purpose of the system and software
- general principles systems and software
- general tasks of the system and software
- general properties of the system and software
29. Graphic models are
+ tools for visualization, description, design and documentation of architecture
systems
- an illustration of the basic principles of the software
- tools for creating new systems and software
- new software testing tools
- tools for debugging new software
30. Architecture means
+ a set of basic rules that determine the organization of the system
- type of software being developed
- a special type of simulated systems
- rules for using systems and software
- the conditions under which the systems and software are supposed to be used
31. The abbreviation UML stands for
+ Unified Modeling Language
- Unfinished Modeling Language
- Unmodified Mini Language
- Useful Morning Language
- Unsuccessful Modeling Language
32. Visual modeling is called
+ the process of graphical representation of the model using some standard set
graphic elements
- building a model based on some visual representation
- restore the system according to its visual model
- creation of any model
- use of any model
33. Visual modeling can be applied
+ in the development and maintenance of software
- only for software development
- only with software support
- it does not apply to software
- there is no correct answer
34. Visual modeling languages are
+ formalized sets of graphic symbols and rules for constructing visual symbols from them
models
- Java, C#, C++, C
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- there is no correct answer
35. Visual modeling languages are
+ UML, BPMN, SDL, MSC, SADT/IDEF0, IDEF1x, WebML
- Java, C#, C++, C
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- any programming languages
- assembly language
36. Currently, when developing software, the SADT language
+ not used, but actively used in business process modeling
- is actively used and is a direct competitor of UML
- not used at all
- as before, does not apply to visual modeling languages
- not used, as it is under development
37. Methods for applying UML are
+ heavy and light weight
- heavyweight only
- only lightweight
- weightless
- there is no correct answer
38. RUP/USDP Industrial Visual Modeling is a heavyweight method because
+ it contains many prescriptions, a complex sequence of steps, defines
different roles of participants, covers all stages of software development. Its implementation in the process
the company requires significant costs and a significant restructuring of the principles of its work
- involves writing large specialized code
- contains a large number of visual elements
- uses UML
- uses SADT
39. UML lightweight methods are called so because
+ do not have rigid prescriptions and allow for variability in use
- can only describe small projects
- can't describe big projects
- ineffective
- final models have a low weight
40. CASE packages are called
+ versatile tools that are boxed and multifunctional
packages intended for the analysis and design of software "in general", that is, without any
specialized orientation; as a rule, today such packages are built on the basis of the UML language
- any package of models created using UML
- any package of visual models
- kit additional libraries to perform specific narrowly focused tasks
- custom project templates on UML
41. In visual modeling software the following levels of abstraction are used
+ All answers are correct
- subject area
- model
- metamodel
- metametamodel
42. When visually modeling software, the following models are usually built
+ analysis models and design models
- analysis models only
- only design models
- only systematization models
- there is no correct answer
43. Modeling point of view (viewpoint) is
+ a certain view of the system, which is carried out to perform some
specific task any of the project participants
- definition of tasks assigned to the model
- definition of tasks assigned to the programmer
- architecture
- software model
44. The most important characteristics of the modeling point of view are
+ purpose (why the model is created) and the target audience(i.e. who is it for)
- model and software
- metamodel and model
- metametamodel and metamodel
- model properties and its architecture
45. Visual specifications are usually divided into
+ model graph and diagrams
- many separate elements
- graphs of varying complexity
- diagrams of varying complexity
- visual elements
46. Model graph is
+ a set of visual model entities, their attributes and relationships
- same as diagram
- external representation of the model
- one of the most important characteristics models
- diagram subtype
47. Chart is
+ external representation of the model: geometric dimensions of entities, their coordinates, colors,
lettering fonts, line thickness, etc.
- same as model graph
- a set of visual model entities
- model specification method
- a subspecies of the model graph
49. Class diagram (Class diagram) is
+ static structural diagram describing the structure of the system, demonstrating
system classes, their attributes, methods and dependencies between classes
- structural diagram, shows the partition software system on structural components and connections (dependencies) between components
50. Component diagram (Component diagram) is
+ static structural diagram, shows the division of the software system into
structural components and links (dependencies) between components
- a static structural diagram that describes the structure of the system, showing the classes of the system, their attributes, methods and dependencies between classes
- a diagram used to model running nodes and artifacts deployed on them
- a diagram showing a complete or partial snapshot of the simulated system at a given point in time
- a structural diagram, the main content of which are packages and the relationships between them
51. What is the application for fixing software sketches of notations with developed semantics, graphics and textual content.
- Abstracting
- Creating an editor
- Architecture
- Analysis of objects
52. What is the software visualization metaphor?
+ ways to match abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some
visually perceived objects.
- boxed and multifunctional packages intended for the analysis and design of software "in general", that is, without any specialized orientation.
- set of non-empty set of vertices and sets of pairs of vertices (connections between vertices);
53. What is a visual modeling language?
+ these are formalized sets of graphic symbols and rules for constructing visual symbols from them
models.
- Simulink
- a discipline that studies the formalization of the meanings of programming language constructs by constructing their formal mathematical models.
54. What are visual modeling tools?
+ methods, languages and related software tools
- description of the operational semantics of structures in terms of low-level programming languages (assembly language, machine code).
- a discipline that studies the formalization of the meanings of programming language constructs by constructing their formal mathematical models.
are formalized sets of graphic symbols and rules for constructing visual models from them.
55. Tools that implement languages and methods of visual modeling are of two types:
+ universal and subject-oriented.
- numbered and enumerated
- physical and linear.
- standard and user defined
- internal and external
56. Visual modeling serves what?
+ increasing the understanding of project decisions by people - different categories involved in
project of specialists (electronic engineers, managers, customer, etc.).
- to allow you to use ready-made libraries of blocks for modeling electric power, mechanical and hydraulic systems, as well as apply a developed model-oriented approach in the development of control systems, tools digital communication and real time devices.
- for analysis and design, but also for documentation, testing, requirements development, etc.
57. Visual modeling can also be used in different types activities of the software development process:
+ mainly in analysis and design, but also in documentation,
testing, requirements development, etc.
- to create methods and design tools information systems with integrated automated tools that can be used in the software development process.
- to compare abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some visually perceived objects.
- increasing the comprehensibility of the project decisions by people - different categories of specialists involved in the project (electronic engineers, managers, customer, etc.).
58. Packages built on the basis of the UML language, which are boxed and multifunctional packages designed for the analysis and design of software "in general".
+CASE-
packages
- Simulink
- WebRatio
- Perl
- PLSQL Developer
59. One of the most famous CASE packages is:
+IBM Rational Rose
- WebRatio
-Microsoft Visio,
- Microsoft DSL Tools
- Eclipse/GMF
60. Under CASE understand:
+ a set of methods and tools for designing information systems with
integrated automated tools that can be used in
software development process.
- a graphical description language for object modeling in the field of software development, business process modeling, system design and display of organizational structures.
- a discipline that studies the formalization of the meanings of programming language constructs by constructing their formal mathematical models.
- ways to compare abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some visually perceived objects.
- is an application for fixing software sketches of notations with developed semantics, graphics and textual content.
61. What packages exist for developing domain-specific visual modeling support?
+ Microsoft Visio, Microsoft DSL Tools
And
Eclipse/GMF
- IBM Rational Rose, Microsoft Visio/UML Add-on.
- Borland Together, Telelogic Tau
- COBOL, Fortran, PL/1, Algol60, C, Pascal
- Microsoft Visual, Team Foundation Server
62. How to bridge the semantic gap between models and programs?
+ creating code generation solutions for certain types of software.
- creating many versions of the same algorithm for processing different types or operators instead of passing higher order functions to a generalized algorithm.
- Setting individual values in imperative code instead of using data binding
- Manual caching of deterministic function results on platforms that do this automatically
63. Semantic gap between models and programs
+ gap preventing automatic generation of program code from visual
models in general, preventing visual modeling from being the next step in
development of programming tools, following high-level algorithmic languages.
- a graphical description language for object modeling in the field of software development, business process modeling, system design and display of organizational structures.
- a set of methods and tools for designing information systems with integrated automated tools that can be used in the software development process.
- ways to compare abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some visually perceived objects.
64. Graphical description language for object modeling in the field of software development, business process modeling, system design and display of organizational structures.
+UML
- Simulink
- CASE
-Microsoft Vision
- WebRatio
65. This is a graphical simulation environment that allows using block diagrams in the form of directed graphs to build dynamic models, including discrete, continuous and hybrid, nonlinear and discontinuous systems.
+ Simulink
- UML
- CASE
- STD
- WebRatio
66. Simulink Interactive Environment:
+ allows you to use ready-made libraries of blocks for modeling electric power,
mechanical and hydraulic systems, as well as to apply a developed model-based approach in the development of control systems, digital communications and
real time devices.
- reach agreement on graphic notation for presentation general concepts(such as class, component, generalization, aggregation, and behavior) and focus more on design and architecture.
- creates a description for object modeling in the field of software development, business process modeling, systems engineering and mapping of organizational structures.
- makes it possible to compare abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some visually perceived objects.
is a graphical simulation environment that allows using block diagrams in the form of directed graphs to build dynamic models, including discrete, continuous and hybrid, nonlinear and discontinuous systems.
67. UML also allows software developers
+ reach agreement on graphic notation to represent common concepts (such
as a class, component, generalization (generalization), aggregation (aggregation) and behavior) and more
focus on design and architecture.
- allows you to use ready-made libraries of blocks for modeling electric power, mechanical and hydraulic systems, as well as apply a developed model-based approach to the development of control systems, digital communications and real-time devices.
- to compare abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some visually perceived objects.
- increase the understanding of the project decisions by people - different categories of specialists involved in the project (electronic engineers, managers, customer, etc.).
68. Which also allows software developers to agree on graphical notation to represent common concepts (such as class, component, generalization, aggregation, and behavior) and to focus more on design and architecture.
+ UML
- Simulink
- Perl
- Borland Together
- CASE
69. Simulink is it?
+ this is a graphical simulation environment that allows using block diagrams in the form of directed graphs to build dynamic models, including discrete ones,
continuous and hybrid, nonlinear and discontinuous systems.
- descriptions for object modeling in the field of software development, business process modeling, systems engineering and mapping of organizational structures.
- ways to compare abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some visually perceived objects.
- a discipline that studies the formalization of the meanings of programming language constructs by constructing their formal mathematical models.
70. UML is it?
+ graphical description language for object modeling in development
software, business process modeling, system design and
display of organizational structures.
- a package intended for the analysis and design of software "in general", that is, without any specialized orientation.
- a discipline that studies the formalization of the meanings of programming language constructs by constructing their formal mathematical models.
- a way to compare abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some visually perceived objects.
- a gap that prevents automatic generation of program code from visual models in the general case, preventing visual modeling from becoming the next step in the development of programming tools, following high-level algorithmic languages.
71. A gap preventing automatic generation of program code from visual models in the general case, preventing visual modeling from becoming the next step in the development of programming tools, after high-level algorithmic languages.
+ semantic gap between models and programs
- software visualization metaphor
- visual modeling
- CASE tools
- VIPR (VIsual Imperative Programming)
72. CASE packages
+ Packages built on the basis of the UML language, which are boxed and
multifunctional packages designed for software analysis and design
"at all".
- A gap that prevents automatic generation of program code from visual models in general, preventing visual modeling from becoming the next step in the development of programming tools, after high-level algorithmic languages.
is a graphical simulation environment that allows using block diagrams in the form of directed graphs to build dynamic models, including discrete, continuous and hybrid, nonlinear and discontinuous systems.
- A graphical description language for object modeling in software development, business process modeling, system design, and mapping organizational structures.
- Ways to compare abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some visually perceived objects
73. Graphical description language for object modeling in the field of software development, business process modeling, system design and display of organizational structures.
+ UML
- Simulink
Case
- software visualization metaphor
- visual modeling
74. Ways to compare abstract and invisible to the human eye software elements to some visually perceived objects:
+ software visualization metaphor
- visual modeling
- visual modeling language
- Abstracting
75. What is visual modeling
+ is an application for fixing software sketches of notations with developed semantics,
graphics and text content.
- methods, languages and related software tools
- Packages built on the basis of the UML language, which are boxed and multifunctional packages designed for the analysis and design of software "in general".
- a graphical description language for object modeling in the field of software development, business process modeling, system design and display of organizational structures.
is a graphical simulation environment that allows using block diagrams in the form of directed graphs to build dynamic models, including discrete, continuous and hybrid, nonlinear and discontinuous systems.
76. What is MATLAB?
+ mathematical modeling program
- graphics editor
- text editor
- operating system
- external library
77. What languages is MATLAB written in?
+ C, Java
- C++
Lisp, Python
- JavaScript
- ActionScript
78. What is a model?
+ reduced reproduction or diagram of something.
- graphics editor
- programming language
- enlarged image
- thumbnail
79. What is UML?
+ graphic language visualization, specification, design and documentation
software.
- plastic bag application programs for solving problems of technical calculations and the programming language of the same name
- spreadsheet program
- DBMS
- interpreter/compiler
80. What is notation?
+ a set of graphic objects that are used in models
- a set of objects that are not used in models
- a diagram that defines the metamodel
- entity interface
81. Not part of the structural diagram
+ activity diagrams
- class diagrams
- component diagrams
- object diagrams
- diagrams of composite structures
82. What is a metamodel?
+ diagram defining notation
- class diagram
- object diagram
- graphic visualization language
- association modeling relationship
83. Within the framework of the UML, what is the function of relationships?
+ bind different entities
- interpreter/compiler
- association modeling relationship
84. Within the framework of the UML, what is the function of diagrams?
+ group collections of entities of interest
- abstractions that are the main elements of the model
- interpreter/compiler
- association modeling relationship
85. In the framework of the work of UML, what function do entities perform?
+ abstractions, which are the main elements of the model
- group collections of entities of interest
- connect different entities
- interpreter/compiler
- association modeling relationship
86. Relationship between classifiers, in which one describes the interface of an entity, and the other guarantees its implementation.
+ Implementation
- Abstraction
- Interface
- Association
- Chart
87. Shows that an object of one class is related to an object of another class and reflects some relationship between them.
+ Association
- Implementation
- Abstraction
- Interface
- Chart
88. Association modeling the relationship "part / whole" between classes, which at the same time can be equal.
+ Aggregation
- Implementation
- Abstraction
- Interface
- Chart
89. The set of basic rules that determine the organization of the system is called
+ architecture
- notation
- diagram
- communication
- attitude
90. Leading visual modeling tool - is a simple and fully integrated solution for software development, including Internet solutions.
+ Rational Rose
- Microsoft Excel
-IBPWin
- Arduino
- Pinnacle Studio
91. The modeling process includes the following elements:
+ subject, object, model
- subject, model
- object, model
- subject, original, model
- object, explanation, phenomenon
92. Replacing a real object or process with its formal description.
+ formalization
- notation
- association
- abstraction
- implementation
93. Material models are
+ natural objects that obey natural laws in their functioning.
- ideal formations, fixed in the appropriate sign form and functioning according to the laws of the logic of thinking
- financial assets
- numerical methods
94. Ideal models are
+ ideal formations fixed in the corresponding symbolic form and
functioning according to the laws of the logic of thinking
- natural objects that obey natural laws in their functioning
- objects indistinguishable from the original
- financial assets
- numerical methods
95. A way to describe the behavior of the system based on the indication of the sequence of transmitted messages.
+ Sequence diagram
- Communication diagram
- Relation chart
- Activity diagram
- Machine Diagram
96. Method detailed description behavior in the UML based on the explicit allocation of states and the description of transitions between states.
+ Automaton diagram
- Communication diagram
- Relation chart
- Activity diagram
97. The main way to describe the structure of the system.
+ Class Diagram
- Sequence diagram
- Communication diagram
- Relation chart
- Activity diagram
98. The most general representation of the functional purpose of the system.
+ Usage Chart
- Sequence diagram
- Communication diagram
- Relation chart
- Activity diagram
99. MATLAB Developer
+ The MathWorks
- Microsoft Windows
- solaris
- Apple
- Sony
100. Who developed MATLAB as a programming language?
+ Cleve Moler
- Steve Yetkins
- Robert Kowalski
- Ivan Grigoriev
- Max Smith
 Tasks of the first level of complexity: 1. An information model of a part of the earth's surface is: a) a description of a tree; b) globe (Earth); c) a drawing of a house; d) map of the area; e) metro map. 2
Tasks of the first level of complexity: 1. An information model of a part of the earth's surface is: a) a description of a tree; b) globe (Earth); c) a drawing of a house; d) map of the area; e) metro map. 2
 2. When creating a toy ship for a child of three years, the following are essential: a) appearance; b) size; c) accuracy; d) color; e) material. 3
2. When creating a toy ship for a child of three years, the following are essential: a) appearance; b) size; c) accuracy; d) color; e) material. 3
 3. The type of information model depends on: a) the number of features; b) the purpose of modeling; c) the size of the object; d) the value of the object; e) the appearance of the object. 4
3. The type of information model depends on: a) the number of features; b) the purpose of modeling; c) the size of the object; d) the value of the object; e) the appearance of the object. 4
 4. How many models can be created when studying the Earth: a) more than 9; b) set; at 5; d) 2; e) 1? 5
4. How many models can be created when studying the Earth: a) more than 9; b) set; at 5; d) 2; e) 1? 5
 5. A geographical map should most likely be considered as a model of the following type: a) mathematical; b) verbal; c) tabular. d) graphic; e) natural. 6
5. A geographical map should most likely be considered as a model of the following type: a) mathematical; b) verbal; c) tabular. d) graphic; e) natural. 6
 6. Among the very first graphic information models should be attributed: a) rock paintings; b) maps of the Earth's surface; c) books with illustrations; d) construction drawings and plans; e) church icons. 7
6. Among the very first graphic information models should be attributed: a) rock paintings; b) maps of the Earth's surface; c) books with illustrations; d) construction drawings and plans; e) church icons. 7
 7. A mathematical model of an object is a description of the original object in the form of: a) text; b) schemes; c) tables; d) formulas; e) drawing. 8
7. A mathematical model of an object is a description of the original object in the form of: a) text; b) schemes; c) tables; d) formulas; e) drawing. 8
 Tasks of the second level of complexity: 1. In the information model of the car, presented in the form of such a description: “a limousine rushed along the road like the wind” reflects its: a) weight; b) color; c) form; d) size; e) speed. 9
Tasks of the second level of complexity: 1. In the information model of the car, presented in the form of such a description: “a limousine rushed along the road like the wind” reflects its: a) weight; b) color; c) form; d) size; e) speed. 9
 2. Recognition of an object feature as essential when building its information model depends on: a) the number of features; b) the purpose of modeling; c) the size of the object; d) the value of the object; e) the structure of the object. 10
2. Recognition of an object feature as essential when building its information model depends on: a) the number of features; b) the purpose of modeling; c) the size of the object; d) the value of the object; e) the structure of the object. 10
 3. It is most convenient to use the information model of the following type when describing the trajectory of an object (physical body): a) structural; b) tabular; c) text; d) mathematical; e) graphic. eleven
3. It is most convenient to use the information model of the following type when describing the trajectory of an object (physical body): a) structural; b) tabular; c) text; d) mathematical; e) graphic. eleven
 4. When describing the appearance of an object, it is most convenient to use an information model of the following type: a) structural; b) mathematical; c) text; d) tabular; e) graphic. 12
4. When describing the appearance of an object, it is most convenient to use an information model of the following type: a) structural; b) mathematical; c) text; d) tabular; e) graphic. 12
 5. Among the documents that are an information model of government, include: a) the Constitution of the Russian Federation; b) a geographical map of Russia; c) Russian dictionary of political terms; d) the scheme of the Kremlin; e) the list of deputies of the State Duma. 13
5. Among the documents that are an information model of government, include: a) the Constitution of the Russian Federation; b) a geographical map of Russia; c) Russian dictionary of political terms; d) the scheme of the Kremlin; e) the list of deputies of the State Duma. 13
 6. Information models that describe the organization of the educational process at school include: a) class magazine; b) the schedule of lessons; c) a list of school students; d) a list of school textbooks; e) a list of visual teaching aids. 14
6. Information models that describe the organization of the educational process at school include: a) class magazine; b) the schedule of lessons; c) a list of school students; d) a list of school textbooks; e) a list of visual teaching aids. 14
 7. The train schedule can be considered as an example of a model of the following type: a) natural; b) tabular; c) graphic; d) computer; e) mathematical. 15
7. The train schedule can be considered as an example of a model of the following type: a) natural; b) tabular; c) graphic; d) computer; e) mathematical. 15
 8. The statement is FALSE: a) "There are no strict rules for building a model." b) "The model can never replace the phenomenon itself"; c) "An object can serve as a model of another object if it reflects its essential features"; d) "The model contains as much information as the modeled object"; e) "When solving a specific problem, the model can be a useful tool." 16
8. The statement is FALSE: a) "There are no strict rules for building a model." b) "The model can never replace the phenomenon itself"; c) "An object can serve as a model of another object if it reflects its essential features"; d) "The model contains as much information as the modeled object"; e) "When solving a specific problem, the model can be a useful tool." 16
 Tasks of the third level of complexity: 1. The concept of a model makes sense if there are (select the full correct answer): a) a modeling subject and a modeled object; b) the purpose of modeling and the object being modeled; c) the modeling subject, the purpose of modeling and the object being modeled; d) the purpose of modeling and two different objects; e) the desire to save information about the object. 17
Tasks of the third level of complexity: 1. The concept of a model makes sense if there are (select the full correct answer): a) a modeling subject and a modeled object; b) the purpose of modeling and the object being modeled; c) the modeling subject, the purpose of modeling and the object being modeled; d) the purpose of modeling and two different objects; e) the desire to save information about the object. 17
 2. The following sequence of human actions: 1) building a model of initial data, 2) building a model of the result, 3) developing an algorithm, 4) developing a program, 5) debugging a program, 6) executing a program, 7) analyzing and interpreting the results are: a ) b) c) d) e) algorithm for solving the problem; list of commands to the performer; plan for the analysis of existing tasks; stages of solving a problem using a computer; plan for constructing a mathematical model. 18
2. The following sequence of human actions: 1) building a model of initial data, 2) building a model of the result, 3) developing an algorithm, 4) developing a program, 5) debugging a program, 6) executing a program, 7) analyzing and interpreting the results are: a ) b) c) d) e) algorithm for solving the problem; list of commands to the performer; plan for the analysis of existing tasks; stages of solving a problem using a computer; plan for constructing a mathematical model. 18
 3. As an example of a behavior model, one can name: a) a list of school students; b) plan of classrooms; c) safety regulations in the computer class; d) fire evacuation plan; e) drawings of the school building. 19
3. As an example of a behavior model, one can name: a) a list of school students; b) plan of classrooms; c) safety regulations in the computer class; d) fire evacuation plan; e) drawings of the school building. 19
 4. The process of building a model of an object, as a rule, involves a description of: a) all properties of the object under study; b) the most significant from the point of view of the purpose of modeling the properties of the object; c) properties regardless of the purpose of modeling; d) all possible spatial and temporal characteristics; e) three essential features of the object. 20
4. The process of building a model of an object, as a rule, involves a description of: a) all properties of the object under study; b) the most significant from the point of view of the purpose of modeling the properties of the object; c) properties regardless of the purpose of modeling; d) all possible spatial and temporal characteristics; e) three essential features of the object. 20
 5. An information model of an object CANNOT be considered a description of the original object: a) using mathematical formulas; b) not reflecting the features of the original object; c) in the form of a two-dimensional table; d) in natural language; e) in formal language. 21
5. An information model of an object CANNOT be considered a description of the original object: a) using mathematical formulas; b) not reflecting the features of the original object; c) in the form of a two-dimensional table; d) in natural language; e) in formal language. 21
 6. A computer simulation model of a nuclear explosion DOES NOT: a) ensure the safety of researchers; b) conduct a full-scale study of processes; c) reduce the cost of research; d) obtain data on the impact of the explosion on human health; d) save the environment environment. 22
6. A computer simulation model of a nuclear explosion DOES NOT: a) ensure the safety of researchers; b) conduct a full-scale study of processes; c) reduce the cost of research; d) obtain data on the impact of the explosion on human health; d) save the environment environment. 22
 7. With the help of simulation modeling, it is IMPOSSIBLE to study: a) demographic processes occurring in social systems; b) thermal processes occurring in technical systems; c) inflationary processes in industrial and economic systems; d) trajectories of planets and spaceships; e) the processes of psychological interaction between people. 23
7. With the help of simulation modeling, it is IMPOSSIBLE to study: a) demographic processes occurring in social systems; b) thermal processes occurring in technical systems; c) inflationary processes in industrial and economic systems; d) trajectories of planets and spaceships; e) the processes of psychological interaction between people. 23
 8. The basis of modeling is: a) the communicative process; b) information transfer; c) formalization process; d) storage of information; d) human interaction. 24
8. The basis of modeling is: a) the communicative process; b) information transfer; c) formalization process; d) storage of information; d) human interaction. 24
 9. The essence of the main thesis of formalization is the fundamental possibility: a) presentation of information on a material carrier; b) transfer of information from one object to another; c) human information processing; d) storage of information in computer memory; e) separation of the object and its designation. 25
9. The essence of the main thesis of formalization is the fundamental possibility: a) presentation of information on a material carrier; b) transfer of information from one object to another; c) human information processing; d) storage of information in computer memory; e) separation of the object and its designation. 25
 10. The idea of modeling follows from the main thesis of formalization, that is, it reflects the possibility of: a) presenting information on a material carrier; b) separation of the object and its name; c) human information processing; d) storage of information in computer memory; e) transmission of information by means of a signal. 26
10. The idea of modeling follows from the main thesis of formalization, that is, it reflects the possibility of: a) presenting information on a material carrier; b) separation of the object and its name; c) human information processing; d) storage of information in computer memory; e) transmission of information by means of a signal. 26